Fracture/Failure
Creep Analysis in Abaqus
In engineering, creep phenomenon refers to the gradual deformation or strain that occurs in a material over time when it is subjected to a constant load or stress (usually lower than yield stress) at high temperatures. It is a time-dependent process that can lead to the permanent deformation and failure of the material if not properly accounted for in design considerations. Creep analysis is vital in engineering to understand material behavior under sustained loads and high temperatures. It enables predicting deformation and potential damage, ensuring safe and reliable structures. Industries like power generation and aerospace benefit from considering creep for long-term safety and durability of components.
In this training package, you will learn about Creep phenomenon and its related matters; you will learn several methods to estimate the creep life of a system’s components, such as Larson-Miller; moreover, all Abaqus models for the creep simulation such as Time-Hardening law and Strain-Hardening law will be explained along with Creep subroutine; also, there would be practical examples to teach you how to do these simulations.
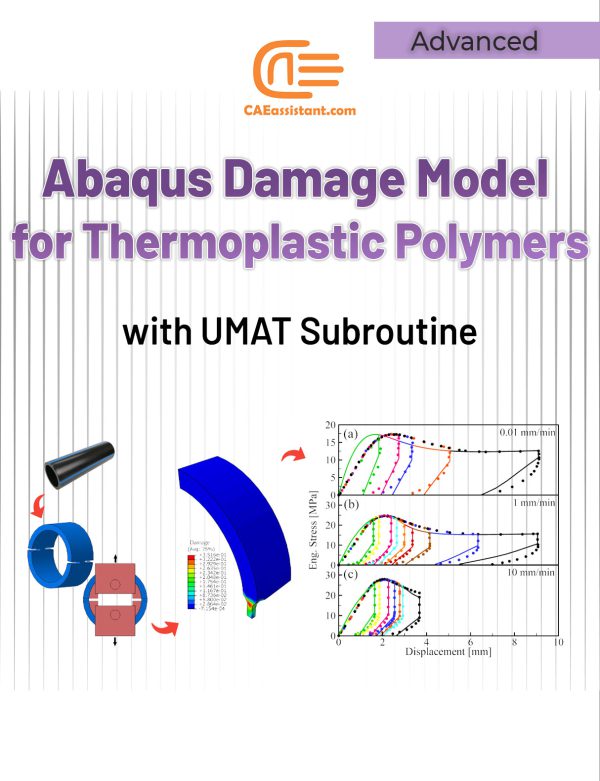
Abaqus Damage Model for Thermoplastic Polymers with UMAT Subroutine
Thermoplastic polymers are materials composed of long molecular chains primarily consisting of carbon. These polymers possess the unique ability to be shaped and molded under heat and pressure while retaining their stability once formed. This high formability makes them widely used in various industries, including furniture production, plumbing fixtures, automotive components, food packaging containers, and other consumer products. This package introduces a thermodynamically consistent damage model capable of accurately predicting failure in thermoplastic polymers. The implementation of this model is explained through the use of an ABAQUS user material (UMAT) subroutine.
The package is structured as follows. The introduction section Provides an overview of thermoplastic polymers and their mechanical properties. In the Theory section, the constitutive damage model and its formulation are reviewed. Then, an algorithm for numerically integrating the damage constitutive equations is presented in the Implementation section. In the UMAT Subroutine section, a detailed explanation of the flowchart and structure of the subroutine is provided. Finally, two simulation examples, namely the T-fitting burst pressure test and the D-Split test, are performed and the obtained results, are investigated.
Notice: Software files and A full PDF guideline (Problem description, theory, ...) are available; Videos are coming soon.
Abaqus for Civil Engineering Part-1
The "Abaqus for Civil Engineering” package is a comprehensive and invaluable resource designed to cater to the needs of civil engineering professionals, students, and enthusiasts alike. This all-inclusive package comprises a collection of several specialized tutorial packages, making it an essential tool for mastering various aspects of civil engineering.
With this package, you gain access to an extensive library of high-quality video tutorials that cover a wide range of topics within civil engineering. Each tutorial provides clear, concise, and engaging explanations of fundamental concepts, advanced techniques, and practical applications.
Modeling Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) in ABAQUS
Dive into the realm of innovative engineering with our comprehensive tutorial package, designed to empower you in modeling Functionally Graded Materials (FGM) using the Abaqus USDFLD subroutine. Uncover the fascinating world of FGMs, materials that ingeniously vary their composition and microstructure, offering a nuanced control over mechanical, thermal, and other properties.
The workshop component takes you on an exploration of crack paths in Spherical Functionally Graded Materials, emphasizing simulation techniques using Abaqus Standard and the USDFLD subroutine. Uncover the secrets of stress distribution within a pressured, empty sphere, and enhance your skills by implementing the XFEM method for precise crack characterization. This training ensures you gain valuable insights into subroutine development, empowering materials engineers and designers to innovate and elevate the performance of structures across various industries. Embark on your journey to mastery with this all-encompassing tutorial package.
Composite Pressure Vessel simulation in ABAQUS
Pressure vessels are made using different methods today, and one of them is filament winding. This package shows the simulation of composite pressure vessels made using the filament winding method.
In this training package, three winding methods, planar, geodesic, and isotensoid, have been taught for filament winding pressure vessels. In this tutorial, two general methods also have been presented for simulating filament wound pressure vessels. One uses the Abaqus graphical user interface(GUI), and the other uses the Python script. On the other hand, two criteria, Tsai-Hill and Puck, have been used to model damage in the composite. A UMAT subroutine has been used to use the Puck criterion.
Composite pressure vessel analysis with Semi-Geodesic winding
Nowadays, pressure vessels are produced using various methods, one of which is filament winding. This package teaches the simulation of composite pressure vessels produced using the filament winding method. Filament winding itself has different methods, and one of the most widely used winding methods for producing composite vessels is the semi-geodesic filament winding method. In this package, first, the semi-geodesic method is described. Then, the simulation of a semi-geodesic vessel is performed using a Python script. Additionally, a UMAT subroutine is used to simulate the failure of composite materials used in the vessel.
Full Composite fatigue Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
This package is designed to instruct users on how to utilize the composite fatigue modeling Add-on, which removes the need to write a subroutine for composite fatigue modeling. Instead, users can select the composite type, input material properties, and generate the subroutine by clicking a button. The Add-on includes four types of composites, and the generated subroutine for all types is the UMAT. These four types are Unidirectional, Woven, short fiber composites (chopped), and wood. The fatigue criteria used for each type are the same as its respective package. For example, the fatigue criteria for woven composites are identical to that used in the "Simulation of woven composite fatigue in Abaqus" package. This Add-on provides a simple graphical user interface for composite fatigue modeling, which can be utilized for both academic and industrial applications.
Pre-Order Now
Coming soon...
Full Composite damage Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
This package will teach you how to use the composite damage modeling Add-on. The Add-on eliminates the need for writing a subroutine for composite damage modeling. Instead, you only need to select the desired composite type, input the material properties, and click a button. The Add-on will then generate the subroutine for you. The Add-on includes four types of composites: Unidirectional, Woven, short fiber composites (chopped), and wood. The generated subroutine for all types is the VUSDFLD. The damage criteria used in each type is the same as the one used in its respective package. For instance, the damage criteria for the woven composite is identical to the one used in the "Simulation of woven composite damage in the Abaqus" package. This Add-on offers a user-friendly graphical user interface for composite damage modeling, which can be used for academic and industrial purposes.
Pre-Order Now
Coming soon...
Bolt Modeling in Abaqus
Bolts and joints play a vital role in the stability and structural integrity of various engineering structures, including buildings, bridges, and machines. Bolts are used to fasten or connect different components together, providing a means of transferring loads and ensuring the continuity of load paths. Joints connect structural elements, allowing them to move and deform while maintaining their overall stability. Proper design and selection of bolts and joints are crucial to ensuring the safety and durability of the structure. Factors such as the type of load, the materials used, and the environmental conditions must be considered when selecting bolts and joints. Failure to properly design and install bolts and joints can result in catastrophic failure of the structure. In this package, you will learn how to model bolts and joints, simulating the failure of connections and other things with practical examples.