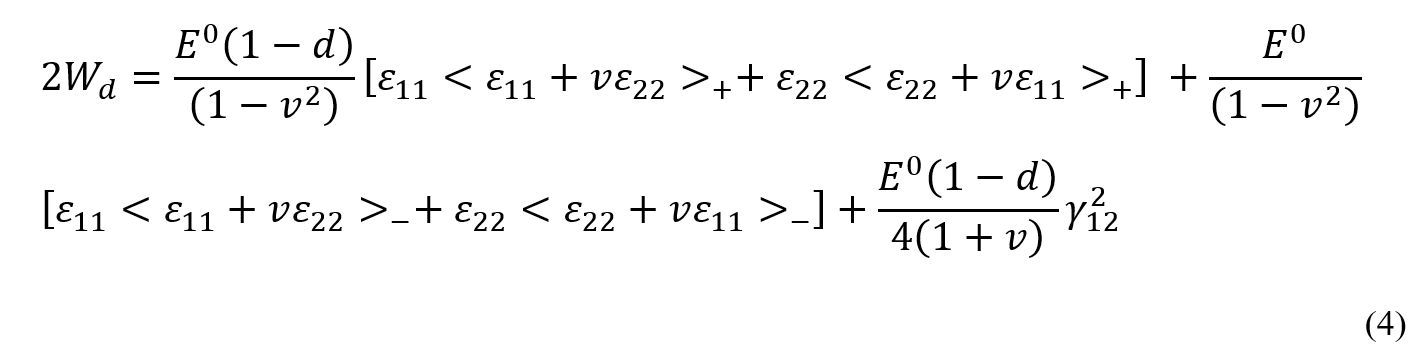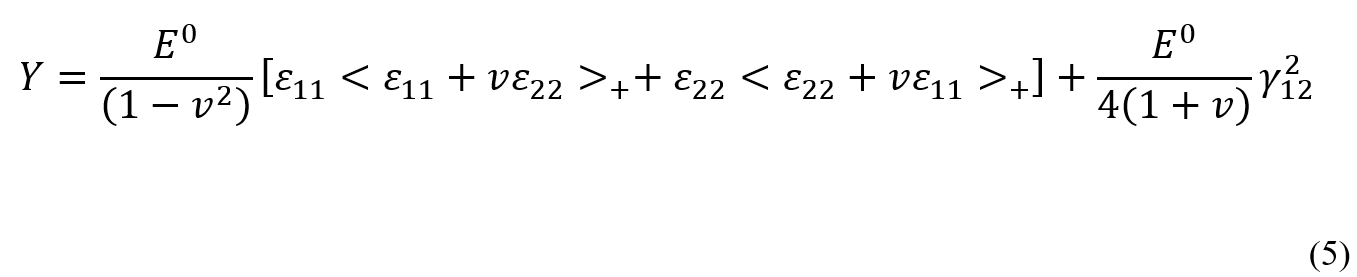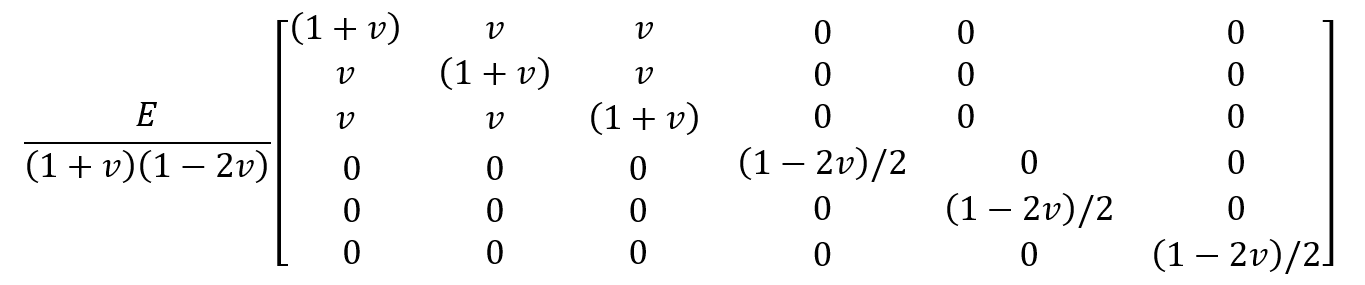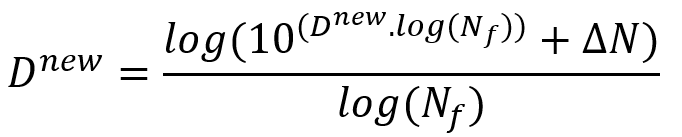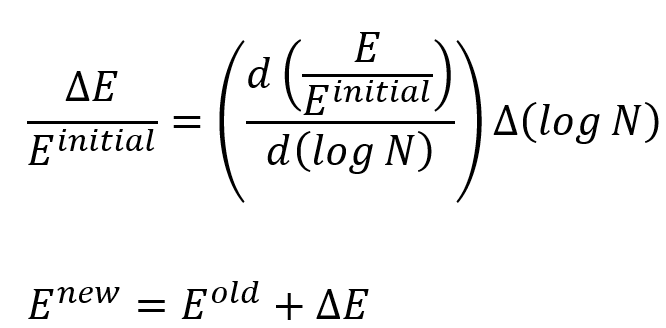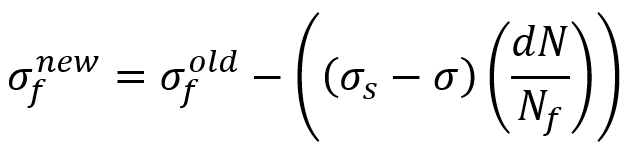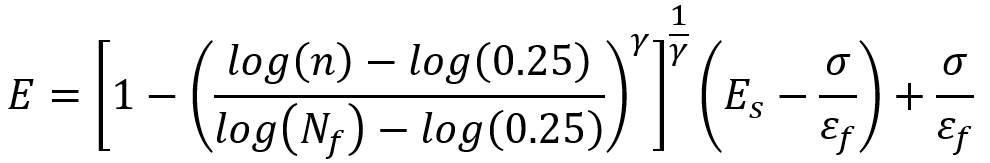Composite Fatigue Analysis: Unidirectional, Short Fiber, Woven, etc.

Did you know that composite materials are increasingly replacing traditional metals in critical applications, yet they face a unique challenge—fatigue damage? Over time, repetitive loading can cause subtle but progressive failures in composites, threatening their durability and performance. This issue is especially critical in industries like aerospace, automotive, and wind energy, where the stakes of material failure are high.
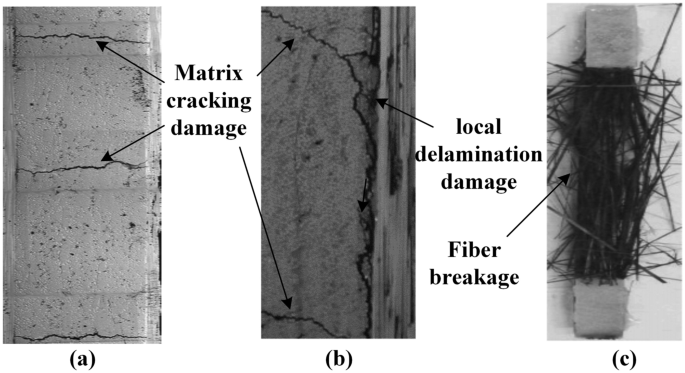
Unlike metals, which typically fail through uniform mechanisms under cyclic stress, composites exhibit complex behaviors due to their heterogeneous structure. Their fatigue damage may involve fiber breakage, matrix cracking, or delamination, each requiring specific analysis techniques. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for designing reliable composite structures that can endure repeated loading without failure.
This article delves into the fatigue behavior of various composite types—short fiber, unidirectional, and woven composites—emphasizing their unique failure mechanisms. It highlights advanced simulation techniques, including the use of Abaqus and UMAT subroutines, to predict fatigue life and optimize composite performance. Whether you’re new to composite fatigue analysis or an experienced engineer, this guide aims to simplify the challenges of simulating and understanding composite fatigue.
1. How to do Composite Fatigue Analysis?
Fatigue in composite materials arises from their exposure to repeated or cyclic loading, similar to traditional materials, but with unique complexities due to their heterogeneous structure. The matrix and reinforcement in composites respond differently to cyclic stresses, potentially leading to localized damage such as matrix cracking, fiber breakage, and delamination. These damage mechanisms interact, progressively weakening the composite and eventually causing failure. The inherent anisotropy of composites and the varying properties of the matrix and fiber further complicate the fatigue behavior, making it essential to consider the loading type, environmental conditions, and material composition in fatigue analysis.
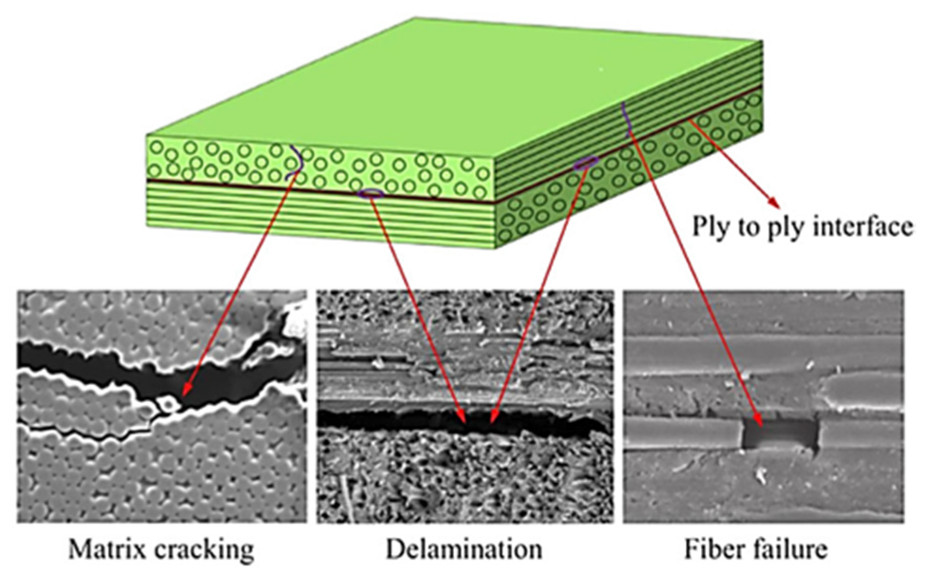
Generally, when damage occurs in composites, such as for composite fatigue analysis the damages can be categorized into four groups:
- Fiber damage: Tensile loading in composites is borne by the fibers. When the loading exceeds the fiber’s tolerance limit, the fibers become damaged, resulting in damage to the composite.
- Matrix damage: In fiber-reinforced composites, compression is usually tolerated by the matrix. When the compression exceeds the matrix’s tolerance limit, the matrix fractures and becomes damaged.
- Delamination: Delamination is one of the mechanisms of damage in composites. In this case, the layers of the composite separate, leading to damage in the composite structure.
- Fiber/matrix interface failure: Cyclic loading can lead to separation between the matrix and composite fibers, resulting in composite failure.
Figure 1: Damage modes in composites
Understanding the failure mechanisms of composites is of great importance in fatigue analysis because by considering the failure mechanism, the appropriate theory can be selected and developed.
To predict the fatigue life of composites, specialized approaches that account for their multi-phase nature are required. As a result, a powerful tool such as the finite element method is needed to predict the fatigue of composites. Abaqus software can provide this tool to users.
2. What is fatigue damage?
Fatigue damage occurs when a material is subjected to repeated or cyclic loading, leading to progressive structural degradation and eventual failure. This phenomenon is critical to engineering, as many structures experience fluctuating stresses during operation, such as bridges, aircraft components, and rotating machinery. Fatigue damage typically develops in three stages: crack initiation, crack propagation, and rapid fracture. Factors like the magnitude and type of cyclic loading, environmental conditions, and material properties influence the onset and progression of fatigue.
If you are interested in obtaining complete and accurate information about the fatigue phenomenon and the factors affecting it, you might find “What is Fatigue Analysis? | Abaqus Fatigue, Fatigue Life Prediction, Cyclic Loading Types” blog informative.
Figure 2: Failure of a crank arm due to fatigue
2.1. Fatigue cycle number
To study fatigue, including short fiber composite fatigue, attention should be paid to the number of fatigue cycles. Fatigue is generally divided into two main categories:
- Low-cycle fatigue
- High-cycle fatigue
If the applied stress exceeds the yield stress, it results in low-cycle fatigue. On the other hand, if the stress is below the yield stress, it leads to high-cycle fatigue.
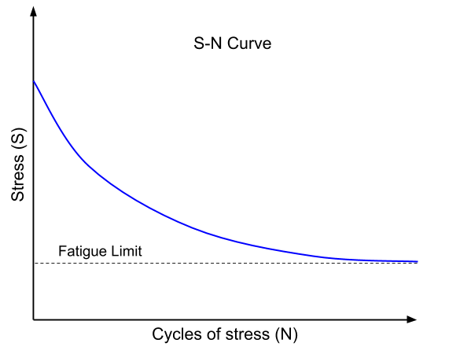
2.2. Fatigue life
Fatigue life is another important parameter in the fatigue analysis of a structure. Fatigue life refers to the number of cycles that a specimen undergoes during testing until fatigue occurs. In the stress-cycle number diagram, there is a theoretical value where the component never experiences fatigue for stresses less than this value. This value is referred to as the fatigue limit.
Figure 3: Fatigue life curve(S-N curve)
3. Four categories of Fiber reinforced composites
Fiber reinforced composites are a type of composites that are made by combining fibers with a matrix, such as resin or polymer. The presence of fibers in the composite can greatly enhance its strength, as the tensile load is borne by the fibers, which have much higher tensile strength than the matrix. The mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites are strongly influenced by the type, volume fraction, length, and orientation of the fibers. Generally, fiber-reinforced composites can be classified into four categories: (More about Abaqus Composite and Composite Analysis)
Continuous aligned fiber composites
Figure 4: Continuous aligned fiber composites schematic
Discontinuous aligned fiber composites
Figure 5: Discontinuous aligned fiber composites schematic
short random fiber composites
Figure 6: Short random fiber composites schematic
Woven composites
Figure 7: Woven composites schematic
4. Composite Fatigue Theories
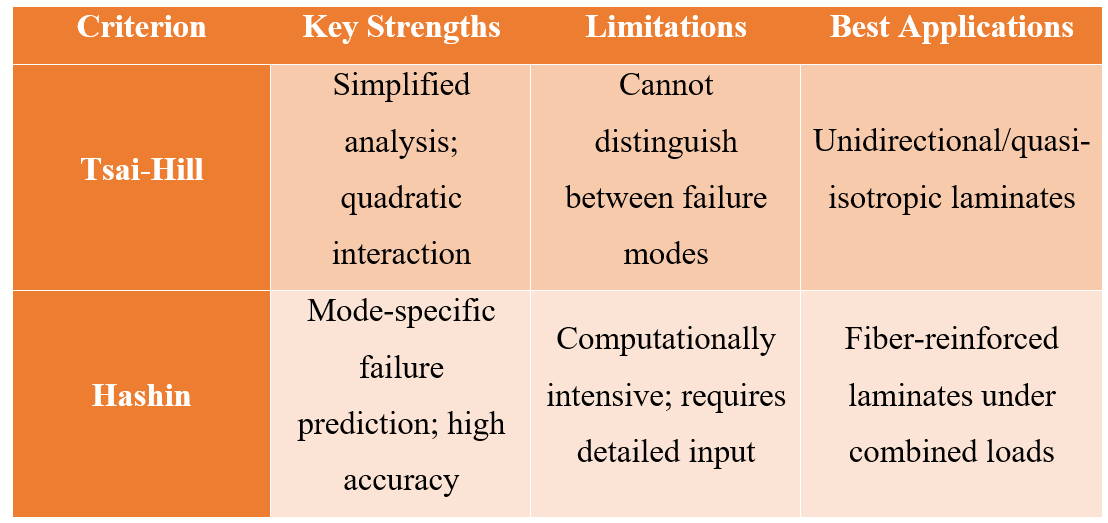
Fatigue analysis in composite materials is a complex field, with numerous theories available to predict damage under cyclic loading. Each of these theories—such as the Maximum Stress Criterion, Tsai-Hill Criterion, Hashin Criterion, and Puck Criterion—offers unique strengths and applications, depending on the type of composite and loading conditions.
Two widely used theories—the Tsai-Hill and Hashin criteria—offer distinct advantages depending on the material type and loading conditions. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Tsai-Hill Criterion
- Overview: A quadratic failure criterion derived from the Hill yield criterion, adapted for anisotropic materials.
- Strengths: Simple and effective for predicting failure in composites with similar tensile and compressive strengths.
- Limitations: Does not distinguish between failure modes (e.g., fiber vs. matrix failure) and assumes homogeneity in the material response.
- Best Applications: Useful for initial assessments of unidirectional or quasi-isotropic laminates under multi-axial stresses.
2. Hashin Criterion
- Overview: A mode-dependent failure criterion that differentiates between fiber and matrix failures, providing a detailed analysis of composite damage mechanisms.
- Strengths: High accuracy in predicting distinct failure modes; suitable for fiber-reinforced composites under complex loading conditions.
- Limitations: Requires detailed material properties and is computationally intensive, particularly in 3D simulations.
- Best Applications: Ideal for fiber-reinforced laminates in aerospace and automotive applications, especially under combined loading scenarios.
Figure 8: Comparison between Tsai-Hill VS Hashin
In the following, we will discuss the composite fatigue in each type of composites (Unidirectional, Short fiber, and woven) in detail.
One other thing, some composites such as short fiber composites have shown different fatigue behavior, other criteria have been developed for this category of composites that are highly accurate.
Two of the most well-known models for short fiber composite fatigue damage are:
- The Nori damage model for short fiber composite fatigue.
- The Avanzini damage model for short fiber composite fatigue.
The Avanzini model for discontinuous fiber composite fatigue analysis has emerged from the development and modification of the Nori model. In this model, the fiber distribution is considered random, assuming a homogeneous and isotropic composite. Don’t worry! We will discuss these theories later in this article.
5. Fatigue Analysis of Composite Materials in Abaqus
As you know, Abaqus is a powerful tool for finite element simulation. With its ability to model the unique anisotropic behavior and heterogeneous structure of composites, Abaqus supports precise analyses of mechanical performance under various conditions, including static, dynamic, and thermal loads. However, when it comes to fatigue analysis of composite materials, the intricacies of composite material behavior, such as matrix cracking, fiber breakage, and delamination, introduce additional complexities.
Simulating the fatigue of composite materials in Abaqus can be particularly challenging for users due to the need to account for multiple damage mechanisms and the interaction between the matrix and reinforcement. The process requires a deep understanding of material properties, fatigue theories, and the correct implementation of simulation techniques. Therefore, it is not possible to reliably simulate the fatigue of composites without using subroutines in Abaqus.
6. Composite Fatigue Analysis using UMAT and VUMAT Subroutines
Fatigue simulation of composite materials is inherently complex, as the failure criteria and cyclic loading cannot be directly modeled using the Abaqus interface. To address these limitations, subroutines like UMAT and VUMAT are employed, which allow users to define and simulate the specific material behavior of composites. These subroutines provide the flexibility needed to incorporate custom stiffness matrices and failure criteria, enabling an accurate representation of composite material responses under cyclic loading.
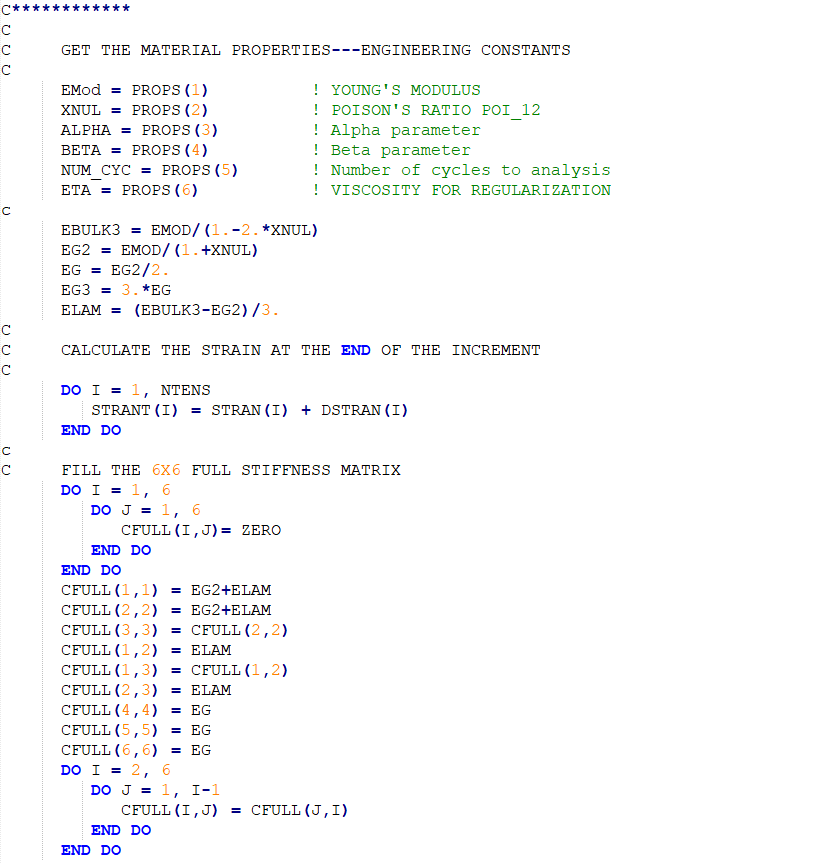
The main idea of UMAT and VUMAT subroutines is to calculate the stiffness matrix as well as the stress and strain matrices for each increment during the simulation. The stiffness matrix plays a central role, as it reflects the material’s mechanical behavior. Defining this matrix requires an understanding of the composite’s behavior, such as whether it exhibits isotropic or anisotropic properties. Each type demands a distinct formulation within the subroutine, ensuring that the material behavior is accurately captured.
Figure 9: Calculating stiffness matrix in UMAT subroutine using two loops
Under cyclic loading, small cracks typically begin to form within the composite’s matrix, signaling the onset of damage and leading to a gradual reduction in the material’s strength. In the UMAT subroutine, the failure criterion selected for the simulation must be evaluated at every increment. Once the criterion is satisfied, the composite’s material properties are adjusted by the damage variable to reflect the damage, and a new stiffness matrix is calculated to account for the altered mechanical behavior.
Another key aspect of modeling fatigue in composites is tracking the number of cycles endured by the material. In the UMAT subroutine, the increments used in the simulation can represent individual loading cycles. For instance, assigning one increment per cycle provides a straightforward method to simulate cyclic loading, ensuring that the cumulative effects of repeated stresses are accurately captured in the analysis.
By the explanations given about the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines and how they worked, we will examine the fatigue simulation of several composite samples.
Now, it is time fulfil our promise and talk about the fatigue in each type of composites in detail.
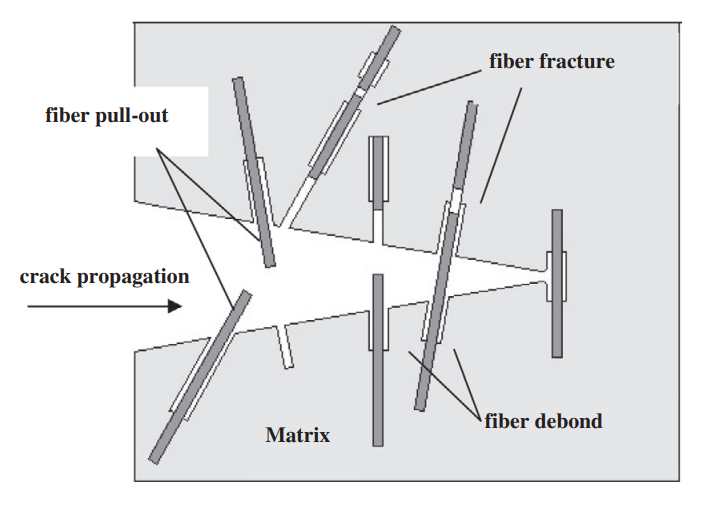
7. Short fiber reinforced composite fatigue
In the short fiber-reinforced composite fatigue analysis process, similar to other composites, various factors such as fiber material, fiber volume fraction, temperature, and creep strain have an impact. However, one of the most important factors in the short fiber composite fatigue analysis is the fiber distribution within the matrix. If the fiber distribution is random, the behavior of the composite material is homogeneous and isotropic. Otherwise, the composite will be anisotropic. Most studies have shown that longer fiber length leads to higher composite strength, and the strength directly affects the fatigue of the composite.
Figure 10: short fiber composite crack growth mechanism [Reference]
What is included in this package?
In this tutorial, we use the Avanzini’s model, which is based on this article: “Fatigue behavior and cyclic damage of peek short fiber reinforced composites”.
7.1. Short fiber composite fatigue behavior
As mentioned, the short fiber composite fatigue behavior depends on various factors, including fiber length, fiber distribution within the matrix, etc. Most studies have shown that longer fiber length leads to higher composite strength, and the strength directly affects the fatigue life of the composite. If the fiber distribution in the composite is not random, the composite is orthotropic, meaning it behaves differently from a composite with a random fiber distribution. There are various models available to simulate the short fiber composite fatigue behavior, and two of the most well-known models for short fiber composite fatigue damage are:
- The Nori damage model for short fiber composite fatigue.
- The Avanzi damage model for short fiber composite fatigue.
In the next section, we will examine the Avanzi model.
But if you need to learn these models with examples, I suggest to visit this link: “Short fiber composite fatigue“.
7.2. Discontinuous fiber composite fatigue analysis by Avanzini’s model
The Avanzini model for discontinuous fiber composite fatigue analysis has emerged from the development and modification of the Nori model. In this model, the fiber distribution is considered random, assuming a homogeneous and isotropic composite. In this model, the strain energy is calculated using equation 4:
By integrating equation 4, the thermodynamic force is obtained from equation 5:
In the above equations, γ represents the damage constant, and d is the damage variable. The damage variable d can be calculated using equation 6:
We can use the Avanzini model to analyze the short fiber composite fatigue in Abaqus software. As mentioned, due to the random distribution of fibers in the matrix, the composite is isotropic, so the stiffness matrix of the material will be in the form:
Now, if any damage occurs in the composite, the stiffness matrix of the composite is reduced using the damage variable, and in this way, we can simulate the fatigue behavior of the composite in a specific number of cycles using the UMAT subroutine. However, there are still many questions about how to implement the Avanzini model in the UMAT subroutine. We introduce the ” fatigue damage simulation of short fiber composites with subroutine “ training package to you. This package provides answers to all your questions regarding simulating short fiber composite fatigue in Abaqus. In addition to comprehensive explanations about fatigue and composites, this package provides complete guidance on Abaqus short fiber composite fatigue simulation using the Avanzini model.
8. Fatigue Analysis of Woven Composites
Woven composites are among the most widely used and popular composites, which are highly susceptible to fatigue due to their wide application. As mentioned, the best way to simulate composites is to use the UMAT subroutine, and woven composites are no exception to this rule.
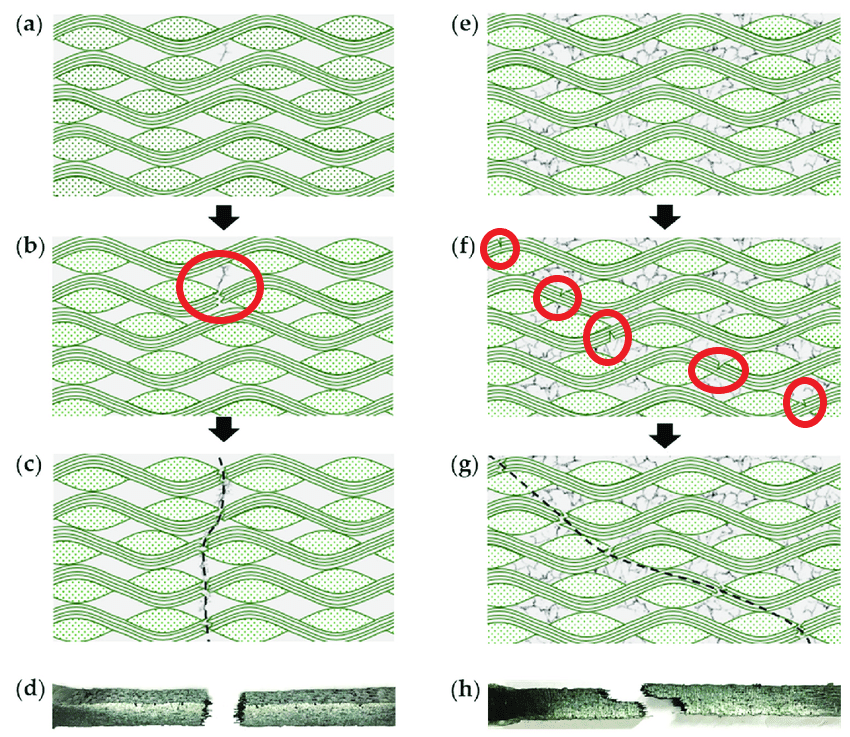
Figure 11: Different crack growth mechanisms for woven composites [Reference]
What is included in this package?
The training package focuses on simulating woven composite fatigue using Abaqus software and the modified Hashin fatigue damage model based on the article titled:
Life prediction of woven CFRP structure subject to static and fatigue loading.
According to the procedure for using the UMAT subroutine, the material behavior and subsequently the stiffness matrix must be determined first. In woven composites, because there are different textures such as planar weave, basket weave, leno weave, etc., their behavior is different and the type of stiffness matrix must be determined according to the texture orientation. If the texture is symmetrical, an isotropic stiffness matrix can be used.
To model fatigue failure in woven composites, we must also implement a failure criterion in the UMAT subroutine. This criterion can be the Puck criterion, the maximum stress criterion, or the Hashin criterion. After detecting the occurrence of damage, a damage variable must be defined to reduce the properties of the composite by this variable. For example, for the maximum stress criterion, we can define the damage variable as follows:
Dnew and Dold the damage variables at the current increment and the previous increment respectively. And Nf is the number of cycles to failure using the S-N diagram. is the difference between the estimated number of cycles and the completed number of cycles. This damage variable should be calculated separately for each increment.
Also, at each increment, the reduced value of the elastic modulus is calculated from the following equation:
Enew and Eold are the elastic modulus at the current increment and the previous increment respectively.
But for the Hashin criterion, the reduced strength value is calculated from the following equation:
In this relation, and
are equal to the reduced strengths in the current and previous increments.
According to the explanation provided about the fatigue simulation process of woven composites, there are still many points to implement these relations in the UMAT subroutine. Our team has a training package for this case. You can benefit from all the points of this simulation by referring to “Simulation of woven composite fatigue in Abaqus”.
9. Fatigue Analysis of Unidirectional Composites
Unidirectional composites are composites material that differ from other composites in terms of their reinforcement structure. In unidirectional composites, the fibers are oriented in a single direction, which gives them high strength and stiffness in that direction. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high strength and stiffness in a specific direction.
Figure 12: Matrix and fiber damage in unidirectional composite specimen [Reference]
What is included in this package?
This training package teaches you to simulate and analyze composite fatigue in Abaqus using the UMAT subroutine.
In unidirectional composites, due to the specific orientation of the fibers, the composite is anisotropic, so the stiffness matrix in the UMAT subroutine must be determined based on the anisotropy of the composite. In the next step, a damage criterion must be specified to simulate the fatigue of composites.
Among the criteria introduced for simulating fatigue of unidirectional composites, the Hashin criterion (due to predicting failure for the matrix and fibers separately) is suitable and can predict failure well. As a result, using this criterion, we can detect damage in the composite and then reduce the properties of the composite, including the stiffness matrix, due to the formation of small cracks and layer separation.
As you know, after a composite fails due to fatigue, the strength and mechanical properties of the composite decrease with the growth of small cracks in each cycle. The following equation can be used to calculate reduced mechanical properties such as elastic modulus in different directions:
In this relation, is stress, n is the number of cycles passed and the constant
is related to the material. Also, Nf and
are the failure life and failure strain, respectively.
This section of the article provides a brief explanation of fatigue simulation of unidirectional composites, but for complete and detailed information on how to implement the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines to simulate the fatigue of these composites, you can refer to the “Composite Fatigue Simulation with UMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional)” and “Composite Fatigue Simulation with VUMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS” packages.
10. Conclusion
This article explored the fatigue behavior of composite materials, focusing on how repeated loading affects their structural integrity. Fatigue in composites is critical to study because it impacts the reliability and durability of components used in industries like aerospace and automotive, where failure can lead to significant consequences.
We discussed key topics, including the mechanisms of composite fatigue, such as matrix cracking, fiber damage, delamination, and fiber/matrix interface failure. Specialized techniques, like using UMAT subroutines in Abaqus, were introduced to simulate fatigue in different composite types, such as short fiber, unidirectional, and woven composites. For example, we reviewed the Avanzini model for short fiber composites and the Hashin criterion for unidirectional composites, emphasizing how damage variables adjust stiffness and strength under cyclic loading.
Through this article, we learned how the complex nature of composite fatigue requires tailored approaches to predict damage and improve material performance. Advanced simulation tools like Abaqus play a crucial role in achieving accurate analyses, making them essential for engineers working with composites.
It would be helpful to see Abaqus Documentation to understand how it would be hard to start an Abaqus simulation without any Abaqus tutorial.
The CAE Assistant is committed to addressing all your CAE needs, and your feedback greatly assists us in achieving this goal. If you have any questions or encounter complications, please feel free to share it with us through our social media accounts including WhatsApp.