What is FSI?|FSI Abaqus analysis
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) refers to the mutual interaction between a fluid flow and a deformable or movable structure. It involves the exchange of forces, momentum, and energy between the fluid and the structure, resulting in dynamic behavior and deformation of the structure in response to the fluid flow.
Here are some practical examples of FSI:
- Aircraft Wing Flexibility: The interaction between the airflow and the flexible wing of an aircraft affects its aerodynamic performance. FSI simulations help analyze the structural deformation and its impact on lift, drag, and stability.
- Bridge and Dam Analysis: Fluid flow around bridges and dams can induce vibrations, oscillations, and even structural damage. FSI simulations assist in understanding the fluid-induced forces and their effects on the structural integrity and stability of these infrastructures.
- Blood Flow in Arteries: The interaction between blood flow and arterial walls is crucial in understanding cardiovascular diseases. FSI simulations aid in studying the impact of blood flow patterns, pressure distribution, and wall deformation on the development of diseases like atherosclerosis.
- Wind Turbine Design: The interaction between wind and turbine blades affects their performance and structural integrity. FSI simulations help optimize turbine designs, considering factors such as aerodynamic efficiency, fatigue life, and vibration response.
- Ocean and Offshore Engineering: FSI is crucial in analyzing the behavior of offshore structures, such as platforms and floating wind turbines, under wave and current loads. It helps examine the dynamic response, fatigue life, and safety of these structures.
- Heart Valve Function: FSI simulations are used to study the functioning of heart valves, considering the fluid flow through the valve and its impact on the valve leaflet motion, stresses, and strains. This aids in evaluating valve performance and designing improved prosthetic valves.
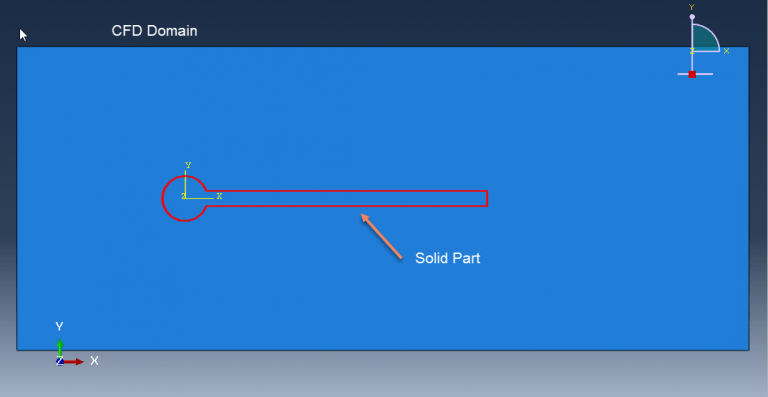
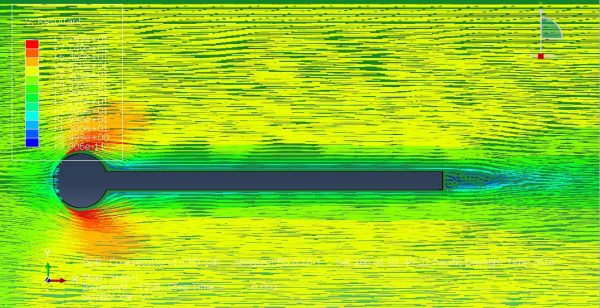
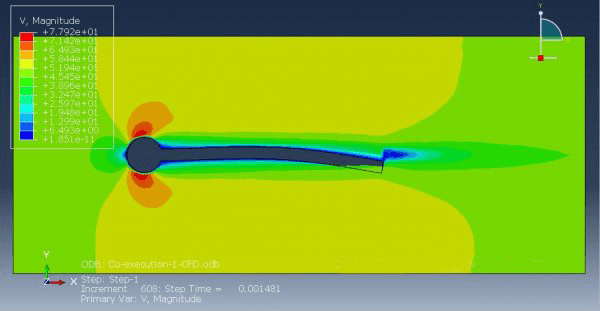
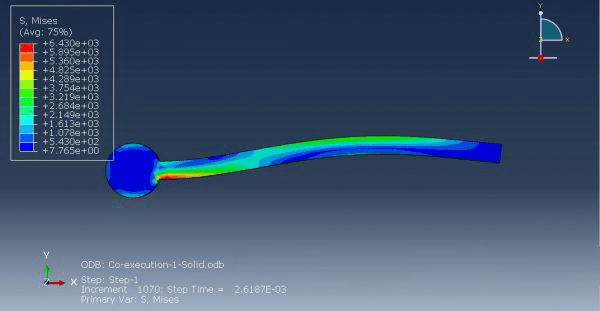
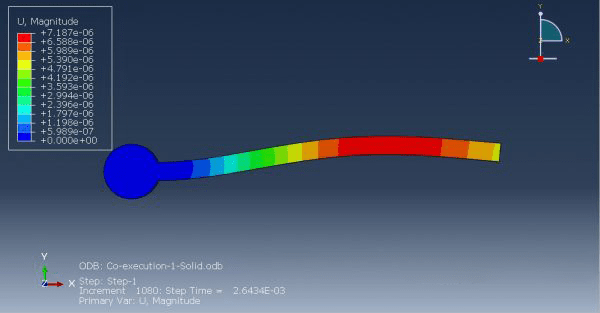
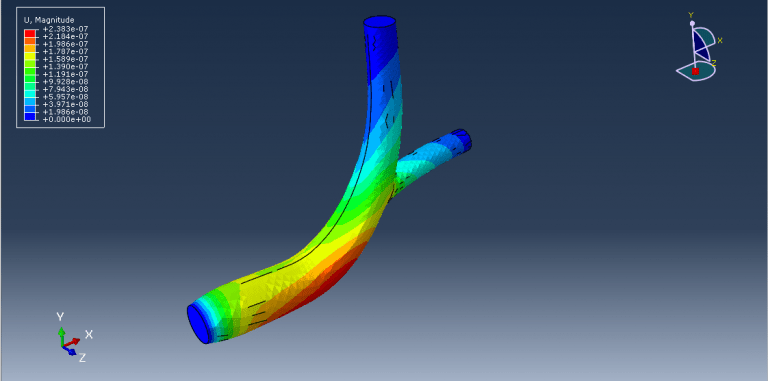
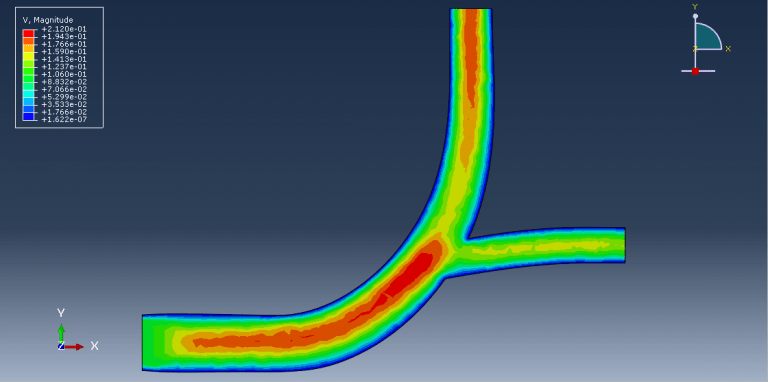
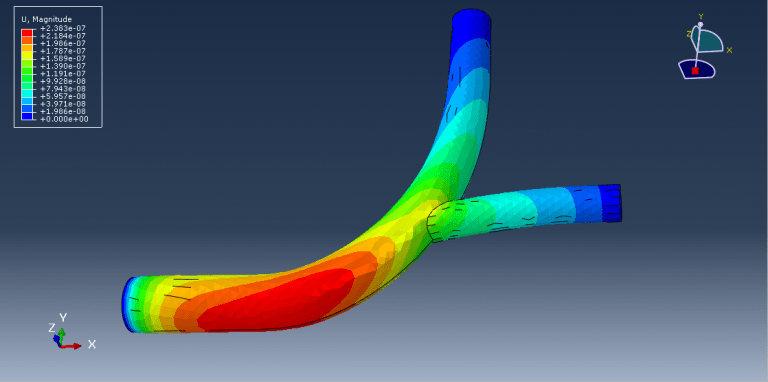
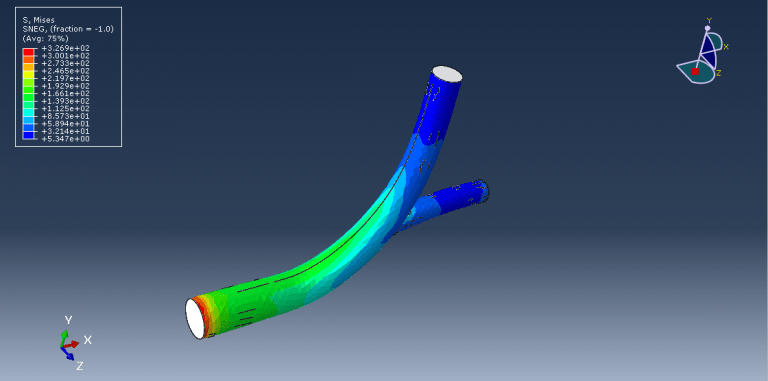
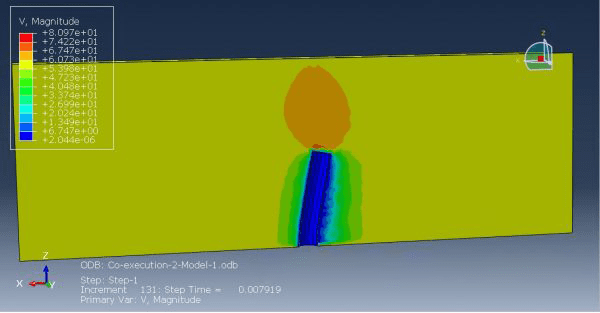
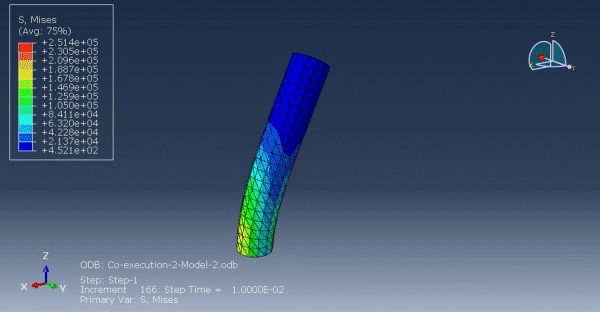
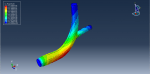
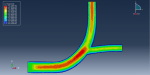
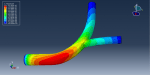
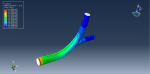
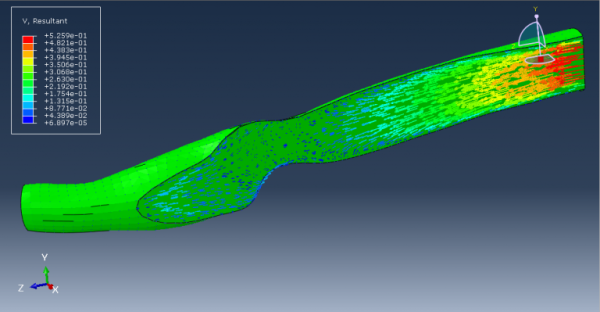
Workshop 1: FSI simulation on the Aluminum body with flexible tail
Fluid-structure interaction (FSI) refers to the interaction between a movable or deformable structure and the fluid flow that surrounds it or is contained within it. These interactions can either be stable or oscillatory. In oscillatory interactions, the strain exerted on the solid structure causes it to move in a way that reduces the strain, returning the structure to its original state before the process repeats. Considering fluid-structure interactions is crucial when designing various engineering systems, such as aircraft, spacecraft, engines, and bridges. Neglecting the effects of oscillatory interactions can have catastrophic consequences, particularly in structures made of materials prone to fatigue. In this video, an FSI simulation was conducted on an aluminum body with a flexible tail to study these interactions.




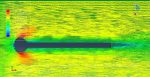
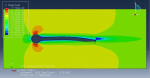
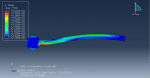
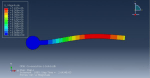





Xu Hui –
Why is Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) analysis important in Abaqus software, and what are the benefits for engineers and researchers? Can FSI analyses identify issues such as vibrations, instabilities, and structural failure through accurate modeling of complex interactions between fluid and structure?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) analysis is crucial in Abaqus software and offers several benefits for engineers and researchers. Here’s why FSI analysis is important and how it can help identify issues like vibrations, instabilities, and structural failure:
Realistic modeling: FSI analysis allows for accurate modeling of complex interactions between fluids and structures. It considers the two-way interaction, where the fluid affects the structure and vice versa. This enables engineers to simulate realistic scenarios and obtain more accurate results.
Dynamic response: FSI analysis helps in understanding the dynamic response of structures subjected to fluid flow. It can capture phenomena such as fluid-induced vibrations, aeroelastic effects, and acoustic resonances. By considering these interactions, engineers can assess the structural integrity and performance under dynamic loading conditions.
Stability and fatigue analysis: FSI analysis can identify potential issues related to stability and fatigue. For example, it can evaluate the effects of fluid-induced instabilities on structures, such as flutter or vortex shedding. By simulating these scenarios, engineers can optimize designs to mitigate risks and ensure structural stability and durability.
Performance optimization: FSI analysis enables engineers to optimize the performance of structures in fluid environments. By studying the fluid-structure interaction, they can identify areas of high stress, pressure, or turbulence that may lead to structural failure or reduced efficiency. This information can guide design modifications to enhance performance and reliability.
Multiphysics simulations: FSI analysis integrates multiple physics domains, such as fluid dynamics and structural mechanics. This capability allows engineers to study problems involving, for example, fluid-structure-acoustic interactions or fluid-structure-thermal interactions. By considering these coupled effects, engineers can gain comprehensive insights and make informed design decisions.