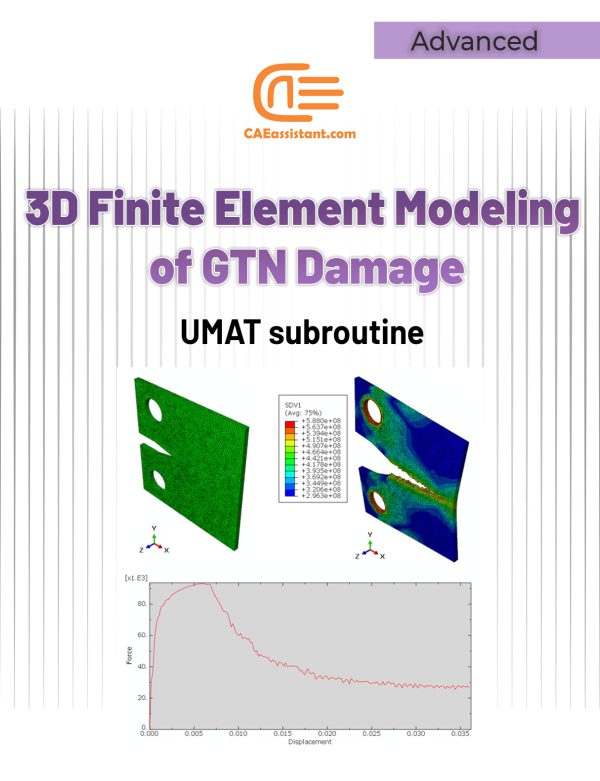
3D Simulation of Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) Damage Model
Abaqus User element tutorial | UEL advanced level
Dynamic Response of Ballasted Rail Track Under a Moving Load
Railway tracks are subjected to moving loads of trains and this causes vibration and degradation of the track. The judgment of these vibrations is important to design the railway tracks. The design involves the permissible speed of trains and the maximum axle load of the train. The model given here creates a 3D geometry of a railway track and applies a moving load in the form of a wheel. A user can change the speeds and the properties of the material including geometry as per their needs.
Laser forming simulation tutorial in Abaqus
Short fiber composite damage (Mean Field Homogenization Model)
Tread wear simulation in Abaqus
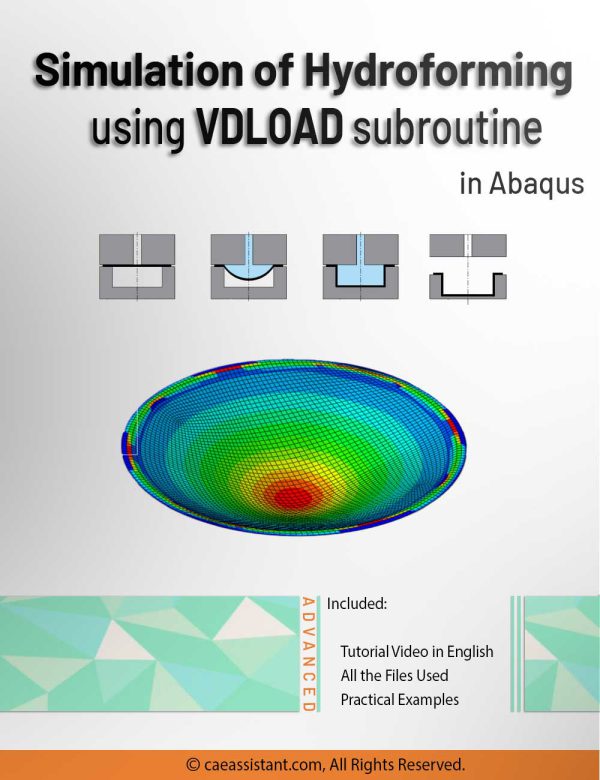
Hydroforming process simulation using VDLOAD subroutine in Abaqus
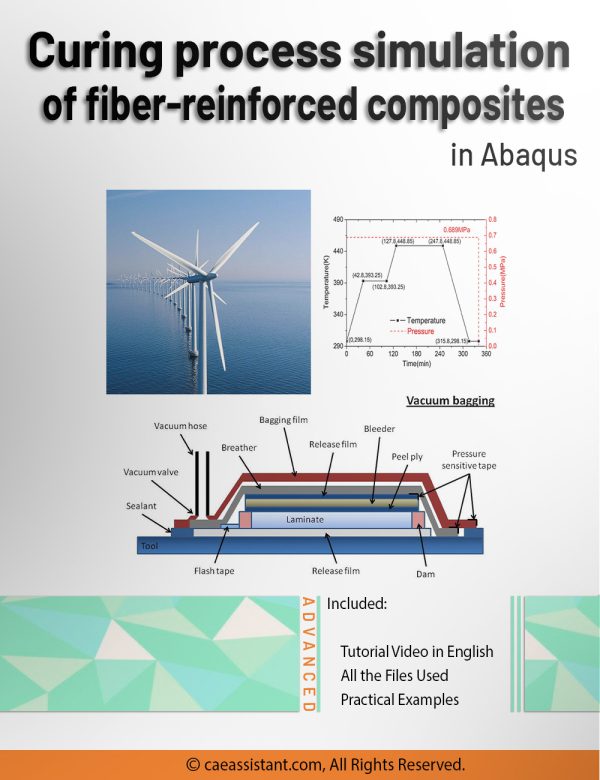
Curing process simulation in Abaqus
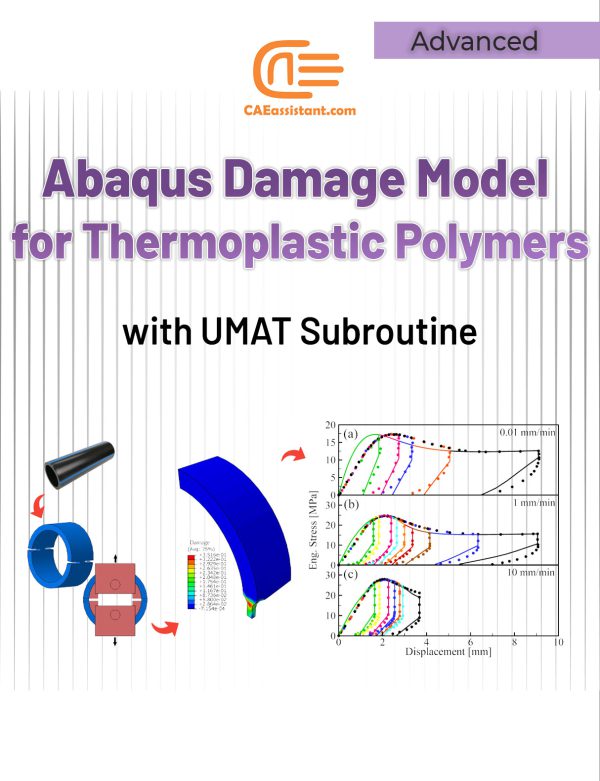
Abaqus Damage Model for Thermoplastic Polymers with UMAT Subroutine
DISP and VDISP Subroutines in ABAQUS
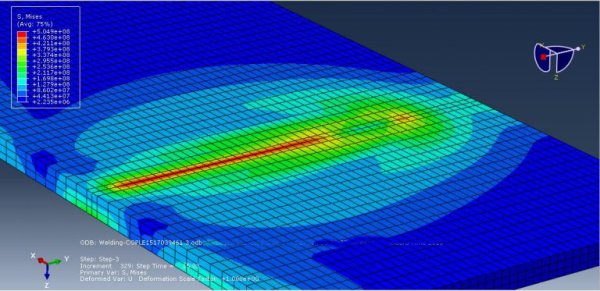
Arc welding simulation in Abaqus
Modeling Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) in ABAQUS
Composite Pressure Vessel simulation in ABAQUS
Composite pressure vessel analysis with Semi-Geodesic winding
Full Composite fatigue Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
Full Composite damage Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
Ductile Damage Abaqus model for 3D continuum element (VUMAT Subroutine)
Composite Fatigue Simulation with VUMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS
Composite simulation for experts-Part-3
Pay attention to the syllabus and availability file details. some of the packages are fully available and some of them are partially available. If this is partially available it takes at least two months to be completely available.
If you are a graduate or Ph.D. student, if you are a university professor or an expert engineer in the industry who deals with simulation software, you are definitely familiar with the limitations of this software in defining the material properties, loading or meshing, interaction properties, and etc. You have certainly tried to define the properties of materials based on advanced fracture theories in finite element software and are familiar with their limitations and problems. Now, here is your solution. Start writing subroutines in finite element software and overcome the limitations. With the tutorials in the Golden Package, you will learn how to write 8 subroutines in Abaqus software professionally.Composite simulation for experts-Part-2
If you are a researcher, student, university professor, or Engineer in the company in the field of composite materials, this training package in simulating these materials in Abaqus software is the best selection. This training package is the second part of the composite for expert package and is focusing on the Simulation of woven composite damage in Abaqus, Composite Fatigue Simulation, Analysis of Composite pressure vessel with Semi-Geodesic winding, Simulation of composite Hashin damage in 3d continuum element (UMAT-VUMAT-USDFLD), and Abaqus composite modeling of Woven & Unidirectional + RVE method.
Hardening plasticity in Abaqus
Simulation of composite Puck damage in 3d continuum element in Abaqus (UMAT-USDFLD-VUMAT)