DFLUX
Laser forming simulation tutorial in Abaqus
The laser forming process is performed by applying thermal stresses to the workpiece surface by heating the surface with a laser beam. These internal stresses induce plastic strains in the part resulting in local elastic-plastic deformation (Laser-induced plastic deformation). In this laser forming simulation tutorial the DFLUX subroutine is used to apply heat flux (Gaussian heat distribution) dependent on location and time in finite element simulation. For example, the linear heating processes of laser forming and welding (with a slight simplification) can be simulated by this subroutine. In the linear heating process, by applying heat flux to the surface of a sheet, a thermal gradient is created in its thickness. This thermal gradient causes permanent deformation of the sheet. To simulate the laser forming process, it is necessary to apply a time and location-dependent heat flux to the sheet. In this type of loading, a heat flux is applied on the plate, which is defined using the DFLUX subroutine, including the laser power, movement speed, beam diameter, absorption coefficient, and laser movement path according to the designed experiments (Laser forming process parameters). To verify this Abaqus laser forming simulation, the simulation results and experimental results of sheet deformation (U) are compared. The displacement of the sheet in the simulation is in good agreement with the experimental results.
Arc welding simulation in Abaqus
Notice: This package will be available one week after purchase.
Arc welding is a fusion process that involves joining metals by applying intense heat, causing them to melt and mix. The resulting metallurgical bond provides strength and integrity to the welded joint. Arc welding is widely used in various industries for fabricating structures and components. Arc welding simulation in Abaqus is essential for optimizing the welding process and ensuring high-quality welds. It allows engineers to predict and analyze factors such as temperature distribution, residual stresses, distortion, and microstructure evolution during welding. By accurately simulating the welding process, parameters like welding speed, heat input, and electrode positioning can be optimized to achieve desired weld characteristics and minimize defects.
Additive manufacturing simulation with Abaqus subroutine & python | 3D printing Python
3D printing is a technique for creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials such as plastic or metal based on a digital design. 3D printing simulation involves the use of software to predict and enhance the printing process, resulting in more efficient and precise production. This training package is based on the use of subroutines and Python scripting. Following an introduction to the 3D printing process, this method with all its details is explained. Two workshops are then conducted for this method. The first workshop covers 3D printing simulation of a gear with a uniform cross-section, while the second workshop covers a shaft with a non-uniform cross-section.
DFLUX Subroutine (VDFLUX Subroutine) in ABAQUS
DFLUX subroutine (VDFLUX Subroutine) is used for thermal loading in various body flux and surface flux states in heat transfer and temperature displacement solvers when flux load is a function of time, place, or other parameters. In this package, you will learn “when do you need to use this subroutine?”, “how to use the DFLUX subroutine”, “what is the difference between DFLUX & VDFLUX?”, “how to convert DFLUX to VDFLUX and vice versa?”, and “How to use it in an example?”. Three workshops are presented so you can learn all these stuff in action: Simulation of welding between two plate with DFLUX subroutine, Simulation of Arc welding between two tube with DFLUX, and Simulation of different types of functional heat flux(Body-surface-Element) in plate with Johnson-cook plasticity with VDFLUX subroutine(Thermomechanical Analysis).
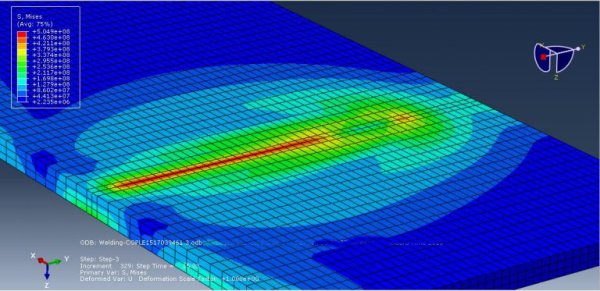
Welding Simulation in ABAQUS
This training package fully covers the various possible methods for welding simulation. First, an introduction to welding and two basic categories of welding, fusion and non-fusion welding. Next, the theories and the elements used to simulate the welding will be explained. These theories are Lagrangian, Eulerian, ALE, and SPH. After that, you will learn how to apply these theories with different methods, such as the death and birth of an element, DFLUX subroutine, etc. Finally, you will learn how to simulate welding with the help of five workshops: Friction Stir Welding (FSW) simulation with the Eulerian element, Explosive welding simulation, simulation of FSW with the SPH method, Butt welding with death and birth of an element method, and Simulation of Arc welding between two tubes with DFLUX subroutine (Thermomechanical Analysis).