Introduction
Fatigue in composites describes the deterioration of a material due to repeated loading or stress cycles over time. When exposed to cyclic loads, small cracks or microscopic damage can develop within the composite, which may expand and eventually result in failure after a specific number of cycles. This factor is crucial when designing and analyzing composite structures, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering, where materials face constant stress.
Considering the significance of this topic, we employed Abaqus in this package to simulate composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D domains. Due to the limitations of Abaqus’s built-in material library for this issue, we leveraged the UMAT subroutine. However, a key question arises: what is the importance of fatigue analysis in composites, and what risks might occur if it is not carried out properly? To answer this, we first examine some of the consequences of the fatigue phenomenon.
Consequences of Fatigue Phenomenon and its Importance
The importance of fatigue in composites can be explored from different perspectives, with the most critical issues discussed here.
- Safety and Durability: Fatigue failure is often gradual and may not be detectable until the material fails catastrophically. Understanding fatigue helps predict the lifespan of composite structures, which is crucial for safety and long-term durability.
- Design Optimization: In engineering, it’s essential to design composites that can withstand cyclic loads. By understanding fatigue behavior, designers can optimize the material choice, ply stacking, and overall structure to ensure longevity under operating conditions.
- Cost Efficiency: Predicting fatigue allows for better material usage. Instead of over-engineering a structure to ensure it lasts beyond its expected lifespan, manufacturers can use more efficient designs that consider the expected fatigue life, potentially lowering costs.
- Performance in Real-world Applications: Many composite materials are used in environments where cyclic loading is common. For example, airplane wings, car chassis, wind turbine blades, and bridges experience repeated loading. Accurate fatigue modeling is essential to ensure that these structures perform reliably throughout their service life.
- Fatigue Testing and Prediction: Understanding fatigue also helps in creating accurate life-prediction models for composites, which involve testing under controlled conditions (e.g., using S-N curves or strain-life models) to predict when a composite will fail.
What is Covered in this Package
In this package, we provide a comprehensive discussion on the phenomenon of fatigue and its importance in analysis. Additionally, we used the UMAT code to analyze composite fatigue in the 2D domain with Abaqus. The package includes detailed tutorials on modeling and how to write the subroutine code for this topic. Furthermore, we extended the modeling to the 3D domain and have included the corresponding 3D UMAT code, which is based on the 2D version, for your use.
What is Fatigue Life
Fatigue life refers to the number of loading cycles (stress) a material can endure before experiencing any form of failure. The fatigue life of composites can be determined using approaches based on strain, stress, or energy. As science and industry continue to advance, there is an increasing demand for the development of materials that offer enhanced benefits. Composite materials have become a viable alternative to traditional materials due to their superior efficiency and economic advantages. Consequently, it is crucial to develop these materials by understanding their production methods, studying their properties, and accurately calculating their fatigue life. Follow this guide to explore the capabilities and features of Composite Fatigue in Abaqus.
Abaqus Simulation
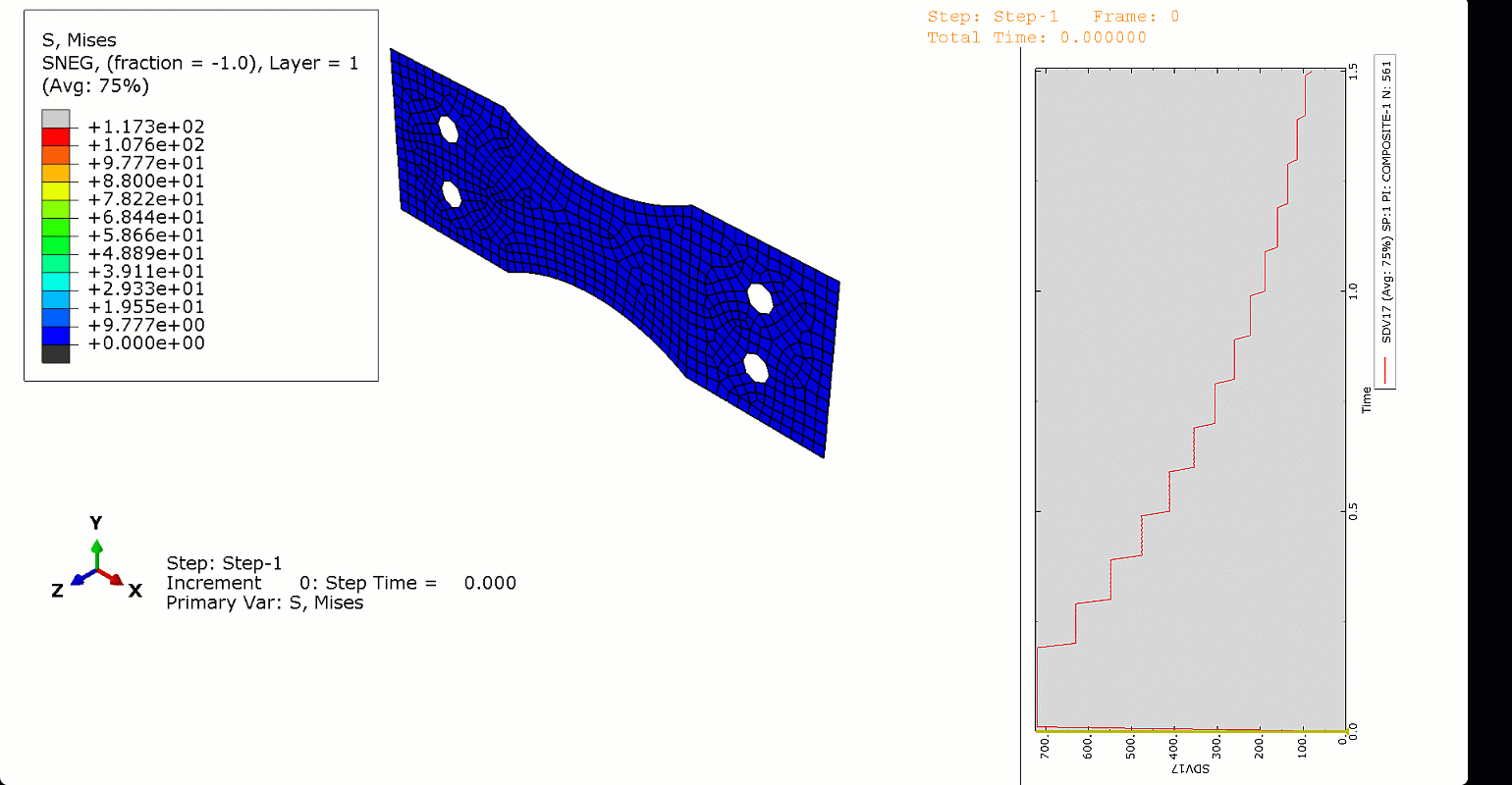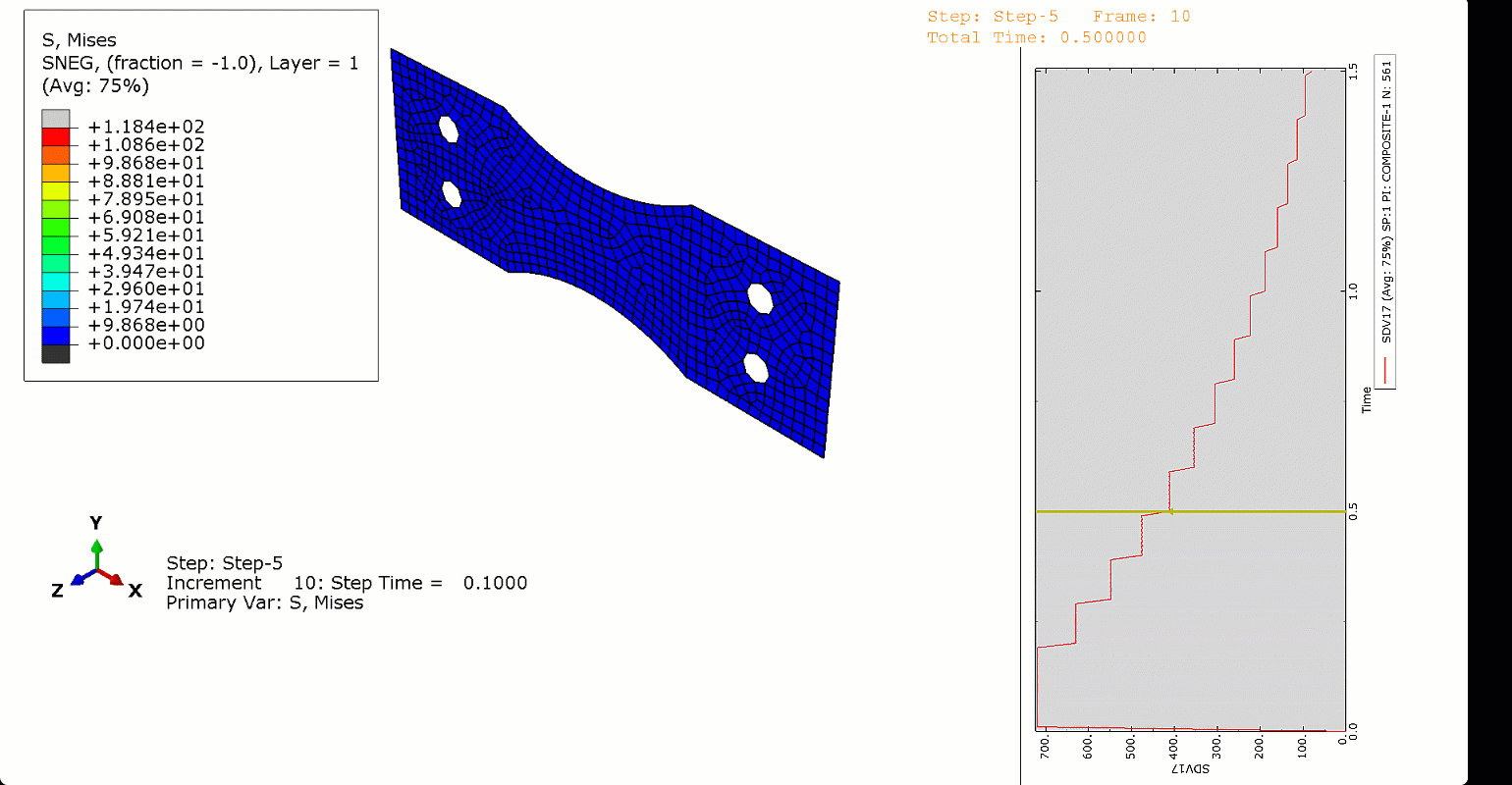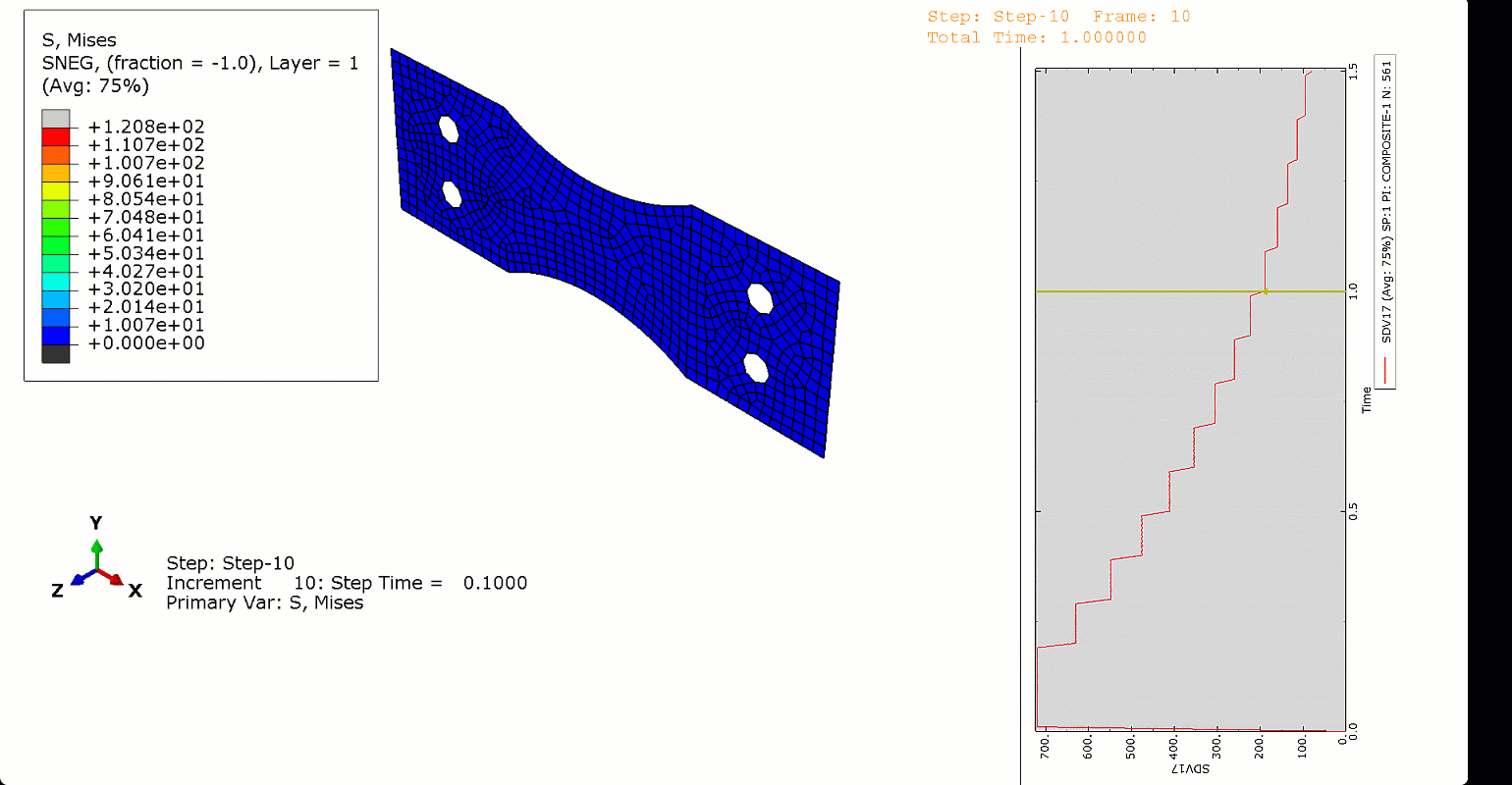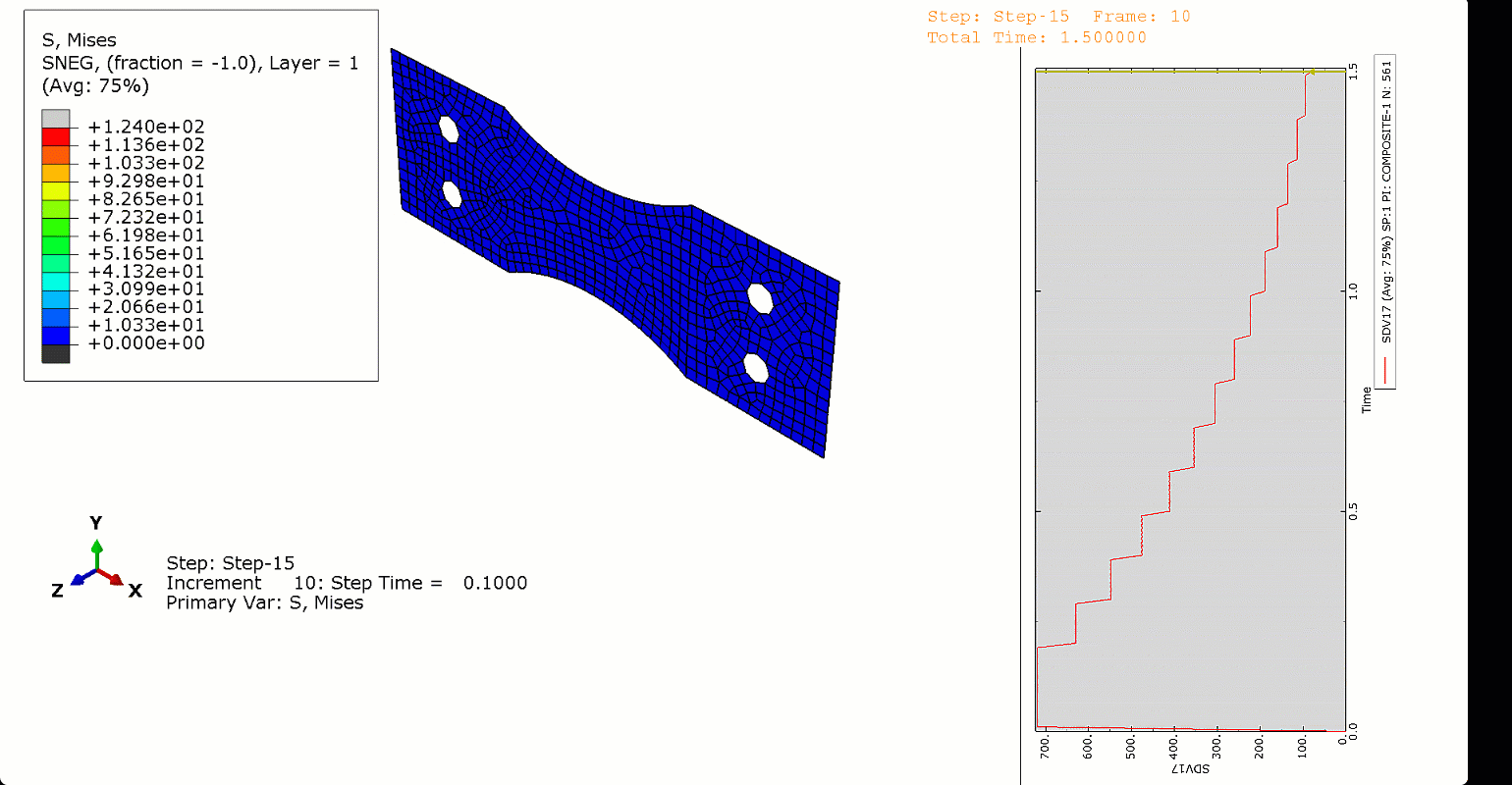
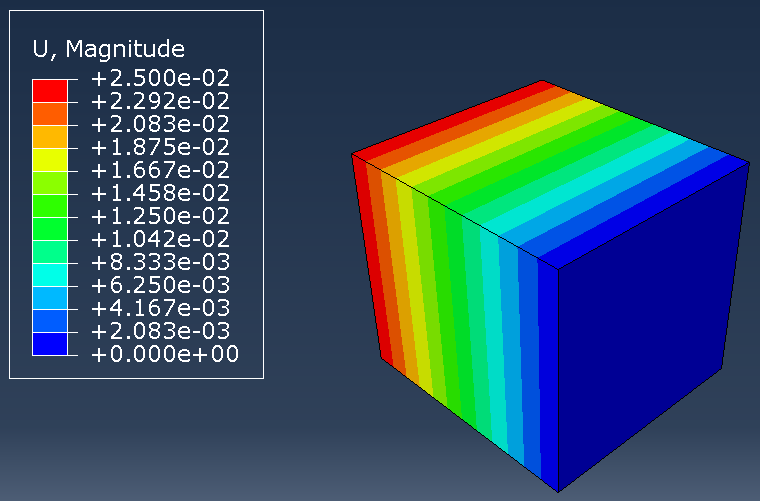
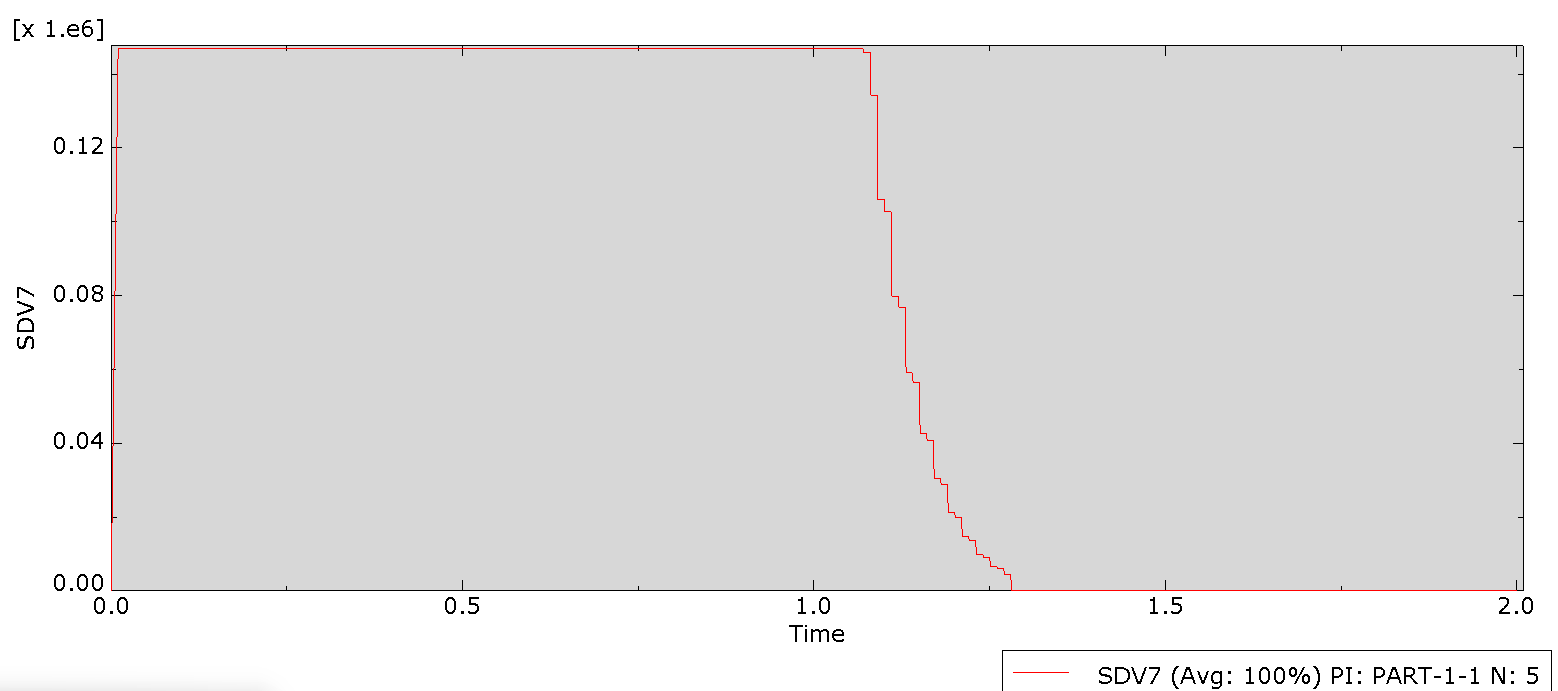
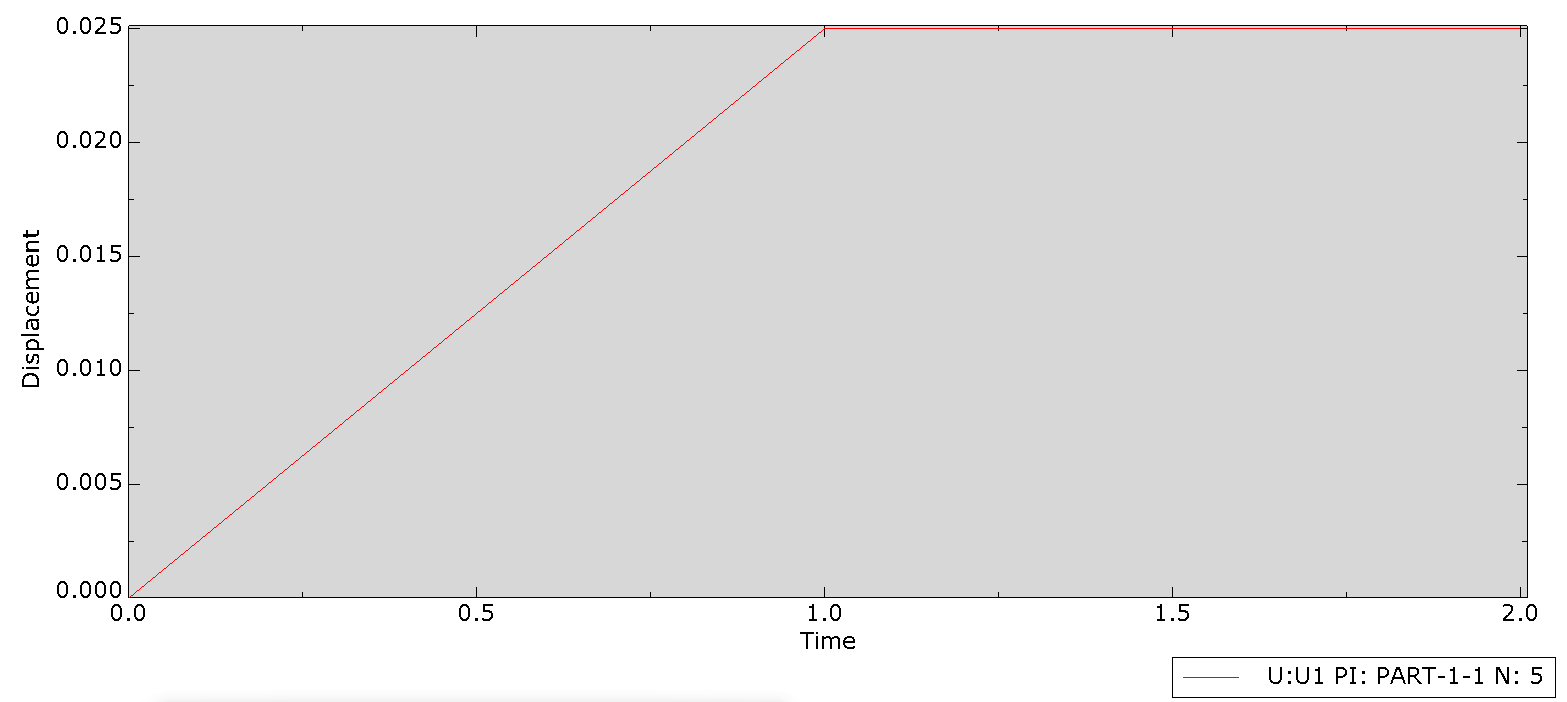
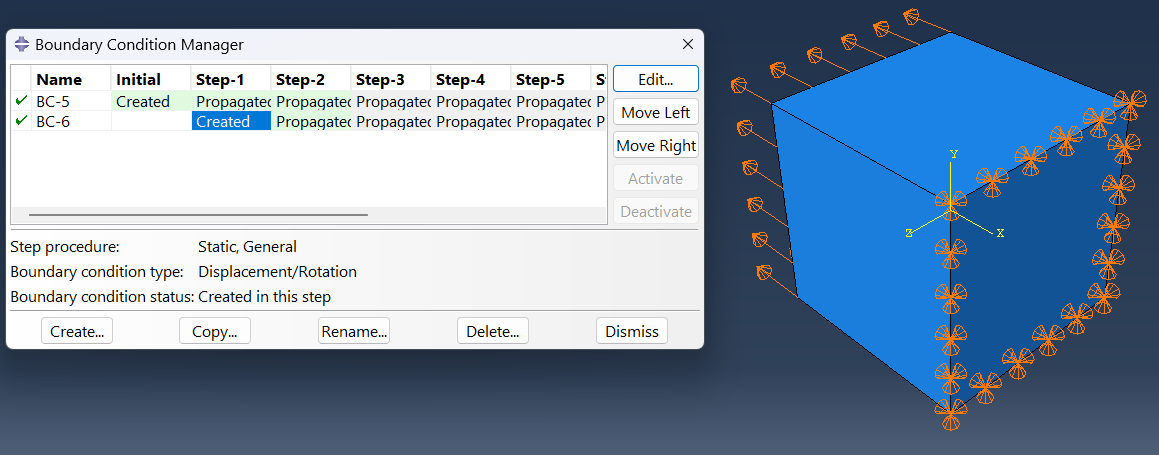
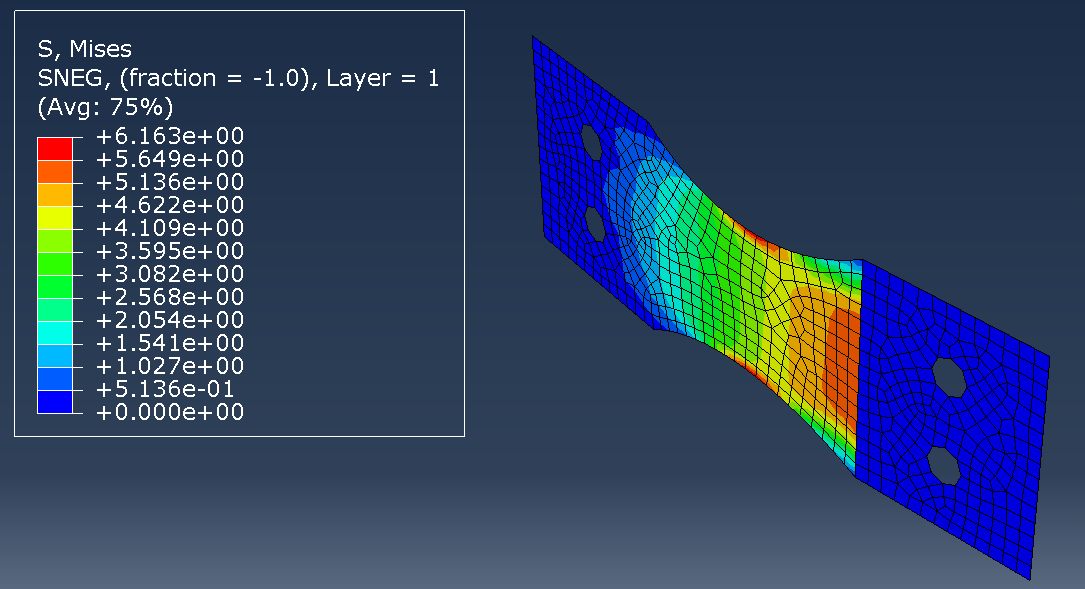
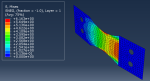
In this project, we used Abaqus’ General Static solver to analyze the fatigue behavior in composites, considering both 2D and 3D domains. By doing so, you will learn how to apply both cyclic and ramped-constant loading histories to the specimens to monitor and capture fatigue in composites. Note that degradation due to fatigue is considered in the model. So, when failure occurs, stiffness and strength reductions will be captured. This project will teach you how to implement 2D and 3D composite fatigue analysis in Abaqus using the UMAT subroutine, enabling you to analyze problems in this area.
















Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.