What is soil impact analysis?
Soil impact analysis is a branch of geotechnical engineering that focuses on studying the behavior and response of soil under impact loading conditions. It involves analyzing the effects of dynamic forces such as vibrations, blasts, or heavy machinery on the soil and the structures supported by it. The importance of soil impact analysis lies in its ability to assess the stability, deformation, and potential damage that may occur in soil and structures due to impact events.
Understanding soil behavior under impact loading is crucial for various industries, including construction, mining, earthquake engineering, and infrastructure development. By conducting soil impact analysis, engineers can evaluate the potential risks and design appropriate foundations, retaining walls, and protective measures to ensure the safety and longevity of structures. Soil impact analysis also helps in predicting the effects of dynamic loads on the soil structure, such as ground vibrations from heavy machinery or seismic events. This information aids in designing structures that can withstand such dynamic forces and minimizes the risk of structural failure or soil liquefaction. (soil impact Abaqus)
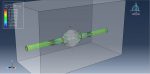
Workshop 1: Soil impact simulation to the metal plate using SPH method
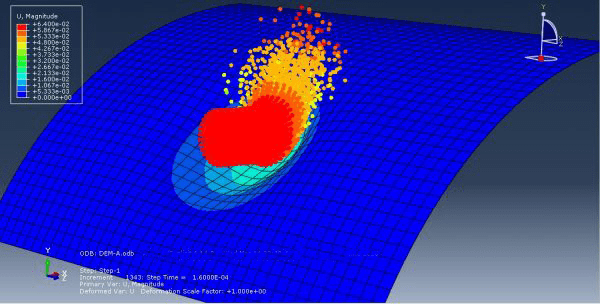
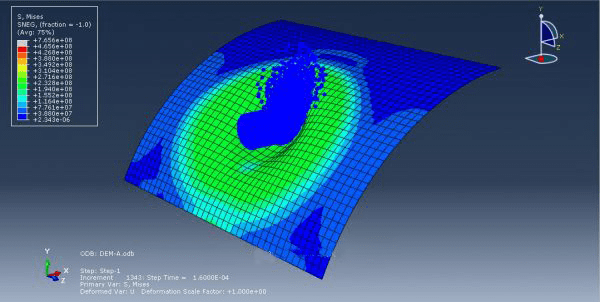
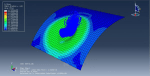
This tutorial demonstrates the simulation of soil impact on a metal plate in Abaqus, utilizing the Smooth Particle Hydrodynamic (SPH) method. The soil is represented as a three-dimensional component with elastic-plastic behavior, employing the Coulomb-Mohr plasticity model. To transform the continuum element into a particle element, the input file was modified using the edit input file capability. Through explicit dynamic analysis, the soil induces deformation in the plate, followed by the separation of soil particles from each other.
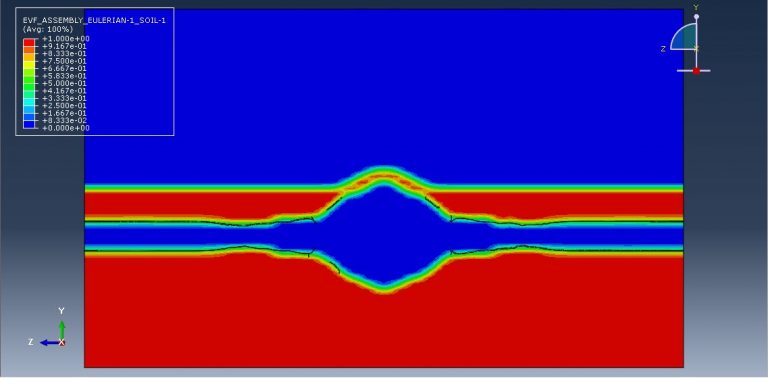
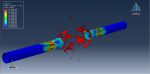
Workshop 2: Soil impact simulation using Eulerian approach
The main objective of this research was to develop and implement a methodology based on explicit nonlinear dynamic finite element analysis. The focus was to investigate the crashworthiness of small lightweight rigid objects impacting soft soil. The behavior of aircraft crashes is greatly influenced by the characteristics of the impact terrain, as different terrains elicit diverse structural responses. This workshop centers on the technique employed to characterize and validate a numerical model for soft soil as an impact terrain.
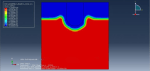
The selected technique primarily relied on a time-explicit Eulerian-based finite element analysis code. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach, penetrometer drop tests into soft soil were conducted using finite element analysis (FEA). The choice of the Eulerian-based approach over the commonly used Lagrangian-based approach was motivated by the need to mitigate numerical instabilities that often arise when analyzing crash scenarios involving large deformations. These instabilities can prematurely terminate analyses and compromise the accuracy of results.
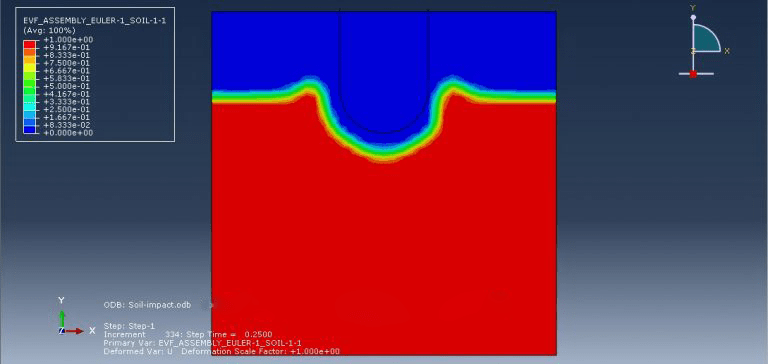
Explicit finite element codes have been widely utilized in nonlinear transient dynamic analyses. In this simulation, the projectile was represented as a rigid body, while the soil was modeled as an Eulerian component. As the analysis progressed, the projectile penetrated the soil, creating a hole in the process.
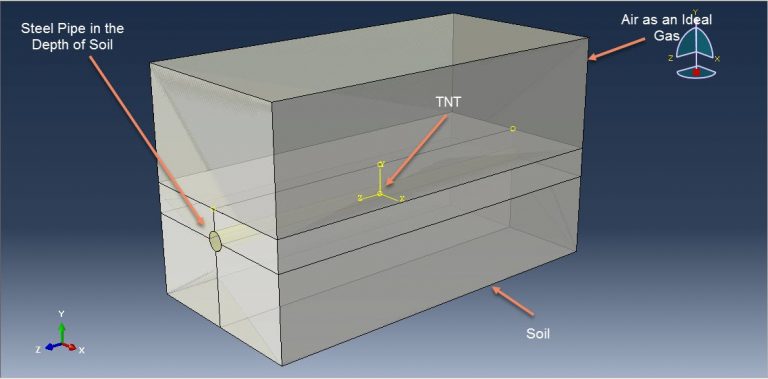
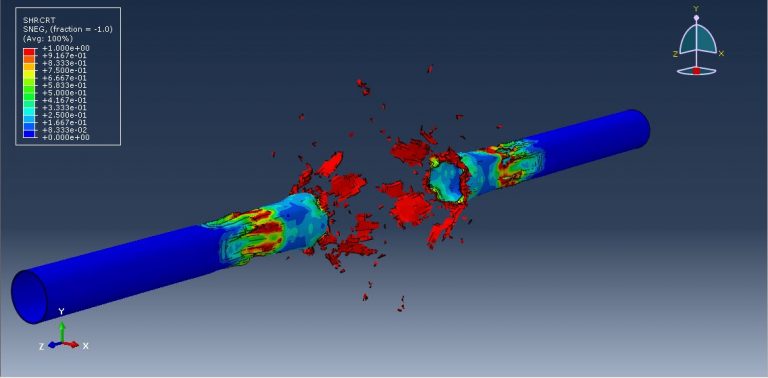
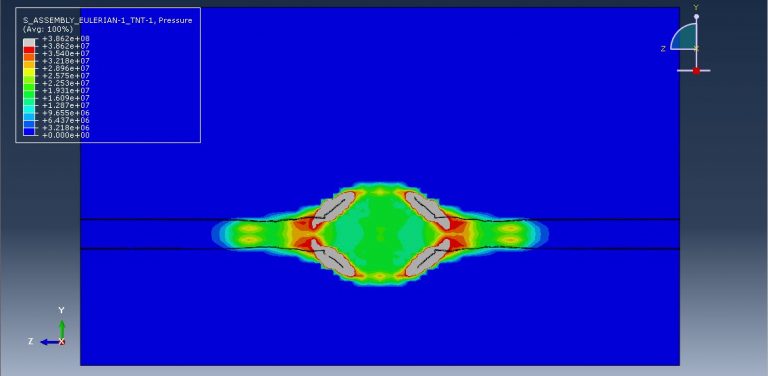
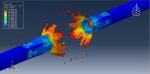
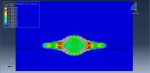
Workshop 3: CEL explosion simulation inside a steel pipe that is buried within the soil
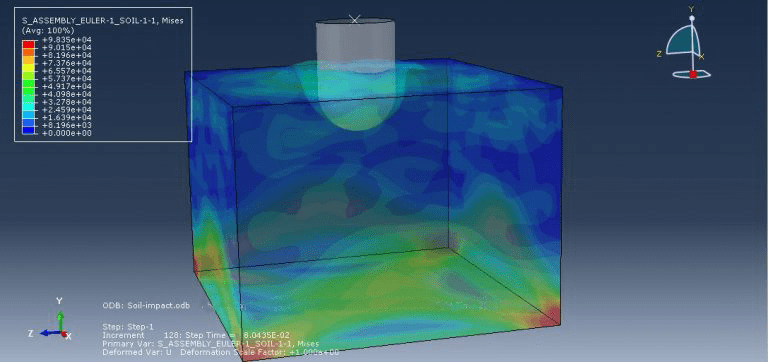
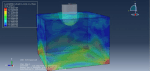
This tutorial focuses on examining the simulation of a CEL explosion within a steel pipe that is embedded in the soil using Abaqus. The steel pipe is represented as a three-dimensional shell component. The TNT, soil, and air are modeled as three-dimensional solid components. Additionally, the Eulerian part is modeled as a three-dimensional Eulerian component.
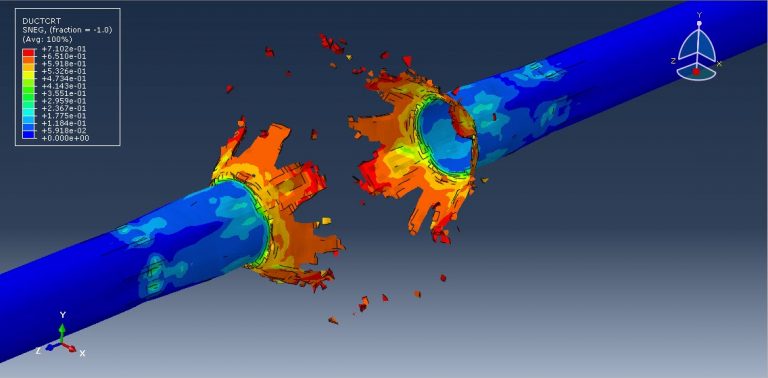
The pipe in this study is made of steel and is modeled as an elastic-plastic material. To predict the areas that may fail after the detonation, the steel material incorporates ductile and shear damage criteria. The behavior of TNT is represented by the JWL equation of state, which converts the chemical energy released during the explosion into mechanical pressure. The air is modeled as an ideal gas with viscosity, while the soil follows Mohr-Coulomb plasticity for its behavior.
For this analysis, the dynamic explicit step is deemed suitable. General contact interaction is employed with appropriate contact properties. The ends of the pipe are assigned fixed boundary conditions, and Eulerian boundaries are assigned to the Eulerian domain. The volume fraction method is utilized to calculate the volume of TNT, soil, and air. It is important to have a fine mesh to achieve accurate and reliable results.
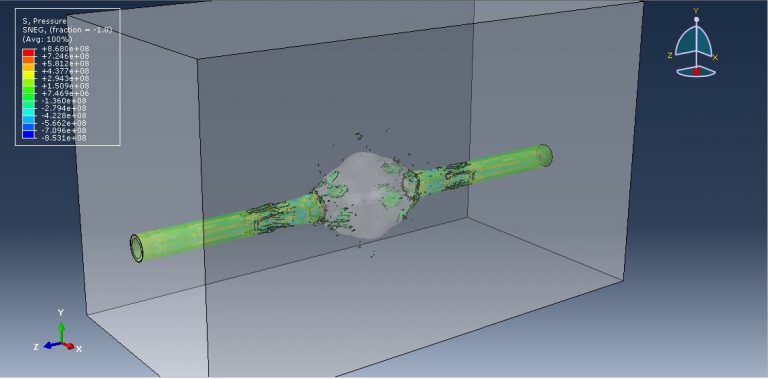
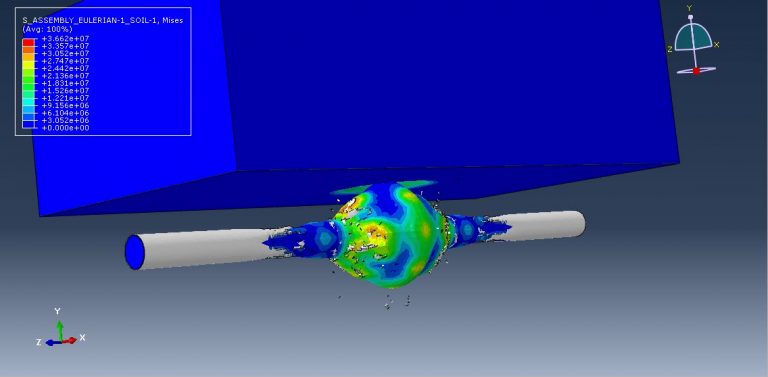
After the simulation, various results such as damage, stress, strain, and failure can be obtained. During the detonation, the TNT wave exerts immense pressure, leading to significant damage to the pipe. It penetrates through the pipe into the soil and air.
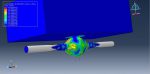
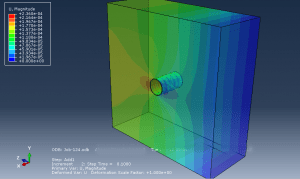
Workshop 4: Penetration of pile to the soil simulation in Abaqus
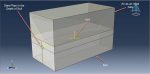
In this instructional guide, the simulation of soil penetration by CEL (Couple Eulerian Lagrangian) is demonstrated. The soil is represented as an Eulerian component with Coulomb-Mohr material characteristics, while the pile is modeled as a three-dimensional Lagrangian component with concrete material properties. The analysis employs an explicit procedure, divided into two steps. Initially, soil body force is applied in the first step, followed by the penetration of the pile into the soil in the second step.
It would be helpful to see Abaqus Documentation to understand how it would be hard to start an Abaqus simulation without any Abaqus tutorial.
















Eun-ji –
Is this training package for Abaqus structured in a systematic manner, covering from basic to advanced concepts? Does it utilize practical approaches and real-world examples to enable me to translate the concepts into practical and understandable applications?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Yes. You can find practical example for soil impact simulation. You learn what you need. However, if you are eager to learn more information for soil simulation, i recommend this package”https://caeassistant.com/product/abaqus-soil-modeling-full-tutorial/”
1143309284 –
I want to get a VUSDFLD subroutine based on CEL method to realize the calculation of excess pore water pressure from stress and strain, and then the excess pore water pressure may affect the soil property parameters (such as density, Young modulus, et al.). Does this training package include relevant content? Thank you!