Abaqus Crack growth simulation | Practical examples
If you are a researcher, student, university professor, or Engineer in the company in the field of fracture mechanics, this training package in simulating crack growth in Abaqus software is the best selection.
In this package, everything you need to simulate crack growth is completely available from simple to advanced. It includes modeling crack growth in Abaqus to crack propagation methods and damage to various materials. Note that crack growth in some cases requires using special features of Abaqus software.
You can see the syllabus and details of this workshop below or the drop-down menu on the right side of this product page.
![]() It will guide you going from the basics up to complex simulation techniques. it is very fluid, and comprehensive and every single detail is explained.
It will guide you going from the basics up to complex simulation techniques. it is very fluid, and comprehensive and every single detail is explained.
![]() Every workshop goes straight to the point, without any worthless piece of content. You will learn what you need at every stage and you will be putting it into practice from the very first day.
Every workshop goes straight to the point, without any worthless piece of content. You will learn what you need at every stage and you will be putting it into practice from the very first day.
In a word, being complete and having support in this course is the essential value of this course.
![]() Most importantly, we support you as you learn in this course. You can contact our experts to ask your questions and enjoy our modeling and simulations step-by-step support.
Most importantly, we support you as you learn in this course. You can contact our experts to ask your questions and enjoy our modeling and simulations step-by-step support.
Read More: abaqus fracture
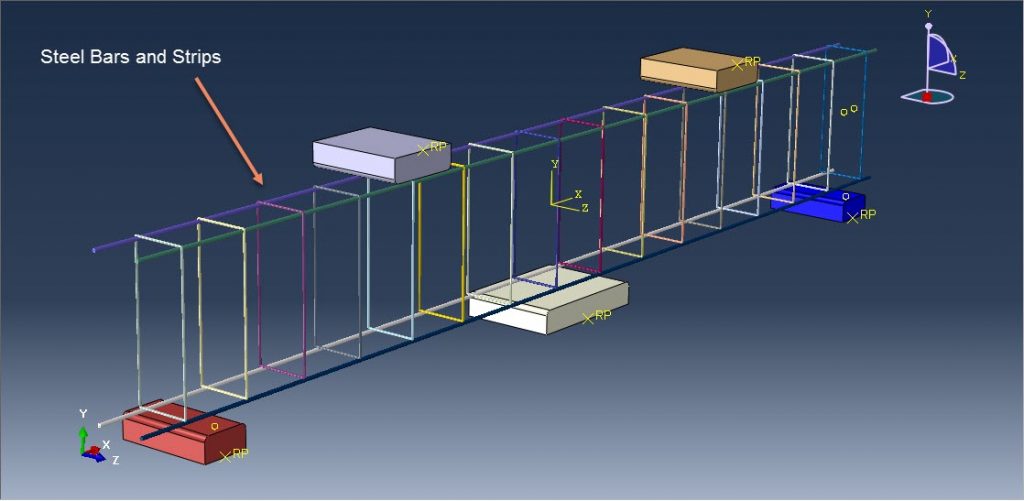
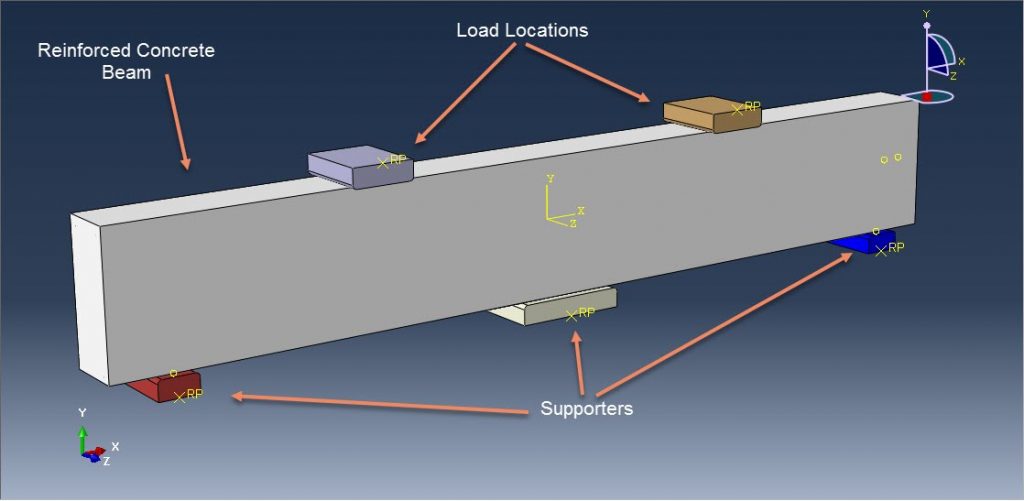
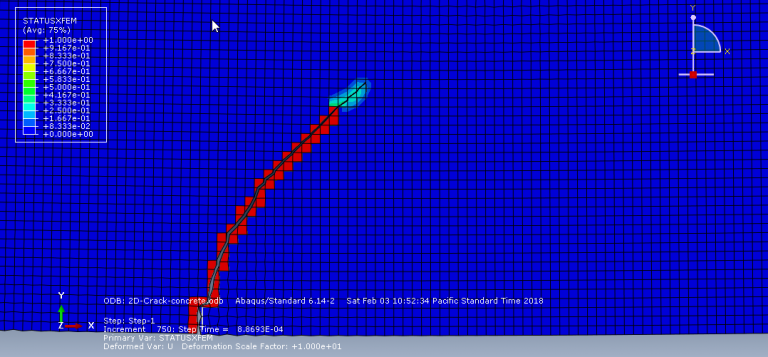
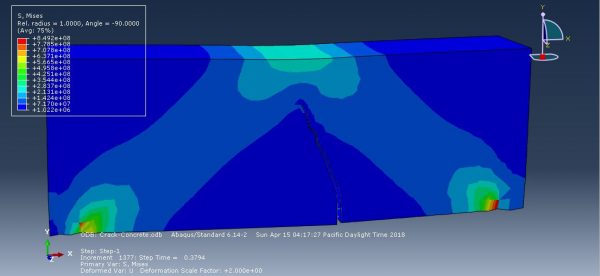
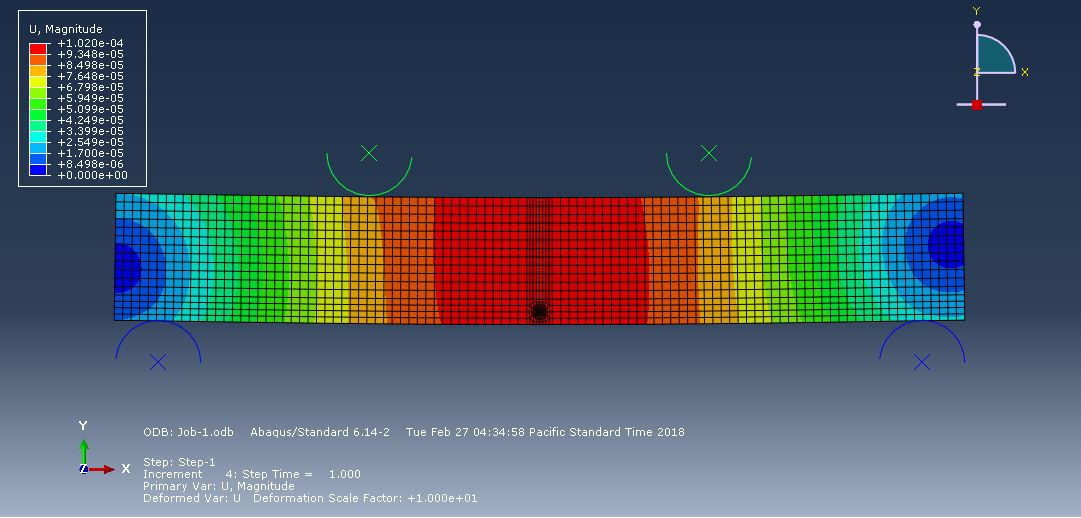
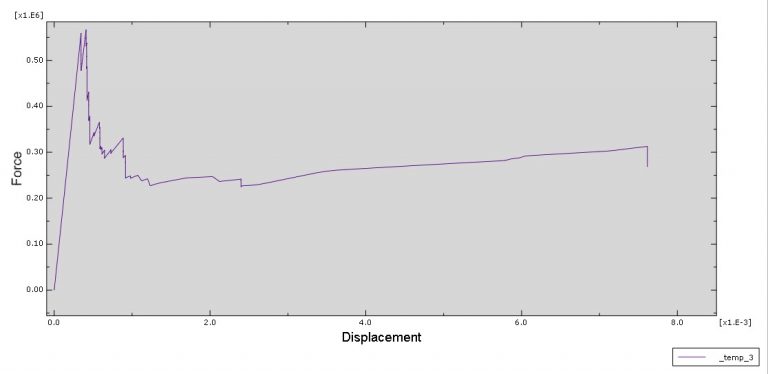
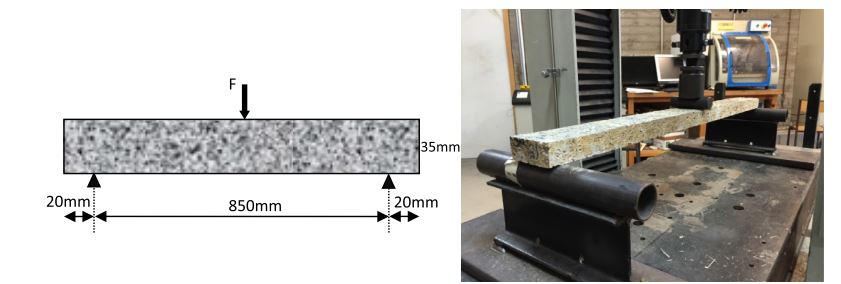
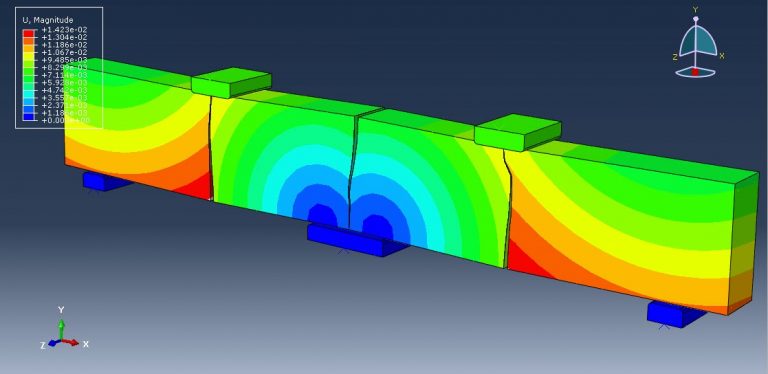
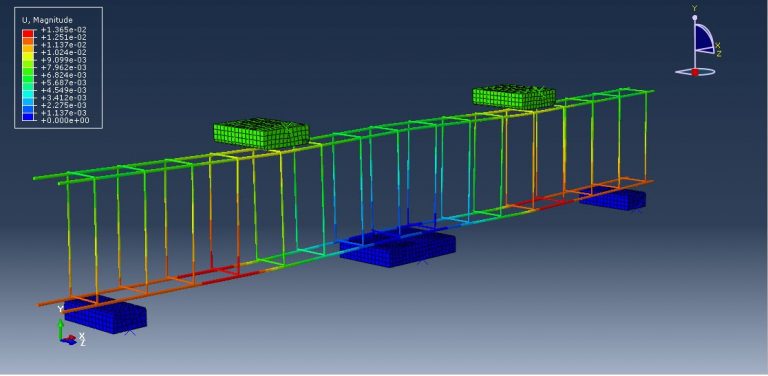
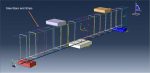
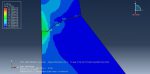
Workshop-1: Abaqus simulation of crack growth in the RC beam under 5 points bending
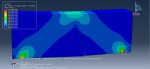
This workshop explores the simulation of crack growth in a reinforced concrete (RC) beam subjected to five-point bending in Abaqus. The concrete beam is represented as a three-dimensional solid component, while the reinforcing bars and strips are modeled as three-dimensional wire elements. The support structures and hydraulic jacks are modeled as three-dimensional rigid shell components.
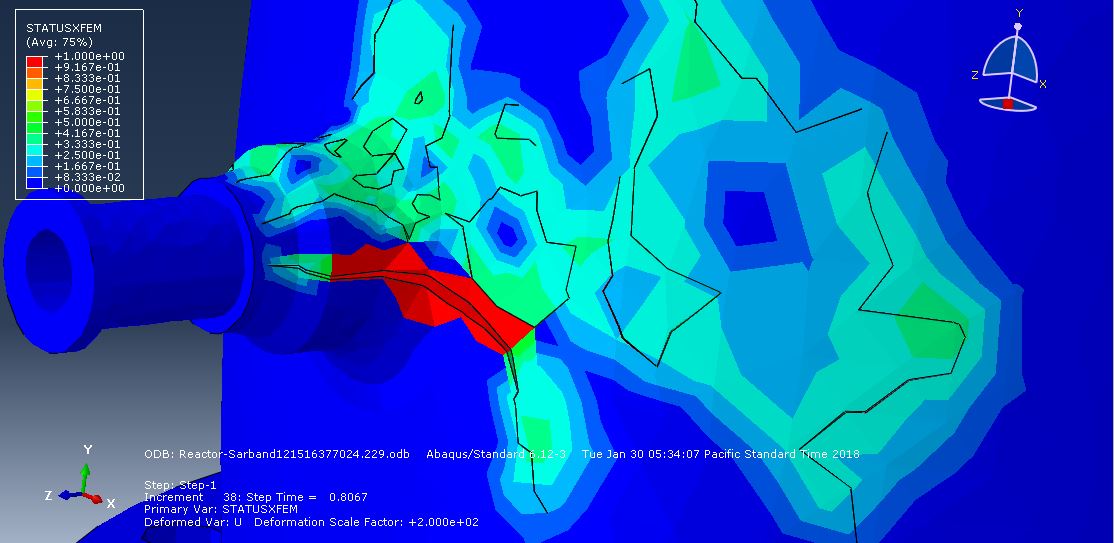
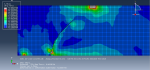
The traction-separation law is employed to represent the concrete’s behavior and crack propagation. The cohesive behavior in the enriched elements is defined, with the maximum principal stress criterion used for initiating damage and an energy-based damage evolution law, following a power-law fracture criterion, applied for damage progression. Steel bars and strips are modeled using elastic-plastic material properties. A general static step is utilized, with adjustments to the convergence algorithm. The steel elements are embedded within the concrete, and surface-to-surface contact with friction is applied between all rigid bodies and the concrete beam. The XFEM method is used to track crack growth within the RC beam. Fixed boundary conditions are applied to the three bottom rigid bodies, while displacement constraints are imposed on the top two rigid bodies. A fine mesh is required for accurate crack path prediction.
Post-simulation results, including crack propagation, stress distribution, displacement, and XFEM outputs, can be accessed.
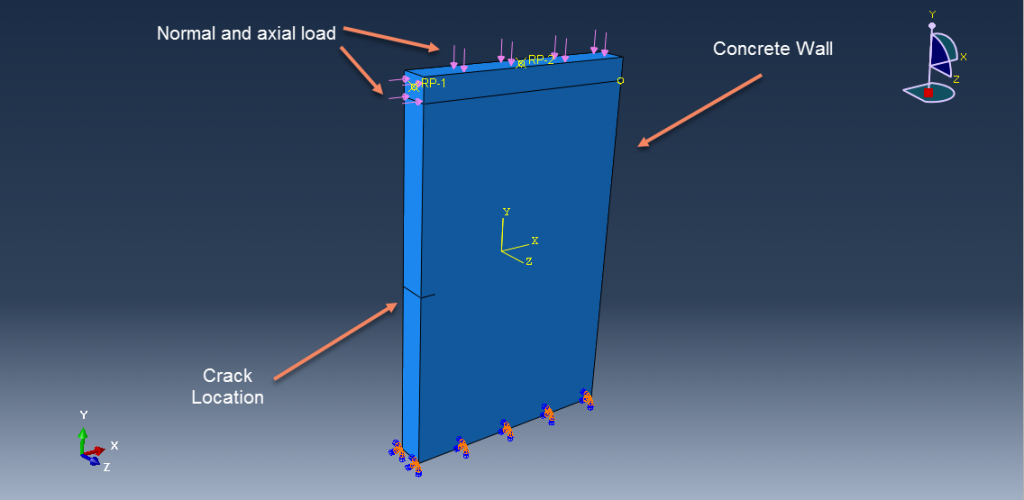
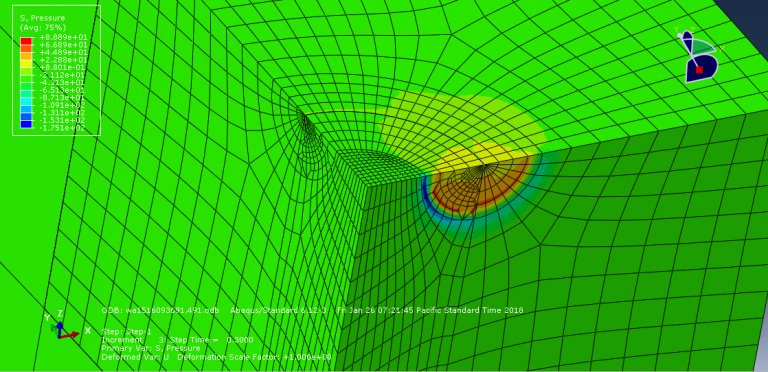
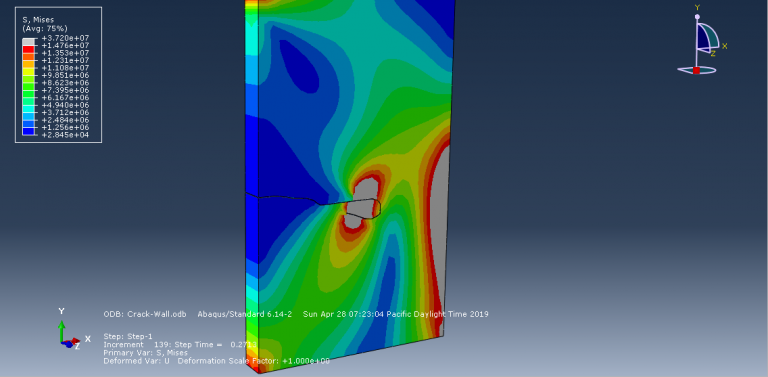
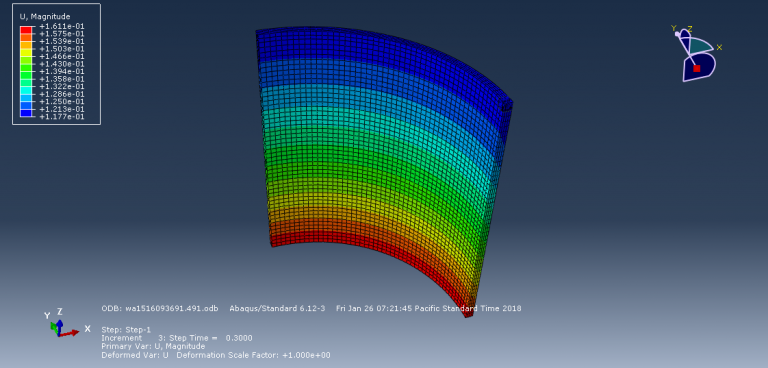
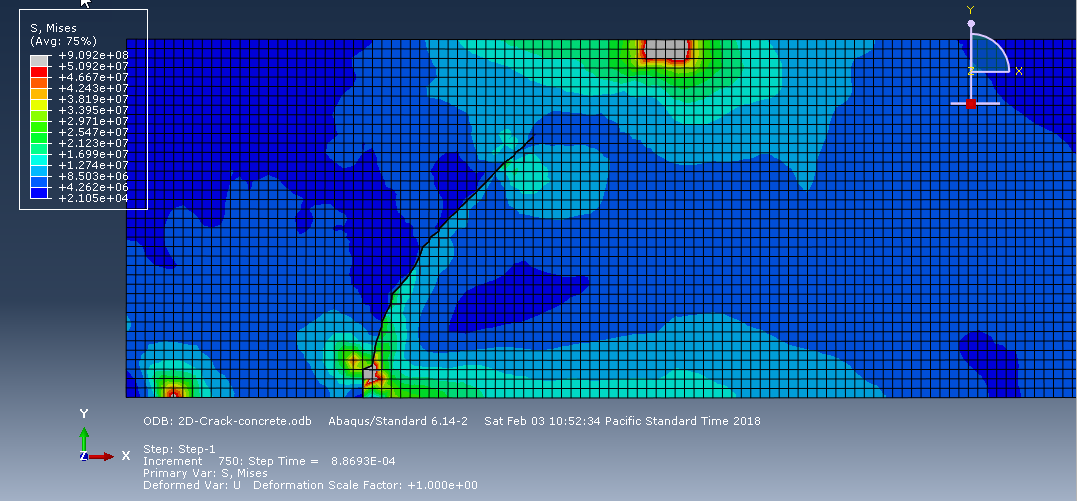
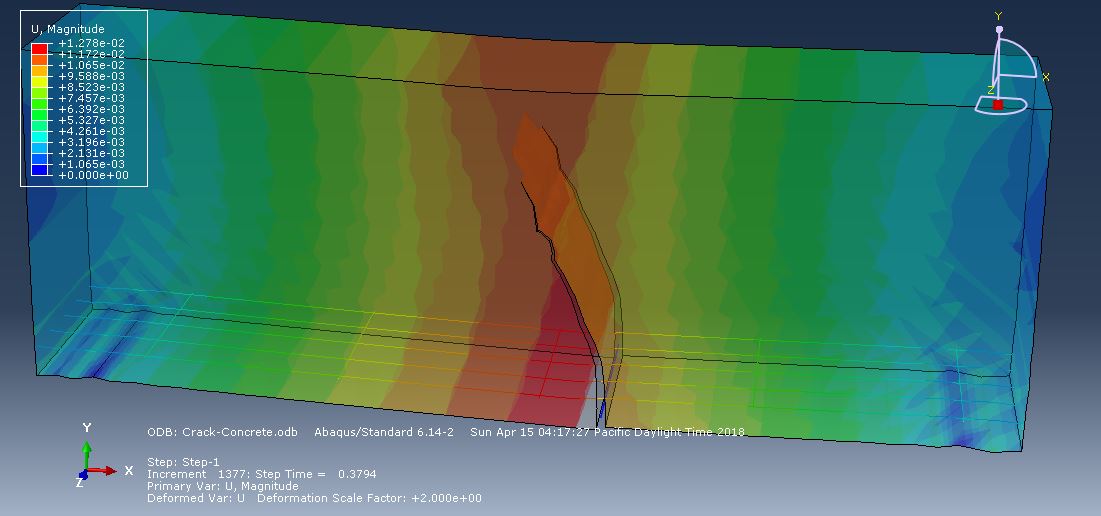
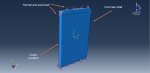
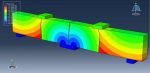
Workshop-2: Abaqus simulation of crack growth of a concrete wall under normal and transverse loading
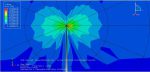
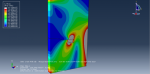
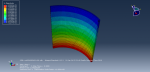
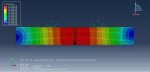
This workshop examines the simulation of crack growth in a concrete wall subjected to both normal and transverse loads in Abaqus. The concrete wall is modeled as a three-dimensional part, and the crack plane is represented as a shell part.
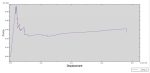
For the concrete, the traction-separation law based on maximum principal stress and fracture energy is used. This material model is crucial for accurately simulating the physical behavior of crack propagation. A general static step is suitable for this type of analysis. The XFEM procedure is applied to model crack growth within the concrete wall, with the crack plane defined as the initial crack location. Fixed boundary conditions are applied at the bottom of the wall, and vertical and horizontal pressure loads are applied to the wall. The mesh size significantly influences the crack growth pattern.
As the vertical and horizontal pressure loads are applied, cracks begin to propagate, growing along the crack plane throughout the simulation.
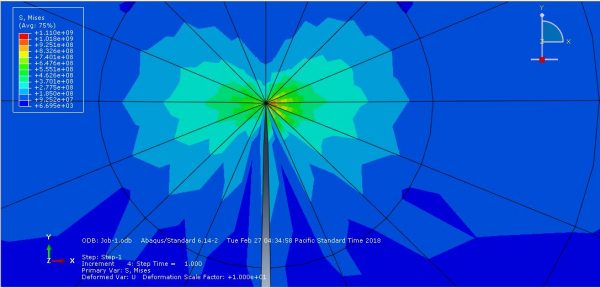
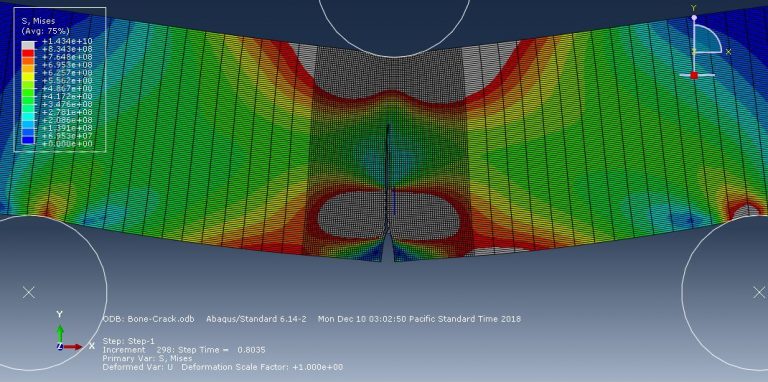
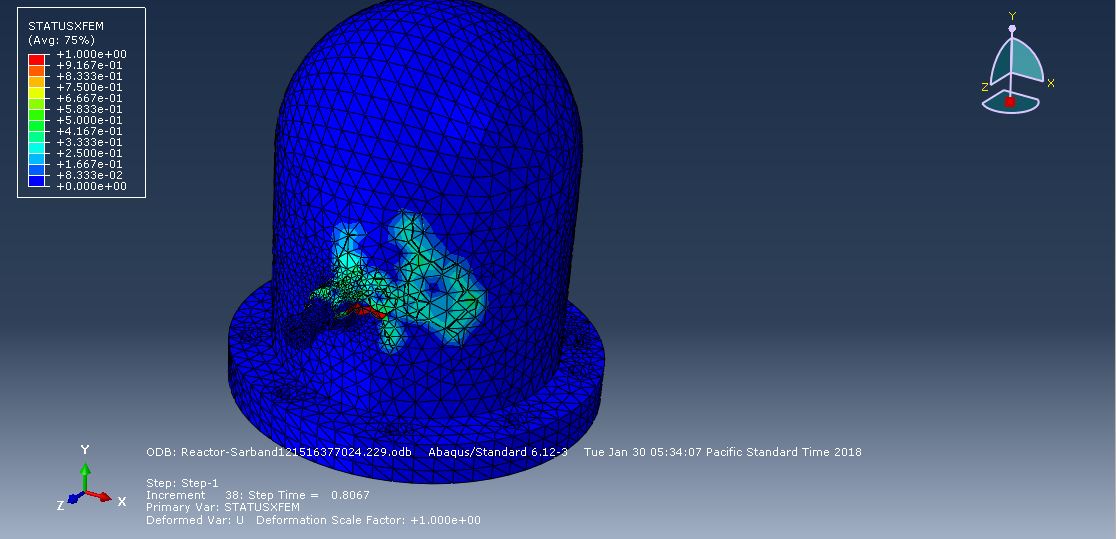
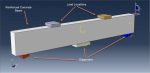
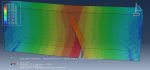
Workshop-3: Abaqus simulation of crack growth of a bone under 3 points bending
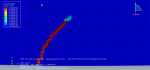
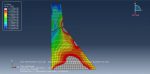
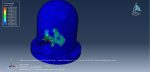
This workshop explores the simulation of crack growth in bone subjected to three-point bending in Abaqus. The structural analysis of bones is an area of active research, with many researchers using the finite element method (FEM) to gain a deeper understanding of bone fracture mechanisms. However, most previous studies have only focused on stress or strain distribution patterns, without illustrating how fractures initiate, progress, or how fracture lines propagate. Bones can fracture in various ways; for instance, a closed fracture occurs when the bone breaks without damaging surrounding tissue or puncturing the skin, whereas a compound (or open) fracture involves damage to the skin and potential infection, making it more severe than simple fractures.
In this simulation, the bone is modeled as a two-dimensional part with elastic material properties, combined with the traction-separation law to simulate crack growth during the analysis. Static analysis and the XFEM procedure are used for this type of study.
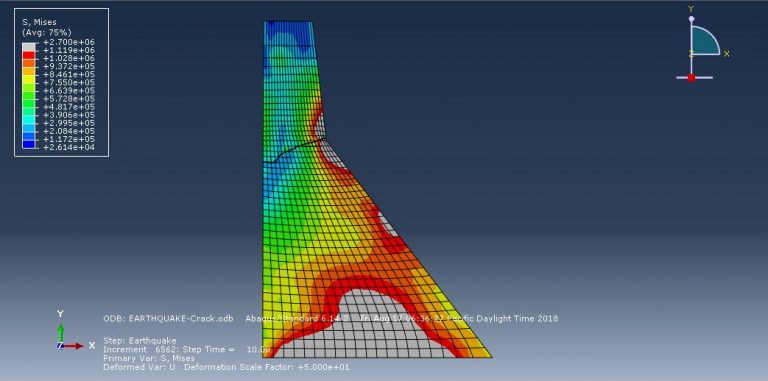
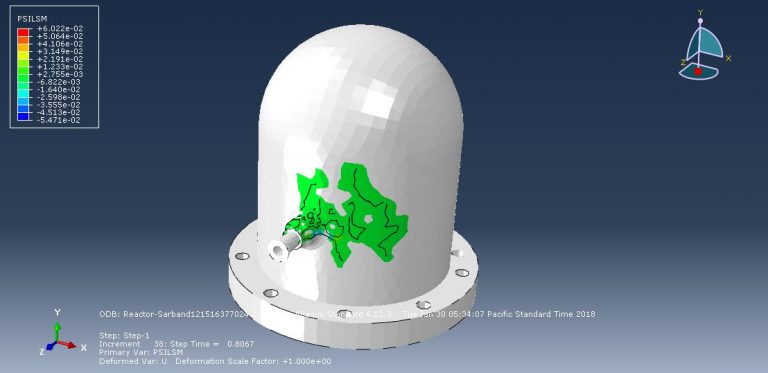
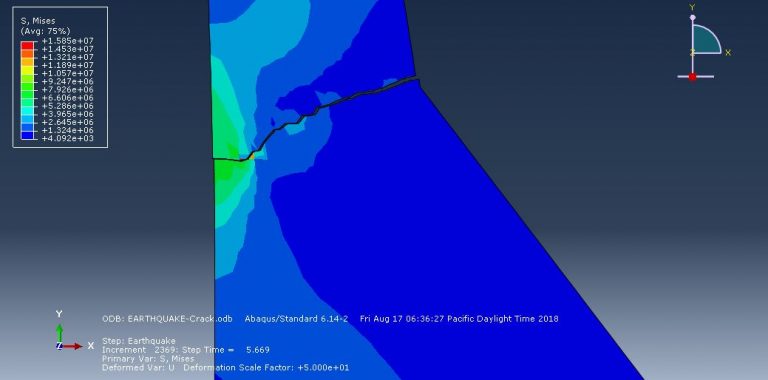
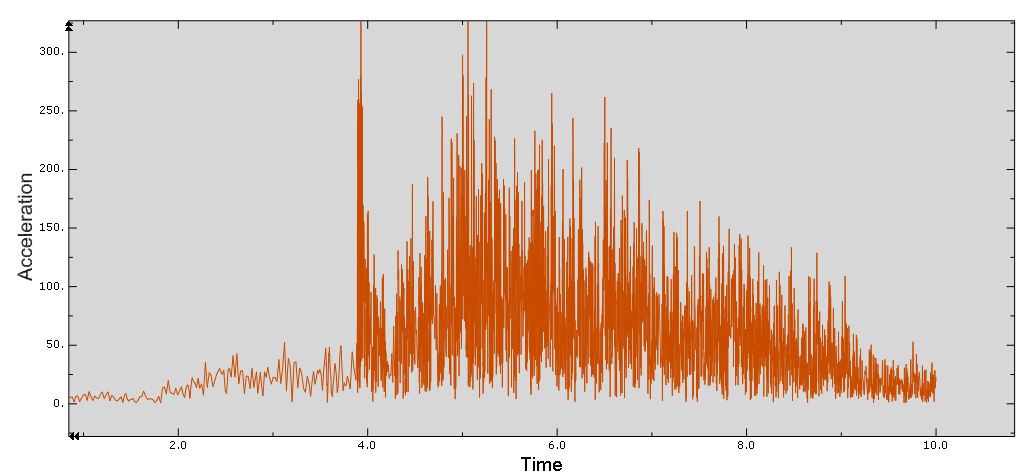
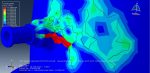
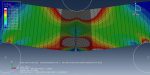
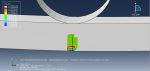
Workshop-5: Abaqus simulation of crack growth in the Koyna dam under seismic loading
In this workshop, we analyze the Koyna Dam, which experienced an earthquake of magnitude 6.5 on the Richter scale on December 11, 1967. The case demonstrates a typical application of concrete damage modeling based on traction-separation laws. The dam is modeled as a two-dimensional component with damaged material properties. Before simulating the earthquake’s dynamic effects, the dam is first subjected to gravity loading and hydrostatic pressure. In the Abaqus/Standard analysis, these loads are applied in two sequential static steps, using a distributed load with labels GRAV (for gravity load) in the first step and HP (for hydrostatic pressure) in the second step. To simulate crack growth, the XFEM procedure is used, and during the analysis, crack propagation within the dam is modeled based on tensile damage, as described in the Abaqus documentation.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet