1. Introduction| Abaqus Thermal Expansion Behavior Simulation
In this tutorial, the user subroutines UEXPAN and VUEXPAN are used to simulate the thermal expansion behavior of a linear elastic material. The geometric model used in this study is a two-dimensional square specimen under temperature loading.
This subroutines are used when the material’s thermal expansion behavior is too complex to model with the “EXPANSION” option in the Abaqus software environment. For example, the subroutines are used in problems where the thermal strains are complexly dependent on temperature, predefined field variables, and state variables, and there is a need to update these variables.
This project is designed to enhance participants’ understanding how to accurately simulate the complicated thermal expansion models of the materials using UEXPAN and VUEXPAN subroutines.
2. Simulation of the Thermal Expansion Behavior of a Linear Elastic Material using UEXPAN and VUEXPAN Subroutine (PDF File)
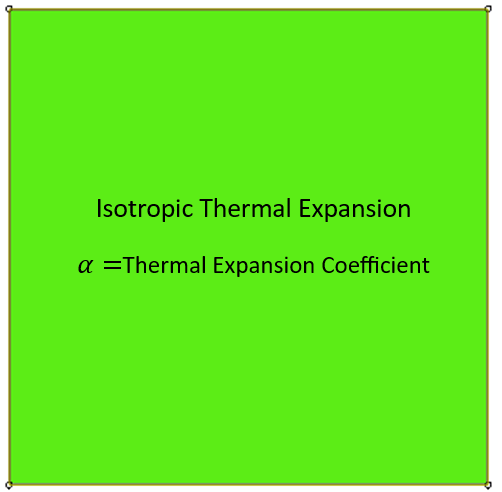
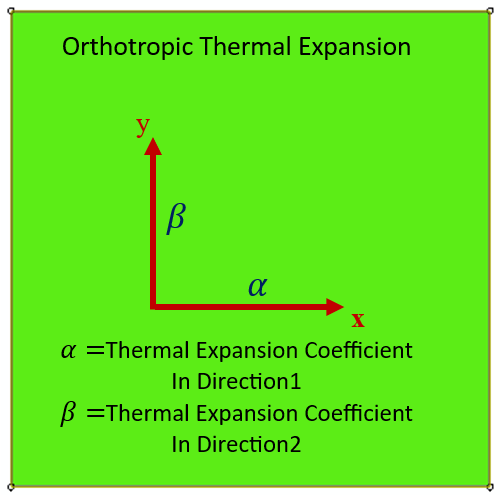
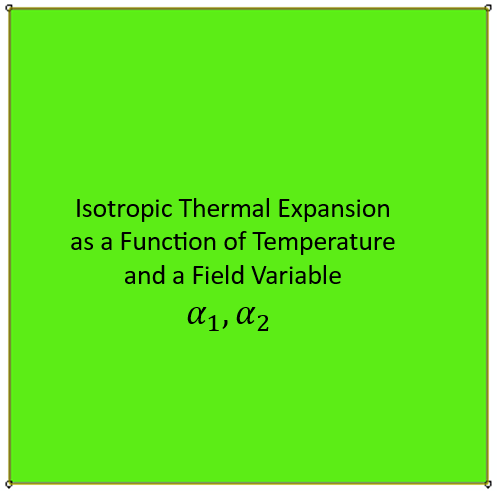
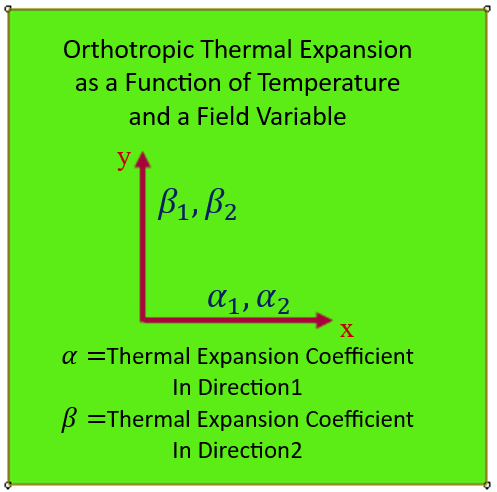
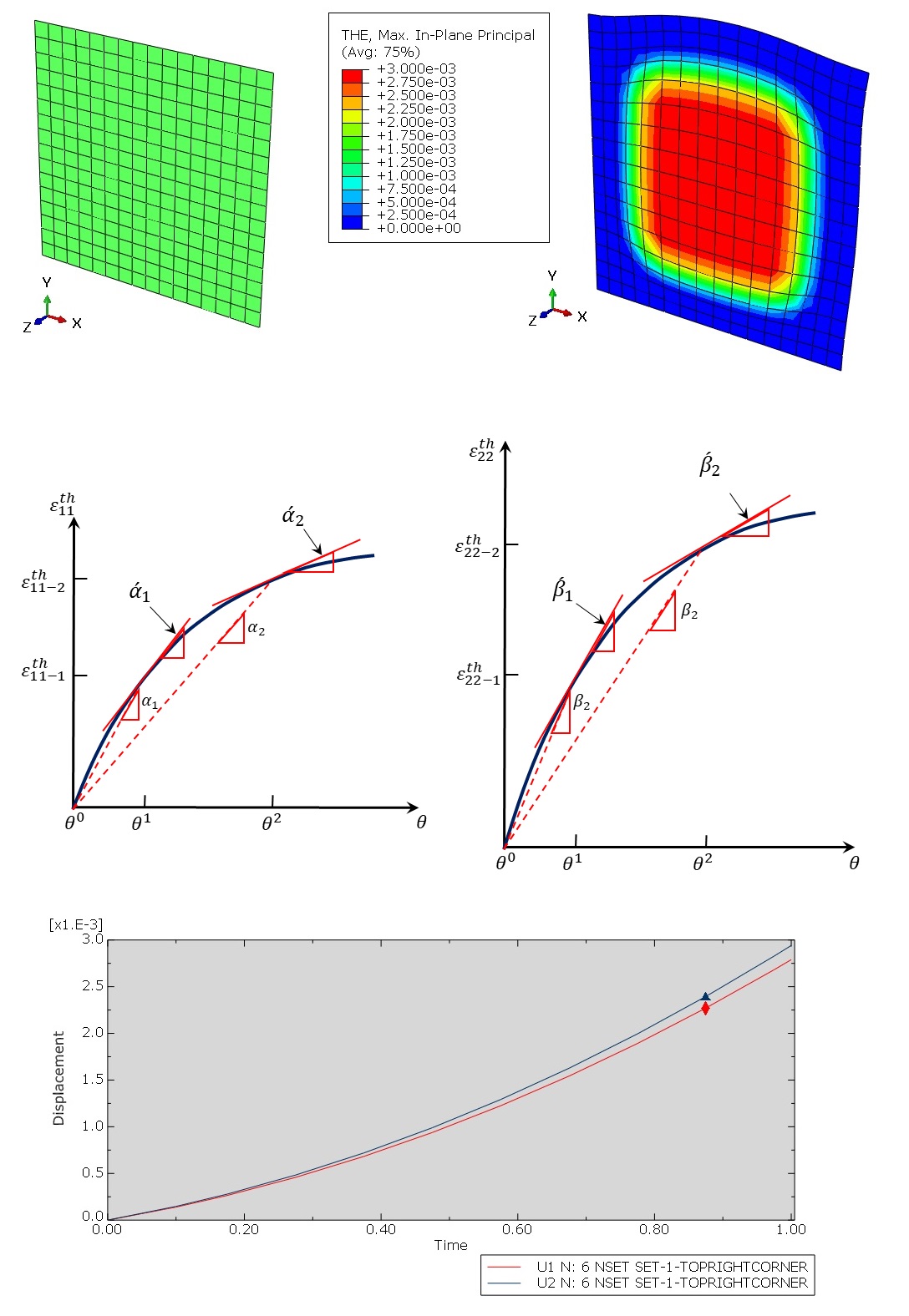
This project, after teaching the basic fundamentals of thermal expansion, presents seven examples of isotropic and orthotropic thermal expansion behaviors to teach the UEXPAN or VUEXPAN subroutine. The implementation of thermal expansion in these examples are done with UEXPAN subroutine for Abaqus/Standard solver (implicit method) and VUEXPAN for Abaqus/Explicit solver.
2.1. Problem Description
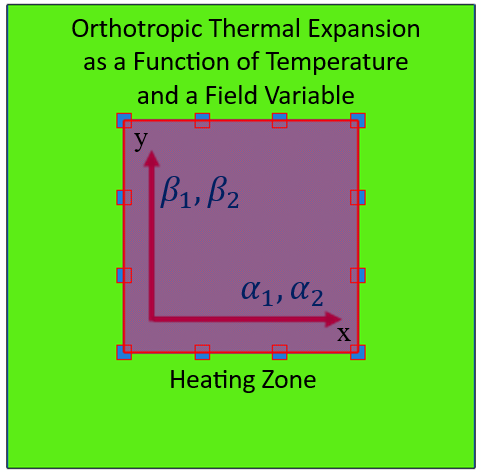
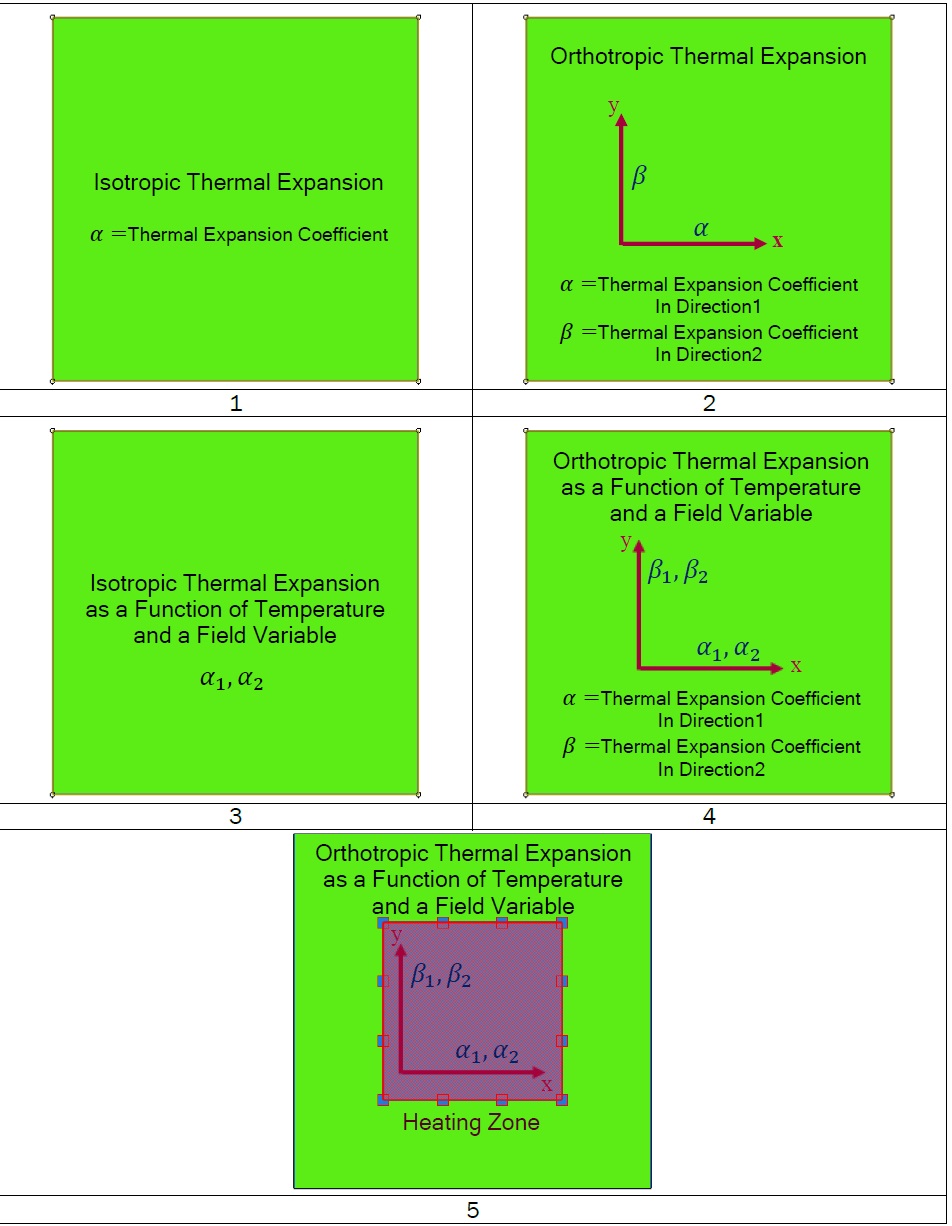
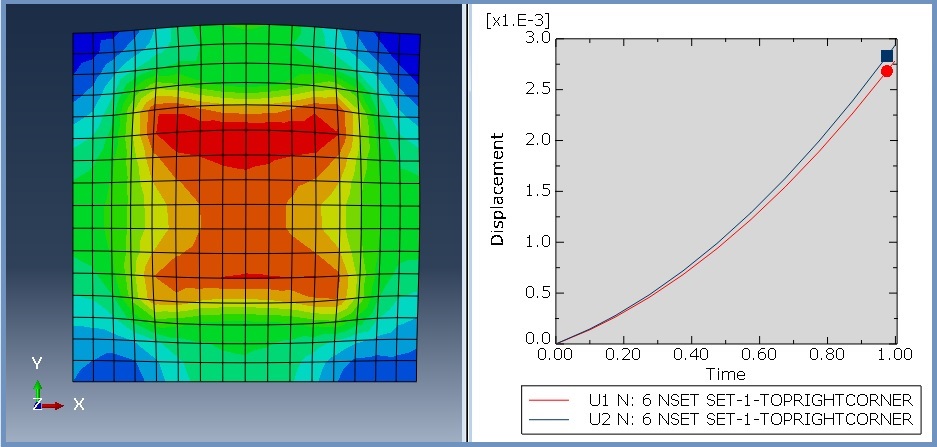
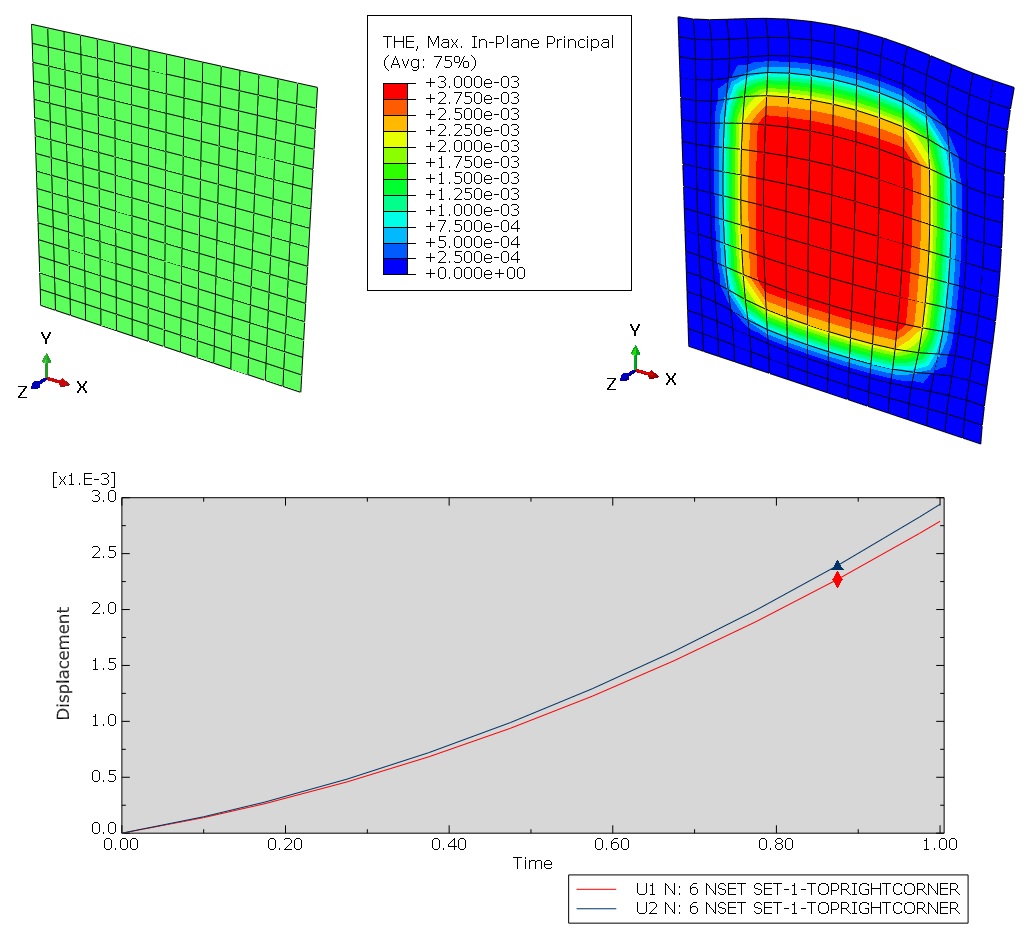
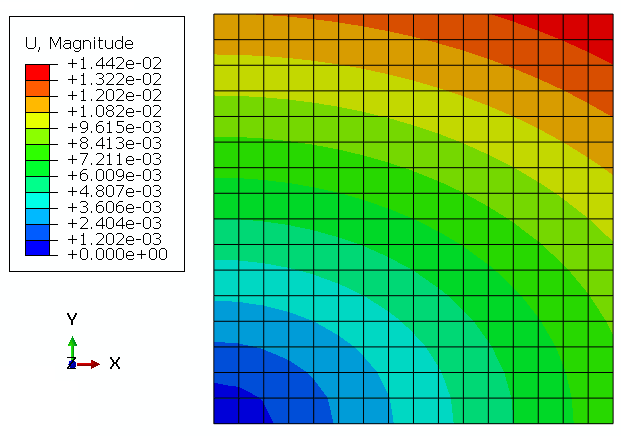
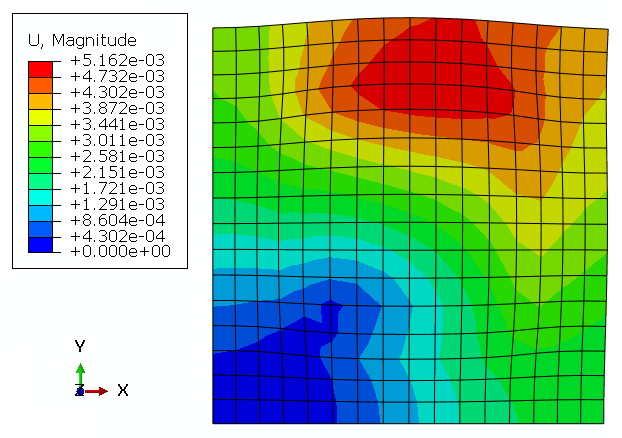
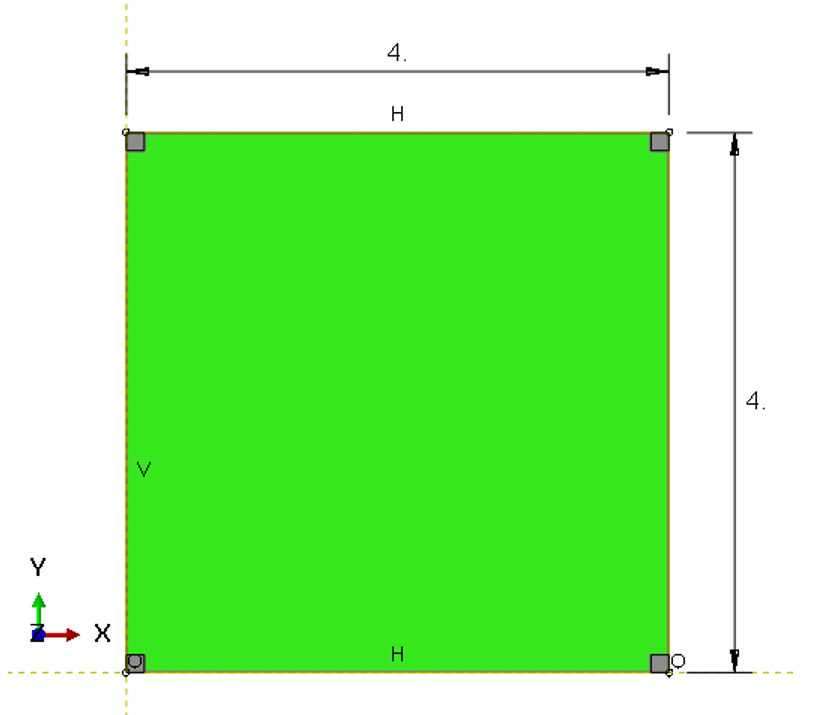
Geometry: The geometric model used in this study is a two-dimensional square specimen under temperature loading. The schematic design of the part is shown in Figure 1. This tutorial contains six examples to teach the UEXPAN subroutine, and one example for VUEXPAN subroutine. These examples are shown in Figure 2.
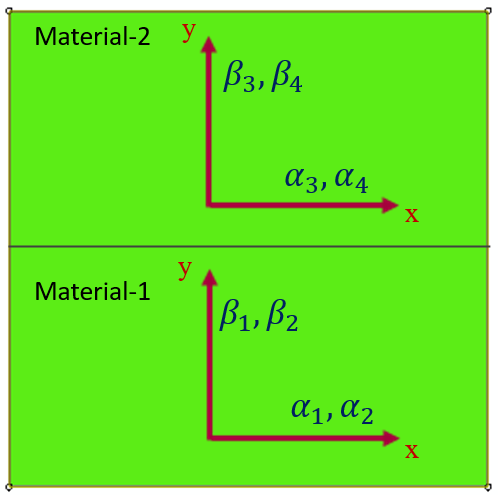
The material properties used in these examples are young’s modulus (E=1e6 Pa) and Poisson’s ratio (ϑ=0.3) for material-1, and young’s modulus (E=0.6e6 Pa) and Poisson’s ratio (ϑ=0.27) for material-2.
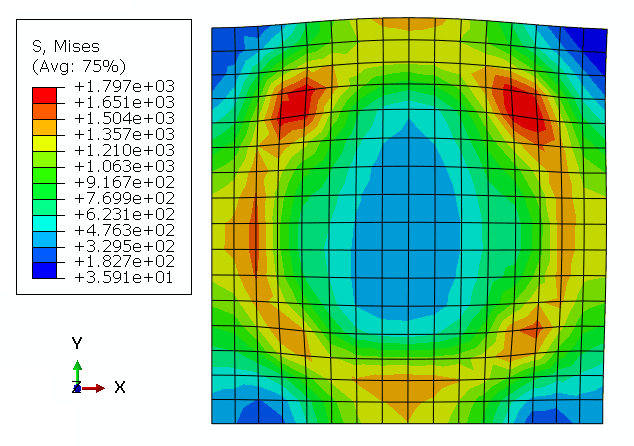
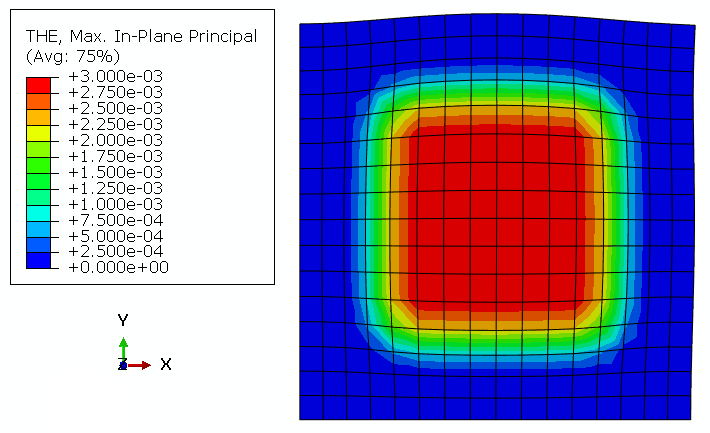
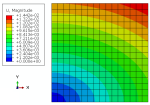
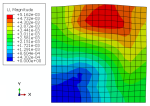
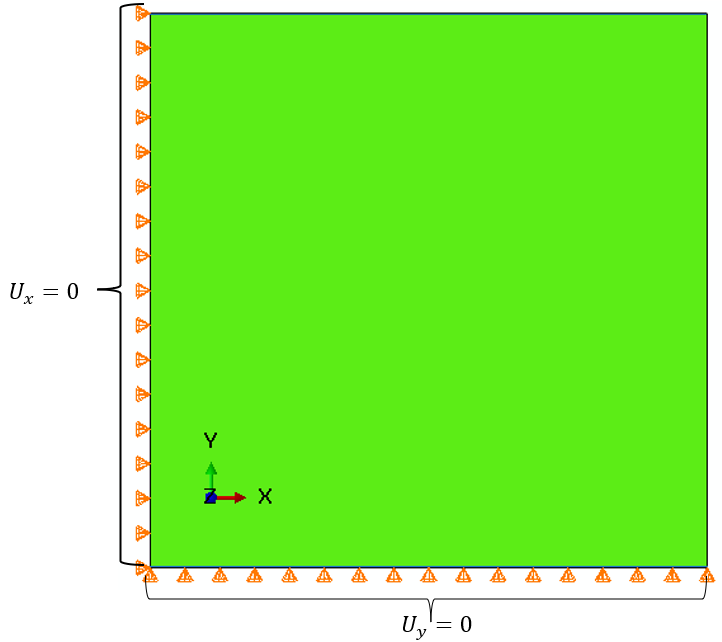
The temperature of the specimen is set to 100 degrees Celsius. The boundary conditions of model are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 1: The schematic design of the two-dimensional square specimen
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
Figure 2: The six examples of the tutorial
Figure 3: The displacement boundary conditions
2.2. Project Procedures
- Setting up the software environment and choosing Abaqus units;
- Creating the two-dimensional square specimen;
- Defining the material properties and creating its relevant section;
- Making an independent instance of the model in the “Assembly” module;
- Creating a “Static, Linear perturbation” step and a “Static, General” step for doing analysis by calling the UEXPAN subroutine or “Explicit” step for VUEXPAN;
- Determining the initial and boundary conditions, etc.;
- Generating elements and assigning element types;
- Preparing the UEXPAN or VUEXPAN subroutines for all the examples of the tutorial;
- Creating seven jobs and calling the relevant UEXPAN or VUEXPAN subroutines;
- Submitting the jobs;
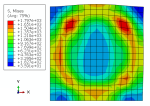
- Viewing the results.





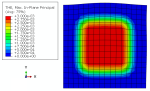
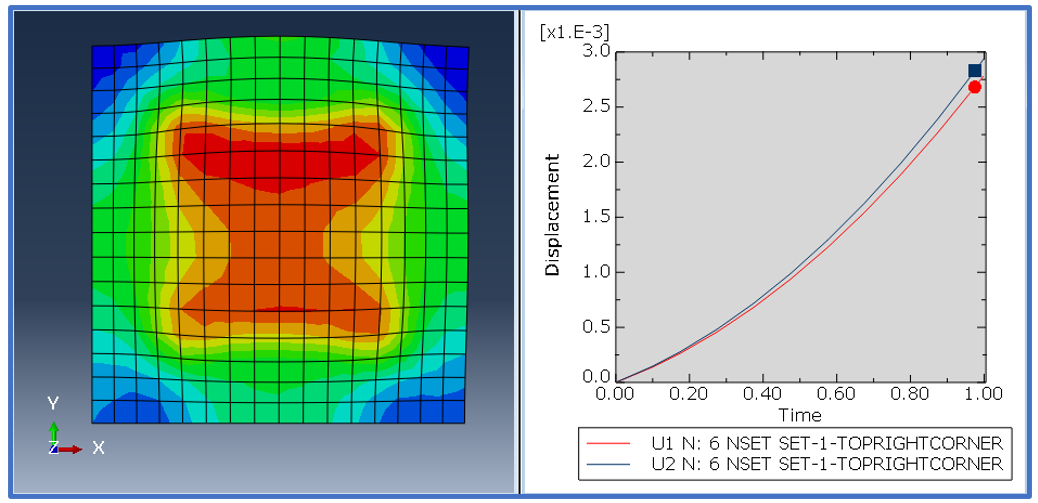
Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.