If some nodes of the slave surface are penetrated the master surface in the initial stages and cause some convergence problems, how can we solve this issue?
- Training Group asked 2 years ago
- last edited 7 months ago
- You must login to post comments
What is surface to surface contact in Abaqus? | Surface contact
In Abaqus the term “surface, to surface contact” refers to a type of interaction between two surfaces. Faces belonging to different bodies or parts in a finite element analysis (FEA) model. It enables the simulation of contact and interaction between these surfaces taking into account factors such as friction, sliding, separation or penetration.
Surface to surface contact is commonly utilized when there is no need to precisely model the contact behavior at a node or point level. Instead, it focuses on considering the interaction between surface areas. This approach is appropriate, for scenarios where the overall behavior of the surfaces interaction takes precedence over localized interactions.
When defining surface-to-surface contact in Abaqus, you typically specify the contact pairs or surfaces involved, the contact behavior (such as friction, separation, or tie constraints), and the contact properties (such as contact stiffness, friction coefficients, and contact parameters). Abaqus then determines the contact forces and interactions between the surfaces during the analysis based on the defined contact behavior and properties.
Surface-to-surface contact in Abaqus allows for the simulation of various real-world scenarios, such as metal-to-metal contact, contact between different materials, contact between deformable bodies, and sliding or separation between surfaces. It enables the accurate representation of contact phenomena and is widely used in structural, mechanical, and multiphysics simulations to analyze the behavior of complex assemblies or systems where contact interactions play a significant role. Surface-to-surface contact can be specified in any step of the analysis, even in the initial step. To define it, go to the main menu bar, click on “Interaction,” then select “Create.” From there, choose the master and slave surfaces involved in the contact interaction.
How to adjust surface contact in Abaqus? | Surface adjustment
If you are faced with this issue at the beginning of the process, as illustrated in figure 1, you can solve this issue through three options in the “Edit Interaction” window (see Figure 2).
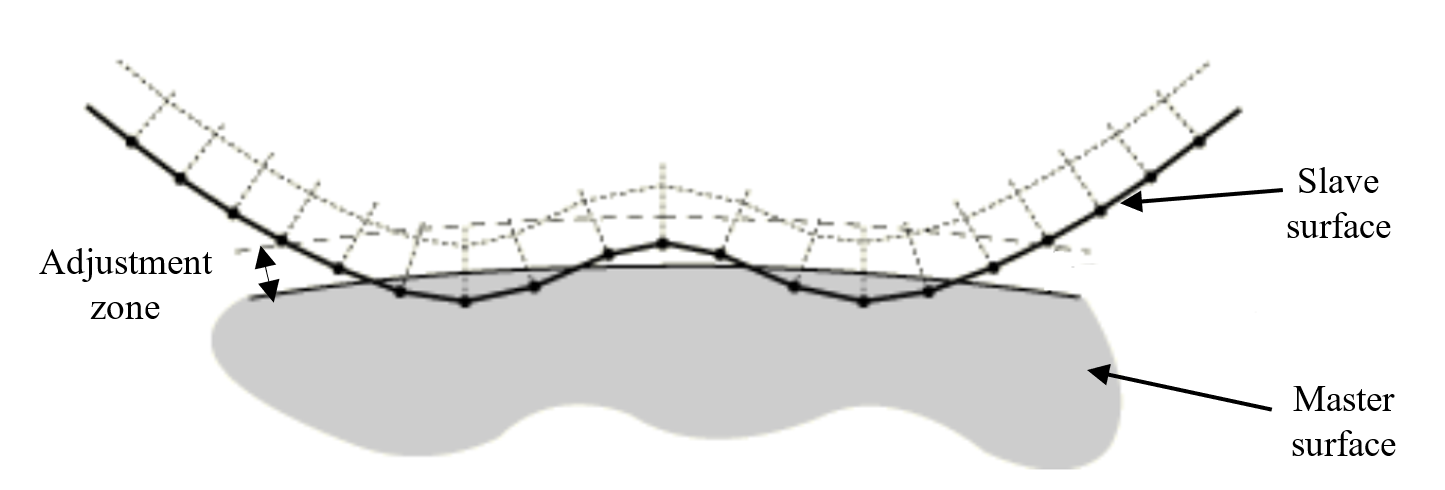
Figure 1: penetration of some slave nodes into the master surface
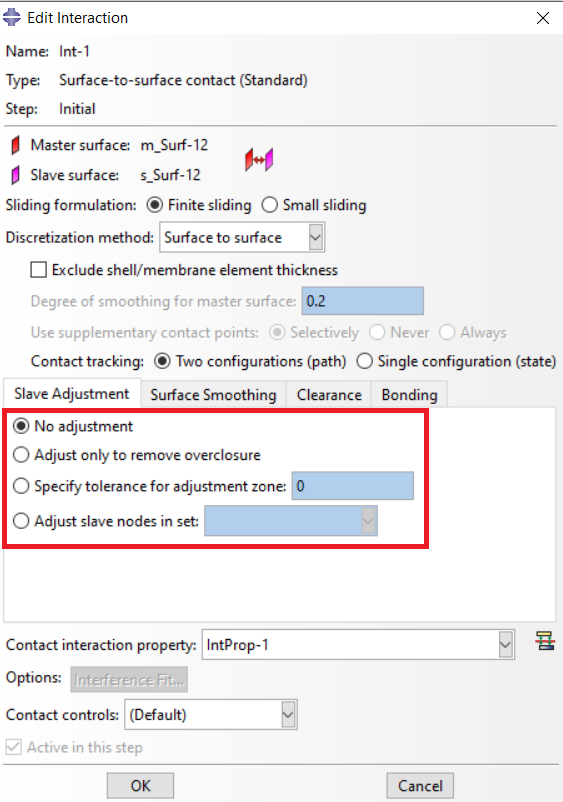
Figure 2: slave adjustment options
Now, if you use the “Adjust only to remove overclosure” or select the “Specify tolerance for adjustment zone” and specify the zero value, the software will only adjust the nodes that penetrated the master surface (see Figure 3).
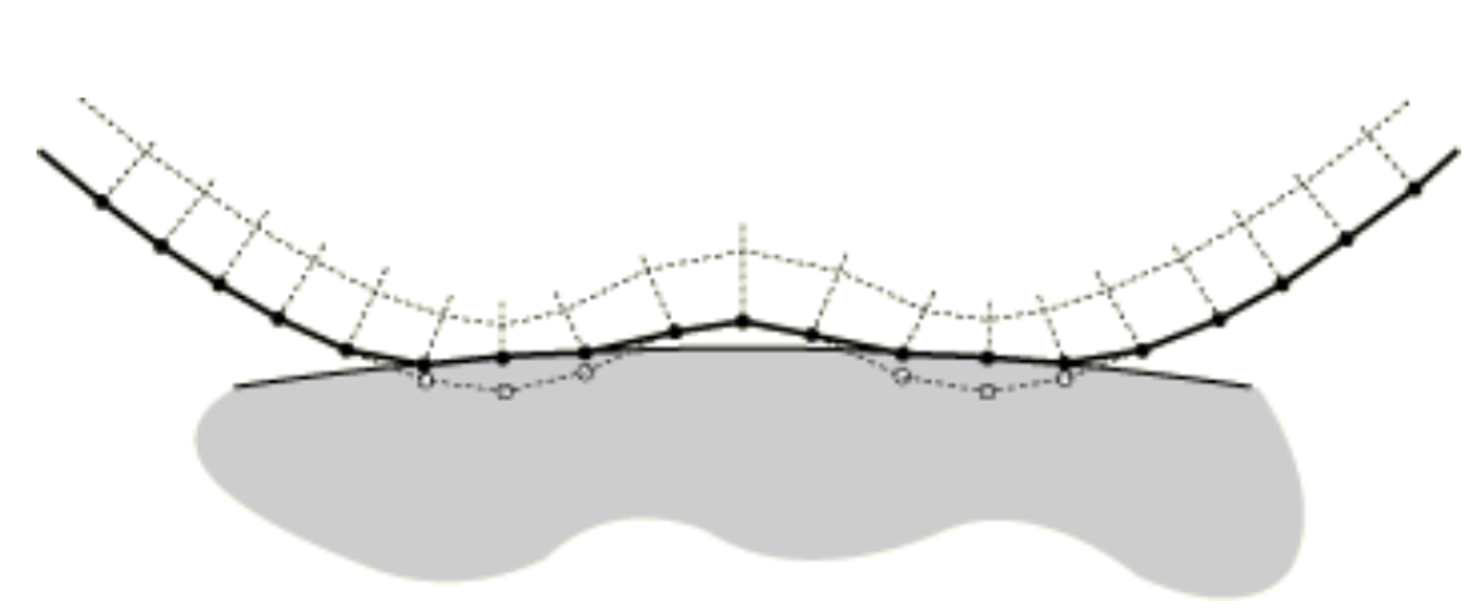
Figure 3: adjusted nodes
If you specify any other value than zero in the adjustment zone, for example, see figure 1, the software will move any nodes within the adjustment zone precisely onto the master surface (see figure 4).
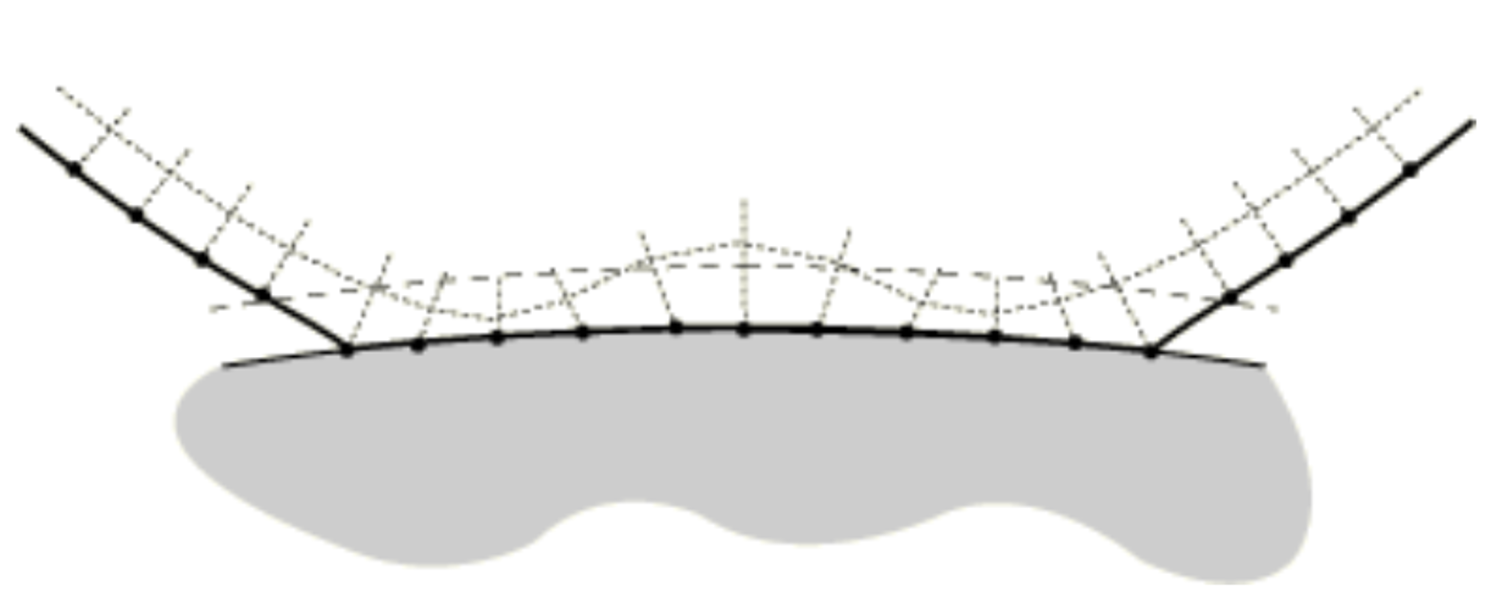
Figure 4: nodes moved on to the master surface
By selecting the “Adjust slave nodes in set”, you would be able to create a node set of those nodes of slave surface that may cause convergence issues, and the software will only check them and take action. If the node set contains nodes not belonging to the slave surface, the software will ignore them.
Surface adjustment | Abaqus contact adjust
To ensure proper conformity between the master (main) and slave (secondary) surfaces in Abaqus, it is recommended to follow the guidelines provided in the Abaqus Manual:
- Increase the element density of the slave surface compared to the master surface.
- Assign the slave surface to the smaller of the two surfaces.
- Assign the master surface to the stiffer body, considering both geometry and material properties.
If it is not feasible to satisfy all three criteria, priority should be given to the first two guidelines for achieving optimal conformity.
You can read more about master (main) and slave (secondary) surfaces in this Q & A: https://caeassistant.com/questions/question/master-slave-surfaces-basic-rules
- Training Group answered 2 years ago
- last edited 7 months ago
- You must login to post comments
Please login first to submit.
