Abaqus shaft slip ring simulation | Using Python scripts for parametric analysis
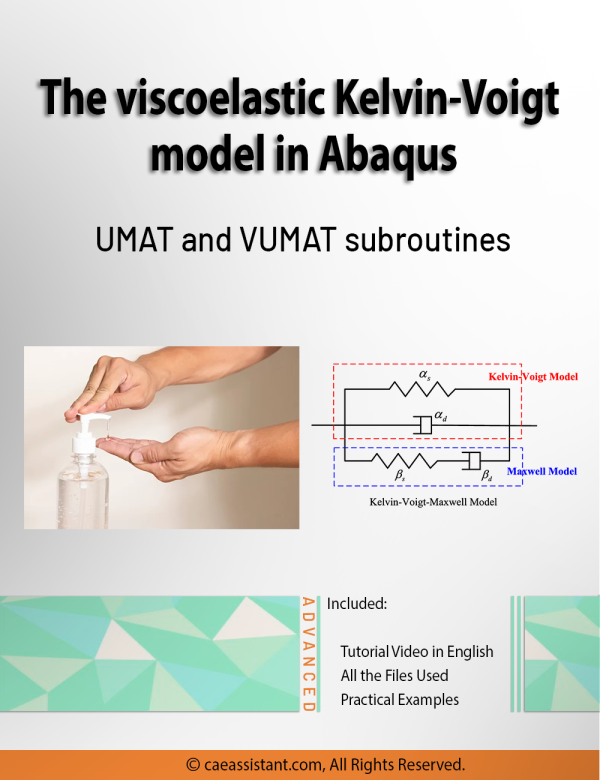
Abaqus Kelvin Voigt Viscoelastic Simulation Using UMAT and VUMAT Subroutines
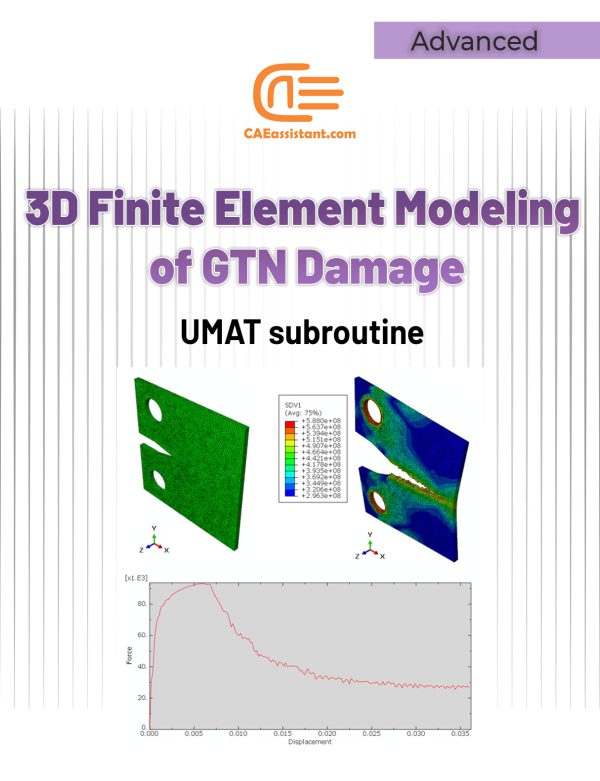
3D Simulation of Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) Damage Model
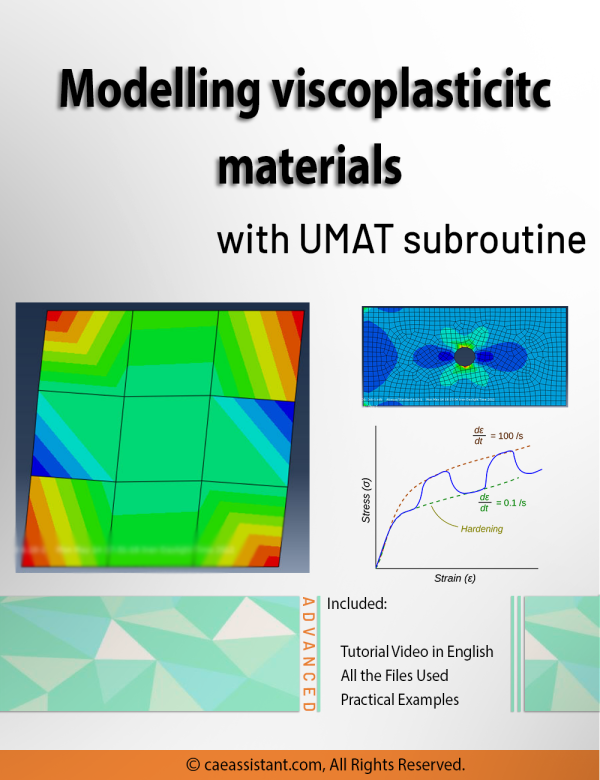
Viscoplasticity Abaqus Simulation Using UMAT Subroutine | Perzyna Viscoplastic Model
Viscoplasticity describes the rate-dependent inelastic behavior of materials, where deformation depends on both stress magnitude and application speed. This concept is crucial in many engineering applications, such as designing structures under dynamic loads, modeling soil behavior during earthquakes, and developing materials with specific mechanical properties. Viscoplasticity Abaqus simulation, especially using Abaqus with UMAT subroutines, are vital for understanding, predicting, and optimizing the behavior of viscoplastic materials. This tutorial focuses on implementing the Perzyna viscoplasticity model in Abaqus. The Perzyna viscoplastic model, a strain rate-dependent viscoplasticity model, relates stress to strain through specific constitutive relations. This involves defining plastic strain rate based on stress state, internal variables, and relaxation time. The tutorial provides general UMAT codes for viscoplastic analysis, yielding results like stress fields essential for various engineering applications. These simulations help in predicting permanent deformations, assessing structural failure points, and analyzing stability under different loads, benefiting fields such as aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and energy.
Abaqus User element tutorial | UEL advanced level
Pultrusion Crack Simulation in Large-Size Profiles | Pultrusion Abaqus
Pultrusion is a crucial task for producing constant-profile composites by pulling fibers through a resin bath and heated die. Simulations play a vital role in optimizing parameters like pulling speed and die temperature to enhance product quality and efficiency. They predict material property changes and aid in process control, reducing reliance on extensive experimental trials. However, simulations face challenges such as accurately modeling complex material behaviors and requiring significant computational resources. These challenges underscore the need for precise simulation methods to improve Pultrusion processes. This study employs ABAQUS with user subroutines for detailed mechanical behavior simulations, including curing kinetics and resin properties. Key findings include insights into crack formation (pultrusion crack simulation), material property changes, and optimization strategies for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This research (pultrusion Abaqus) provides practical knowledge for implementing findings in real-world applications, advancing composite material production.
Elastomeric Foam Simulation Using Abaqus Subroutines
Creep is one of the most significant failure modes in many components where the working temperature and stresses are high for a prolonged period of time. Existing creep models in commercial analysis software like Abaqus are not adequate to model all stages of creep namely – primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. Theta projection method is a convenient method proven to predict all stages of creep, especially the tertiary stage where strain rates are high leading to internal damage and fracture. The aim of the project is to develop a user subroutine for Abaqus to model creep in components using the Theta projection method. The constitutive model for the Theta projection method based on the accumulation of internal state variables such as hardening, recovery, and damage developed by (R.W.Evans, 1984) is adopted to compile a Fortran code for the user subroutine. The user subroutine is validated through test cases and comparing the results with experimental creep data. Creep analysis of a sample gas turbine blade (Turbine Blade Creep) is then performed in Abaqus through the user subroutine and the results are interpreted.
Results of test cases validate the accuracy of the Theta Projection Method in predicting all primary, secondary, and tertiary stages of creep than existing creep models in Abaqus (Creep Failure in Turbine Blades). Results at interpolated & extrapolated stress & temperature conditions with robust weighted least square regression material constants show the convenience in creep modeling with less input data than existing models. The results of creep analysis not only predicted the creep life but also indicated the internal damage accumulation. Thus, creep modeling of components through the user subroutine at different load conditions could lead us to more reliable creep life predictions and also indicate the regions of high creep strain for improvements in the early stages of design.
Simulation of an Ultrasonic Transducer (3D Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Turning Tool)
Since the invention of ultrasonic vibration assisted turning, this process has been widely considered and investigated. The reason for this consideration is the unique features of this process which include reducing machining forces, reducing wear and friction, increasing the tool life, creating periodic cutting conditions, increasing the machinability of difficult-to-cut material, increasing the surface quality, creating a hierarchical structure (micro-nano textures) on the surface and so on. Different methods have hitherto been used to apply ultrasonic vibration to the tip of the tool during the turning process. In this research, a unique horn has been designed and constructed to convert linear vibrations of piezoelectrics to three-dimensional vibrations (longitudinal vibrations along the z-axis, bending vibrations around the x-axis, and bending vibrations around the y-axis). The advantage of this ultrasonic machining tool compared with other similar tools is that in most other tools it is only possible to apply one-dimensional (linear) and two-dimensional (elliptical) vibrations, while this tool can create three-dimensional vibrations. Additionally, since the nature of the designed horn can lead to the creation of three-dimensional vibrations, there is no need for piezoelectric half-rings (which are stimulated by a 180-phase difference) to create bending vibrations around the x and y axes. Reduction of costs as well as the simplicity of applying three-dimensional vibrations in this new method can play an important role in industrializing the process of three-dimensional ultrasonic vibration assisted turning.
In this example, how to model all the components of an ultrasonic transducer and its modal and harmonic analysis are taught in full detail.
Simulation of pitting corrosion with scripting in Abaqus
Dynamic Response of Ballasted Rail Track Under a Moving Load
Railway tracks are subjected to moving loads of trains and this causes vibration and degradation of the track. The judgment of these vibrations is important to design the railway tracks. The design involves the permissible speed of trains and the maximum axle load of the train. The model given here creates a 3D geometry of a railway track and applies a moving load in the form of a wheel. A user can change the speeds and the properties of the material including geometry as per their needs.
Continuously Reinforced Concrete Pavement (CRCP) Cracking Analysis
|
The increasing adoption of continuously reinforced concrete pavement (CRCP) in highway pavement design is driven by its demonstrated superior performance. Critical to evaluating the long-term effectiveness of CRCP is the understanding of early-age cracks (CRCP crack analysis), which has garnered significant interest from highway departments. This Abaqus Continuously reinforced concrete pavement modeling project aims to establish precise design parameters for CRCP and analyze the formation of crack patterns. By accounting for stress factors such as environmental conditions and CRCP shrinkage modeling, the project offers valuable insights into predicting the likelihood of crack initiation and propagation within the concrete slab. These insights are instrumental in enhancing the durability and performance of CRCP structures, thus advancing the efficiency and effectiveness of highway infrastructure. |
Laser forming simulation tutorial in Abaqus
Friction Stir Welding simulation Tutorial | FSW Advanced level
Airfoil simulation with different angles of Attack | Ansys fluent
Short fiber composite damage (Mean Field Homogenization Model)
Tread wear simulation in Abaqus
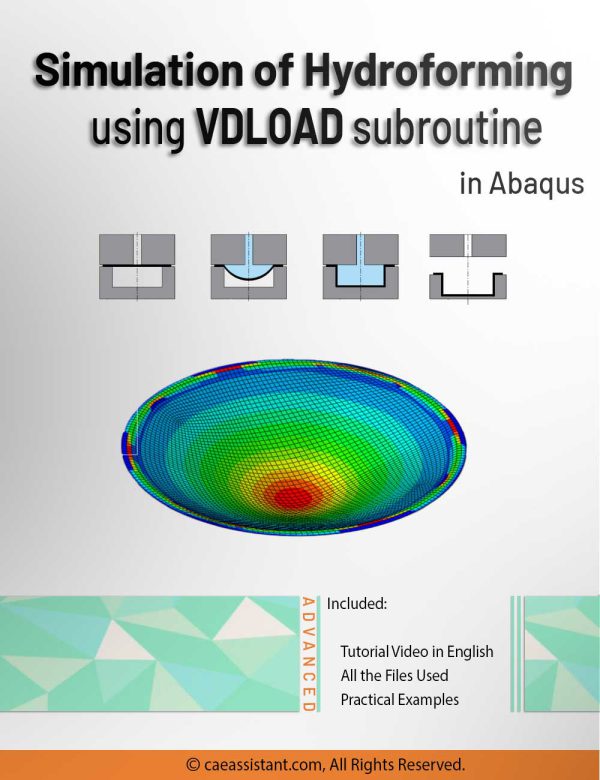
Hydroforming process simulation using VDLOAD subroutine in Abaqus
Topology Optimization in Abaqus
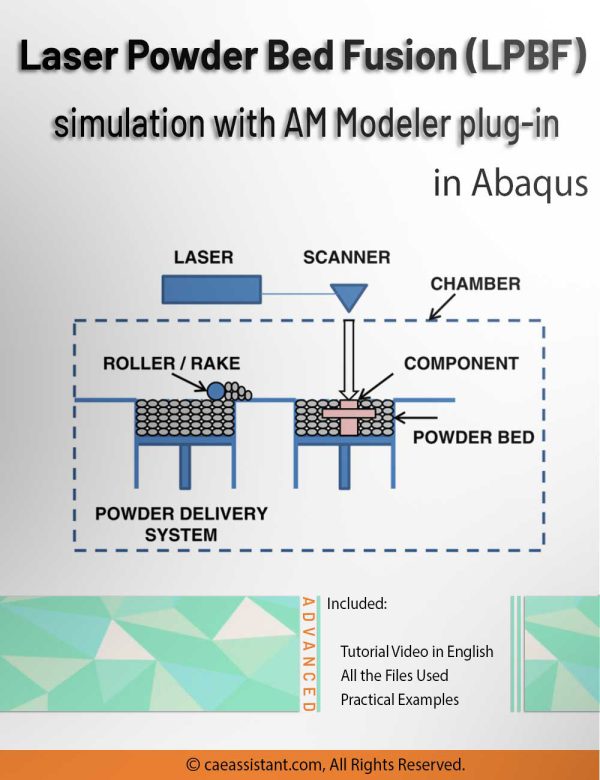
3D printing simulation with Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) method in Abaqus
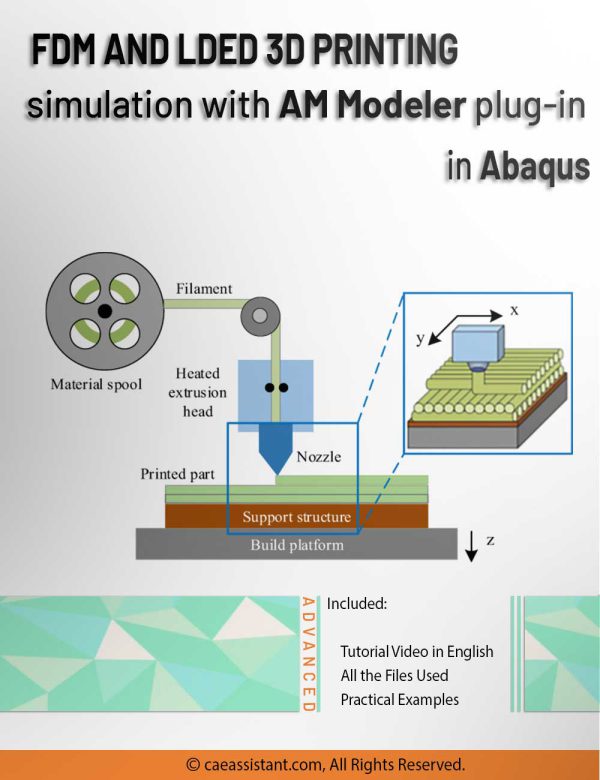
3D printing simulation with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) in Abaqus
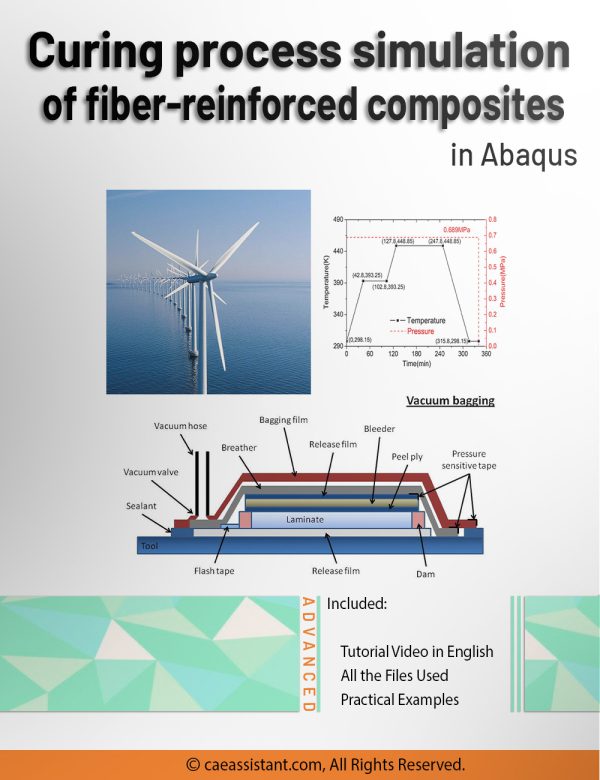
Curing process simulation in Abaqus
Different Techniques for Meshing in Abaqus