What is Hydroforming? | Hydroforming Abaqus
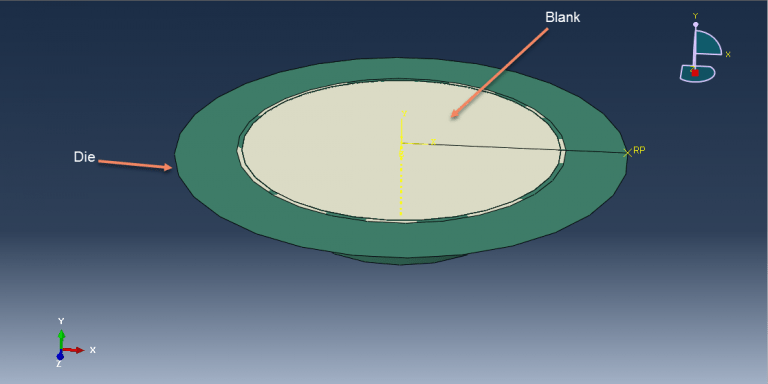
Hydroforming is a specialized manufacturing process used to shape metal components by utilizing fluid pressure. It involves the use of a high-pressure hydraulic fluid to form and reshape metal sheets or tubes into desired shapes without the need for extensive cutting, welding, or joining. In the hydroforming process, a metal blank or tube is placed within a specially designed die. The die contains a cavity that matches the desired shape of the final component. The die is then closed, and high-pressure hydraulic fluid is introduced into the die, exerting uniform pressure on the metal. This pressure causes the metal to deform and take the shape of the die cavity, resulting in the desired formed component.
Hydroforming finds applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing. It is commonly used to produce complex and structurally efficient components such as automobile frames, exhaust systems, aerospace structural parts, and kitchen sink basins.
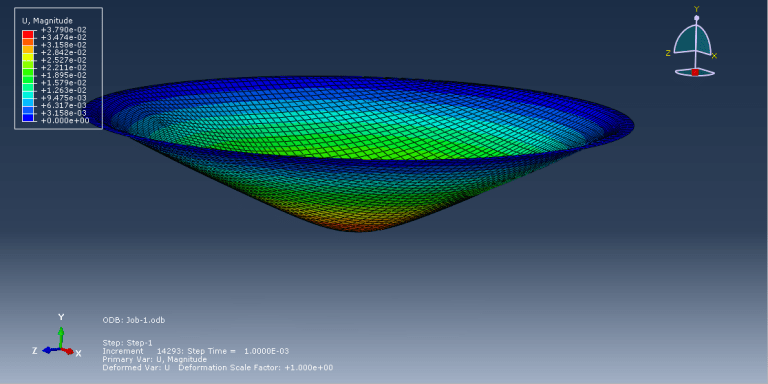
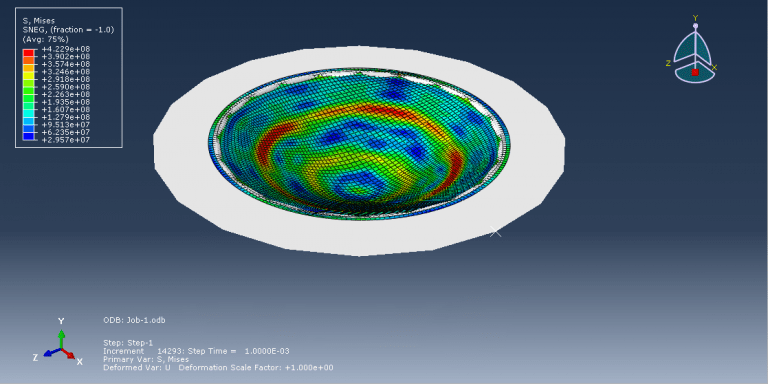
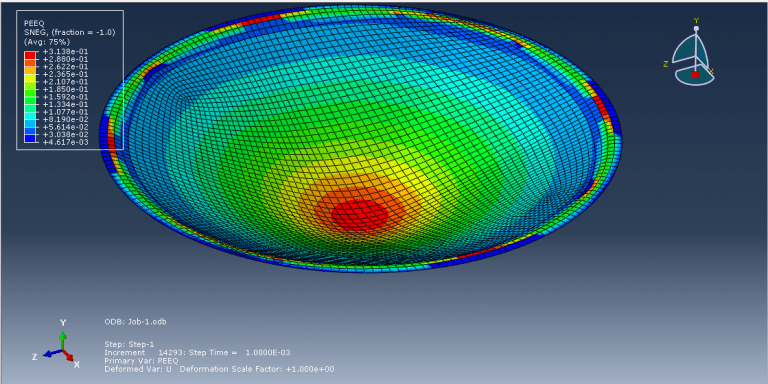
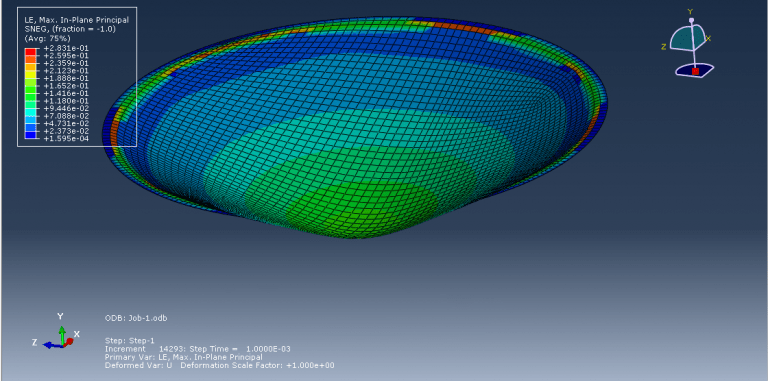
Analyzing and simulating the hydroforming process is important for several reasons (Hydroforming Abaqus). Firstly, it allows engineers to evaluate the feasibility and efficiency of using hydroforming for specific components. By simulating the process, they can assess factors such as material flow, thinning, and wrinkling, and determine if hydroforming is suitable for achieving the desired part geometry and structural integrity. Simulation also helps in optimizing the process parameters, such as fluid pressure, die design, and material properties. By analyzing the forming process, engineers can predict the effects of different parameters on the final component quality, including wall thickness distribution, strain distribution, and potential defects. This information aids in making informed decisions on process optimization and ensures the production of high-quality hydroformed components.
Additionally, simulating hydroforming allows for the evaluation and mitigation of potential issues such as springback, wrinkling, or material fracture. By analyzing the forming process, engineers can identify critical areas prone to these problems and implement corrective measures such as adjusting tooling design, modifying process parameters, or applying pre-forming techniques. Moreover, simulation is valuable for predicting and managing residual stresses and distortions induced during the hydroforming process. It helps in understanding the material behavior and mechanical properties under high-pressure conditions, enabling engineers to design appropriate post-forming treatments or compensation strategies to achieve the desired final component shape and dimensional accuracy.

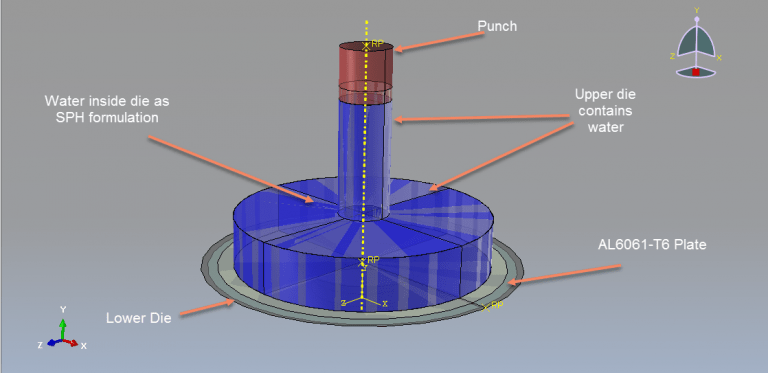
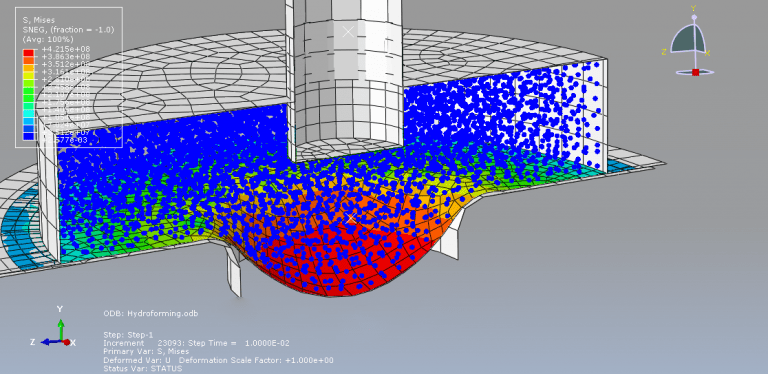
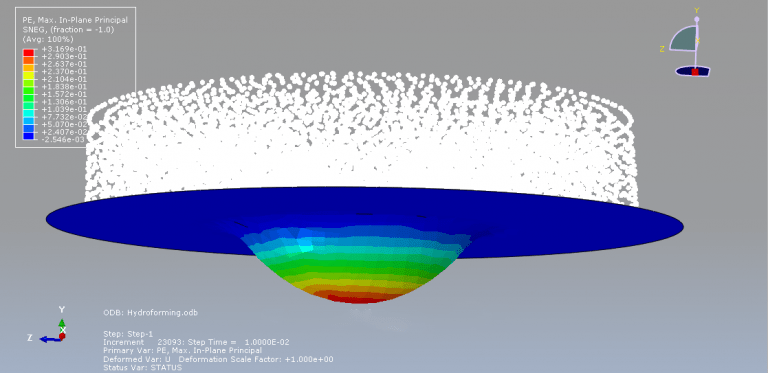
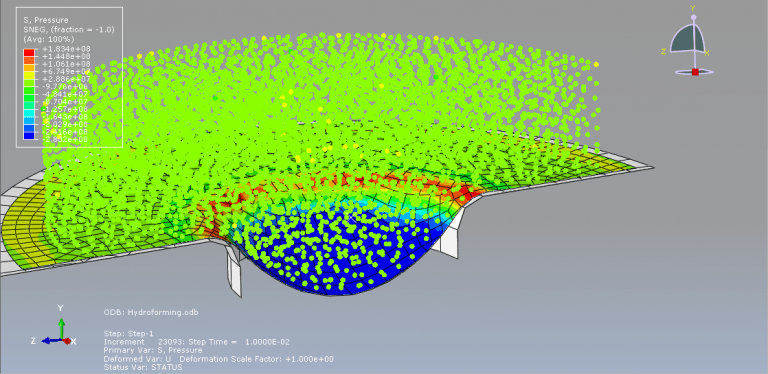


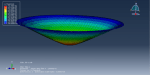
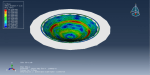
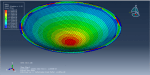
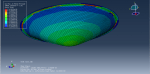







Victoria –
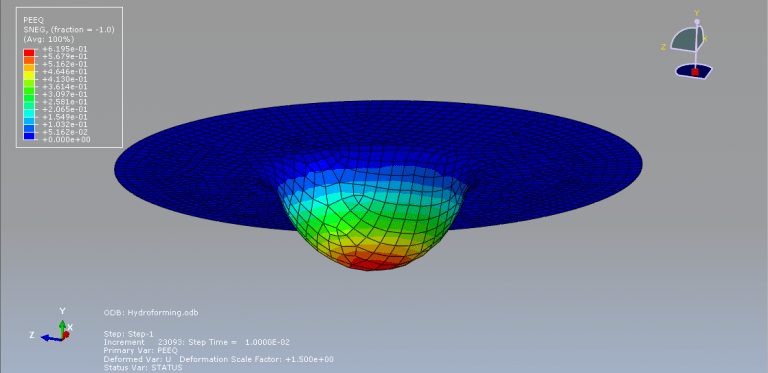
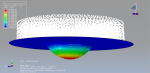
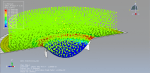
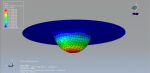
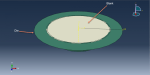
The purpose of my hydroforming simulation is to assess the possibility of material failure and to investigate the level of wrinkling. I would like to determine if this package is effective in addressing my needs?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Yes, it works for you dear Victoria