The package aims to teach a specific subject
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
Fatigue in composites refers to the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads or stress cycles over time. When a composite material is subjected to cyclic loading, small cracks or microdamage can form within the material, which may grow and lead to failure after a certain number of loading cycles. This is a significant consideration in the design and analysis of composite structures, especially in applications subjected to repeated stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering.
In one of our other packages, we have used the UMAT subroutine in Abaqus to simulate fatigue in composites in two-dimensional space. The current project is more comprehensive, as it addresses composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D spaces. So you can use it for the simulation of both shells and solids. In this project, you will first become familiar with simulating composite fatigue in 2D space using the Abaqus UMAT subroutine. Then, we will provide a complete UMAT code along with Abaqus files for extending the simulation to 3D space, enabling the 3D simulation of composite fatigue in Abaqus.
Essential Abaqus Training for Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Techniques
This beginner-friendly Abaqus course offers a complete guide to mastering finite element simulations through step-by-step tutorials and practical workshops. It covers essential topics such as Abaqus/CAE basics, finite element theory, composite material simulation, and thermal and impact analyses. Advanced sections delve into UMAT/VUMAT subroutines and Python scripting, equipping users with skills to automate workflows and solve complex engineering problems. Workshops include real-world examples like cantilever beams, forming processes, and fracture simulations. Perfect for engineering students and professionals, this course helps you build a solid foundation in Abaqus and expand your simulation capabilities.
Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation with Scripting in Abaqus
This Package offers a comprehensive tutorial on using Abaqus for Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation. To do so, it combines theoretical knowledge with practical application in Finite Element Method (FEM) simulations. The package guides users through both detailed lessons and interactive workshops. In fact, it focuses on developing 2D Fretting-Fatigue models in Abaqus with three core areas: model creation with exclusively designed meshing methodologies, the development of custom Field Outputs for detailed analysis, and automated parameter selection and post-processing through Python scripting.
Throughout the tutorial, participants master critical aspects of Fretting Fatigue Failure simulation. It includes basics from mesh refinement techniques and step control optimization to complete workflow automation. The program distinctively integrates command prompt operations for extracting Field Outputs and modifying simulation parameters. For example, we can refer to the Coefficient of Friction (CoF). Users gain practical experience in creating robust models while understanding the fundamental principles of the Fretting Fatigue Failure phenomenon.
Upon completion, participants will acquire the skills to independently develop and analyze Fretting Fatigue failure simulations. Moreover, they can automate post-processing tasks, and implement custom analysis parameters for precise fatigue prediction in mechanical systems.
How to use ABAQUS Documentation
Laser Assisted Machining (LAM): Modeling and Simulation in Abaqus/CAE
In this tutorial, a comprehensive discussion on modeling and simulation of laser assisted machining is presented. It includes building FEM-based models of machining, laser heating, and laser-assisted machining models in Abaqus/CAE. The finite element method (FEM) simulation is based on the coupled thermo-mechanical behavior. The package walks learners through building models that simulate the impact of laser heating on the workpiece. Detailed lessons cover constructing basic machining and laser heating models, setting boundary conditions like cutting speed and laser power, and writing subroutines such as DFLUX and VDFLUX to simulate laser heat sources. Additionally, learners will perform analyses to study temperature distribution, and stress-strain behavior. Through parametric analysis and comprehensive result evaluation, learners will gain a deep understanding of temperature distribution, stress behavior, and how laser heating can improve the machining process.
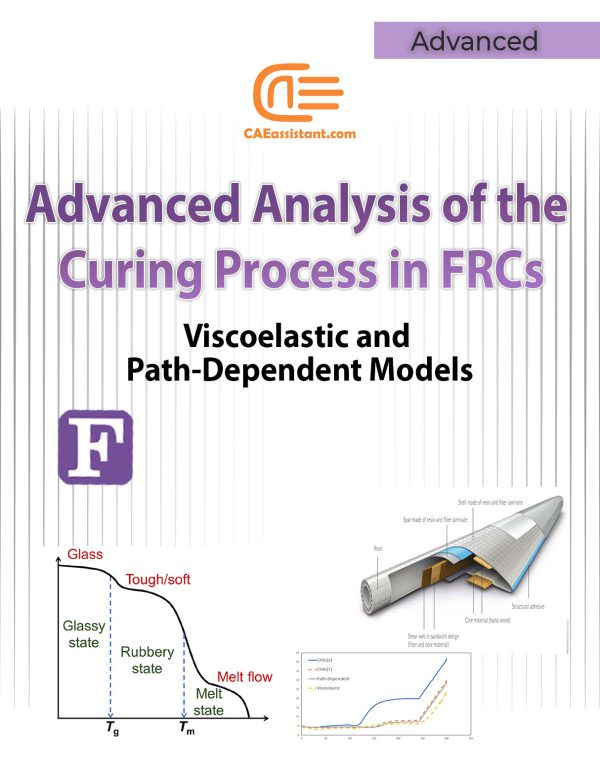
Using Viscoelastic and Path-Dependent Models for Analyzing the Curing Process in Fiber-Reinforced Composites With Abaqus subroutines
Brittle Damage in Abaqus | Brittle Cracking Abaqus
Brittle materials, such as ceramics, glass, and concrete, break or fracture easily under stress without extensive deformation. Unlike ductile materials, brittle materials snap suddenly, lacking the flexibility to rearrange their atomic structure under strain. These materials have low tensile strength but strong compressive resistance, making them vulnerable to brittle cracking Abaqus simulations when stretched or pulled.
Understanding brittle material damage is crucial in safety-critical fields like civil engineering, aerospace, and manufacturing, where unexpected fractures can lead to catastrophic failures. Simulations help engineers predict when and how brittle materials may break, guiding safer design choices. Brittle cracking Abaqus can be modeled using various methods, including the Johnson-Holmquist (JH) model, XFEM, and energy-based approaches, each suited to different types of loading conditions.
For dynamic, high-strain applications like impacts, the JH model is effective, particularly in Abaqus/Explicit with specific damage parameters. For general crack modeling, XFEM is versatile, allowing cracks to form naturally without predefined paths. The energy-based method is useful for slow-loading scenarios, defining an energy threshold for fracture initiation. Each method requires careful input of material properties, mesh refinement, and load conditions to reveal potential failure points and improve material performance in real applications.
Concrete Damage Plasticity Simulation of FRP-Confined Concrete Columns in Abaqus
This tutorial package provides a comprehensive guide to implementing USDFLD subroutine in the context of Concrete Damage Plasticity Material Model. The tutorial focuses on key modeling aspects such as definition of concrete material properties using Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) Model. A theoretical background of the model will be presented and detailed explanation of the definition of all material properties will be given. The package will also explain the usage of the USDFLD subroutine to modify concrete material properties dynamically during simulation. Examples of implementing USDFLD in the context of CDP will be presented with focus on material properties that vary in function of pressure and axial strain defined as field variables.
All other modeling details will also be explained including boundary conditions, meshing, loading, and interactions.
By following the detailed steps in this tutorial, you will be able to create and analyze advanced FEM simulations in Abaqus with a focus on concrete having properties that vary during simulation.
Computational Predictions for Predicting the Performance of Structure
This package focuses on developing and applying predictive models for the structural analysis of steel and concrete components subjected to fire and subsequent earthquake loading. To accurately simulate the complex behavior of these structures, finite element analysis (FEA) using ABAQUS is employed. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept. However, due to the computational demands of FEA, various machine learning techniques, including regression models, Gene Expression Programming (GEP), Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS), and ensemble methods, are explored as surrogate models. These models are trained on large datasets of FEA results to predict structural responses efficiently. The performance of these models is evaluated using statistical metrics such as RMSE, NMSE, and coefficient of determination.
Damage Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Tunnels under Internal Water Pressure
This tutorial package equips you with the knowledge and tools to simulate the behavior of reinforced concrete tunnels (RCTs) subjected to internal water pressure. It combines the power of finite element (FE) modeling with artificial intelligence (AI) for efficient and accurate analysis. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques such as regression, GEP, ML, DL, hybrid, and ensemble models, we significantly reduce computational costs and time while achieving high accuracy in predicting structural responses and optimizing designs.
A Comprehensive Tutorial for Soft Body Impact Composites Simulation
This comprehensive tutorial package focuses on simulating soft body impact composites on laminated composite materials using the Finite Element Method (FEM) in Abaqus. The course covers key topics such as soft body modeling, metal material modeling, composite material modeling, composite to composite interface modeling, metal to composite interface modeling, interaction between soft bodies and FML, interaction between layers, and Python scripting for parametric studies. Users will explore different material models and learn about impact failure mechanisms, including matrix failure, fiber failure, shear failure, and delamination. The course is structured into lessons that cover theoretical aspects, followed by hands-on workshops to model soft body impacts, apply material properties, and analyze post-processing results such as forces, displacements, and energy dissipation. It also includes an advanced section on Python scripting, enabling users to automate parametric studies for complex simulations. This package is ideal for engineers, researchers, and students looking to deepen their understanding of soft body impact phenomena and composite material behavior.
Computational Modeling of Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) Behavior
This course equips engineers with the tools to design and analyze Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) and Reinforced Concrete Shear Walls (RCSW) subjected to explosive loads. Traditional Finite Element (FE) simulation is time-consuming and requires numerous samples for accurate results. This package offers a more efficient approach using Artificial Intelligence (AI) models trained on FEA data. You'll learn to develop FE models of SPSW and RCSW in ABAQUS software, considering material properties, interactions, and boundary conditions. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
We then delve into AI modeling using MATLAB. Explore various methods like regression, Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and ensemble models to predict the behavior of SPSW and RCSW under blast loads. Statistical analysis helps compare model accuracy. By combining FE analysis with AI models, you'll gain a powerful tool for designing blast-resistant structures while saving time and resources.
Abaqus advanced tutorials on concrete members
Welcome to the "Abaqus Advanced Tutorials on Concrete Members" course, designed to provide civil and structural engineers with cutting-edge expertise in finite element modeling (FEM) and simulation using Abaqus. This advanced-level course focuses on the detailed modeling of complex concrete and composite columns under various loading conditions. Topics include the simulation of tubed reinforced concrete columns, concrete-filled double skin steel columns, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite columns. Participants will delve into axial and eccentric compression loading scenarios, with a special focus on hollow and tapered cross-sections. The course also emphasizes comparing simulation results with experimental data from published research, ensuring practical relevance and accuracy. By the end of the course, learners will be equipped with the necessary skills to tackle advanced structural analysis challenges using Abaqus, reinforcing their understanding of concrete member behavior in real-world applications.
Bicycle Stress Analysis with Ansys Mechanical
This tutorial package offers a comprehensive introduction to linear-static analysis using Ansys Mechanical, focusing on a bicycle stress analysis with the case study which is a bicycle crank made from Aluminum 6061-T6. Whether you're a beginner looking to get started with FEA or an experienced engineer seeking to refine your skills, the package provides a strong foundation in the fundamental techniques needed to succeed in real-world applications.
The tutorial covers the essential steps in finite element analysis (FEA), including the model setup, simulation, and interpretation of results. By leveraging Ansys Mechanical, users will perform a full simulation on the crank geometry to assess stress distribution, deformation, and safety under load conditions. Key topics include mesh generation along with mesh refinement, and the application of boundary conditions. The tutorial guides users through material property assignment, mesh independence, and validation with hand calculations, ensuring accuracy.
Ansys-specific features, including post-processing tools for analyzing total deformation, bending stress, and the factor of safety, are thoroughly demonstrated. This package also highlights the power and efficiency of Ansys Mechanical, emphasizing its user-friendly interface and ability to handle complex simulations with greater precision compared to competitors, making it one of the best-in-class structural analysis FEA software.
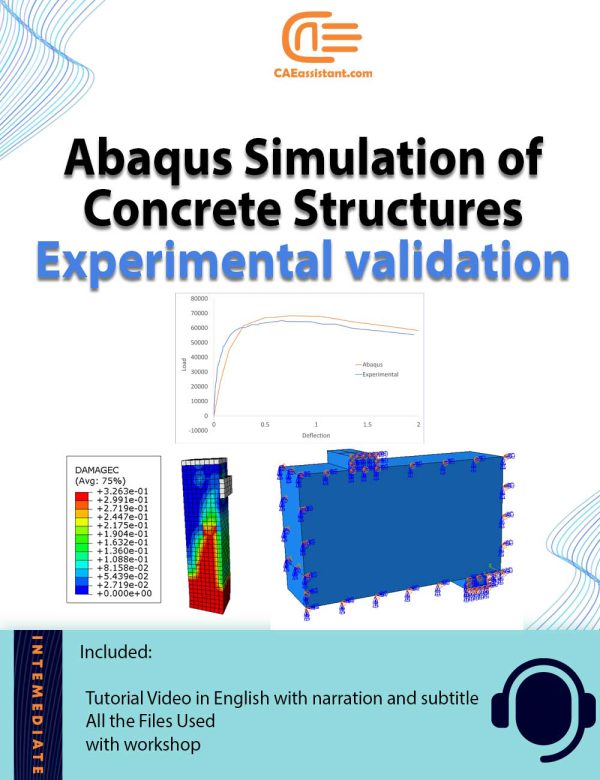
Analysis of Plain and Reinforced Concrete Structures with ABAQUS | Validation with Experiments
This comprehensive package offers four different workshops focused on the analysis of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete structures using ABAQUS. Designed for professionals, researchers, and students, it provides hands-on learning in modeling, simulating, and validating concrete structures under various conditions. Each workshop dives into specific aspects of concrete behavior, from flexural to compressive strength, incorporating the latest sustainable practices through the use of recycled materials. The package ensures mastery of ABAQUS, offering practical insights and a cost-effective path to advanced concrete analysis and safer, more durable infrastructure design.
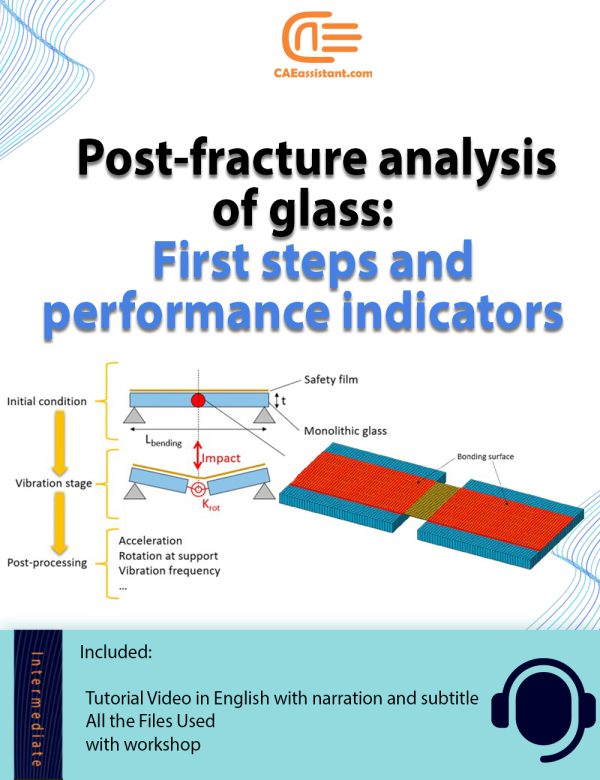
Note: Only the first workshop has video.Glass Fracture Analysis with Abaqus | Post-Fracture
This tutorial explores a finite element method (FEM) simulation using Abaqus to analyze the post-fracture behavior of structural glass members retrofitted with anti-shatter safety films. In particular, it focuses on simulating and calibrating the vibration response of cracked glass elements under repeated impacts and temperature gradients, contributing to a comprehensive analysis of critical phenomena that take place in the post-fracture stage. This tutorial follows the methodology outlined in the research article “Effects of post-fracture repeated impacts and short-term temperature gradients on monolithic glass elements bonded by safety films”.
Key aspects include modeling glass fracture, assigning material properties, and defining boundary conditions to assess the vibration frequency and load-bearing capacity of cracked monolithic glass members. Additional topics cover basic concepts of dynamic identification techniques, definition of performance indicators for glass retrofit efficiency, and frequency sensitivity analysis of monolothic retrofitted glass elements under various operational and ambient conditions. The simulation results help quantify the expected contribution and residual strength of safety films in post-fracture scenarios, providing a robust framework for structural engineers to extend this investigation to other glass configurations.
This tutorial is ideal for users who want to understand FEM modeling in Abaqus and perform detailed simulations involving complex material interactions, with a focus on practical applications in glass retrofit technology.
Machine Learning for Composite Materials with Abaqus
This tutorial package delves into an advanced inverse modeling approach for predicting carbon fiber properties in composite materials using a machine learning (ML) technique. Focused on machine learning for composite materials applications, it covers the use of Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) to build a surrogate model for accurate predictions of fiber properties based on data from unidirectional (UD) lamina. By leveraging Finite Element (FE) homogenization, synthetic data is generated for training the GPR model, accounting for variations in fiber, matrix properties, and volume fractions. This framework’s efficiency and accuracy are validated using real-world data, highlighting its potential as a computational alternative to traditional experimental methods. The package includes detailed explanations, case studies, and practical exercises, equipping users with hands-on experience in applying this ML-based approach to composite material analysis.
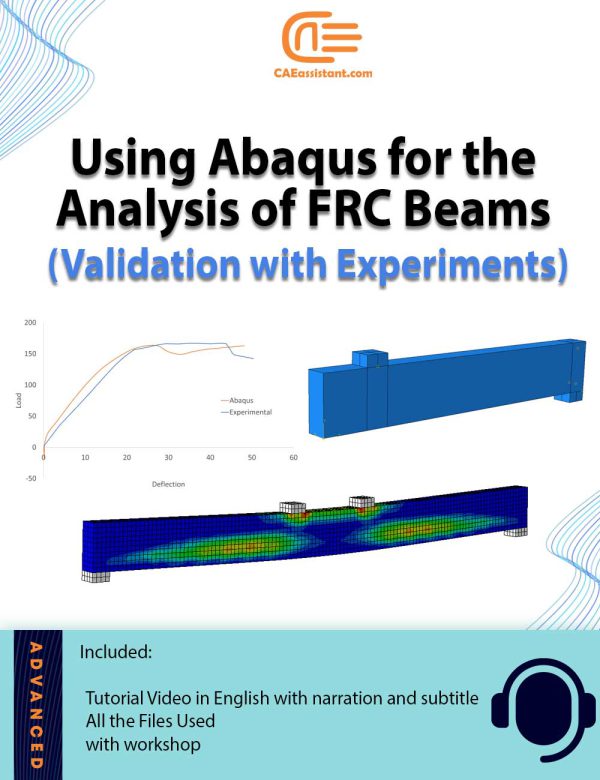
Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams | An Abaqus Simulation
Abaqus basic tutorials on concrete beams and columns
Welcome to the “Abaqus Basic Tutorials on Concrete Members,” a comprehensive course tailored for civil and structural engineers seeking to master finite element modeling (FEM) of concrete structures. This tutorial covers key concepts such as plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforced concrete members, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. The course guides learners through the application of boundary conditions, material properties, and various loading conditions in Abaqus. Key topics include plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforcement modeling with steel bars and stirrups, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement techniques. Participants will also explore comparing simulation results with experimental data, as well as interpreting critical outcomes such as stress distribution and failure modes. Through hands-on workshops, learners will simulate structural behaviors under axial, lateral, and compression loads, ensuring a practical understanding of FEM for concrete members. By the end of this course, participants will be proficient in using Abaqus to model and analyze concrete structures, reinforced elements, and advanced composites, providing them with a strong foundation for structural analysis and design.