3D printing simulation using the Abaqus AM Modeler plugin
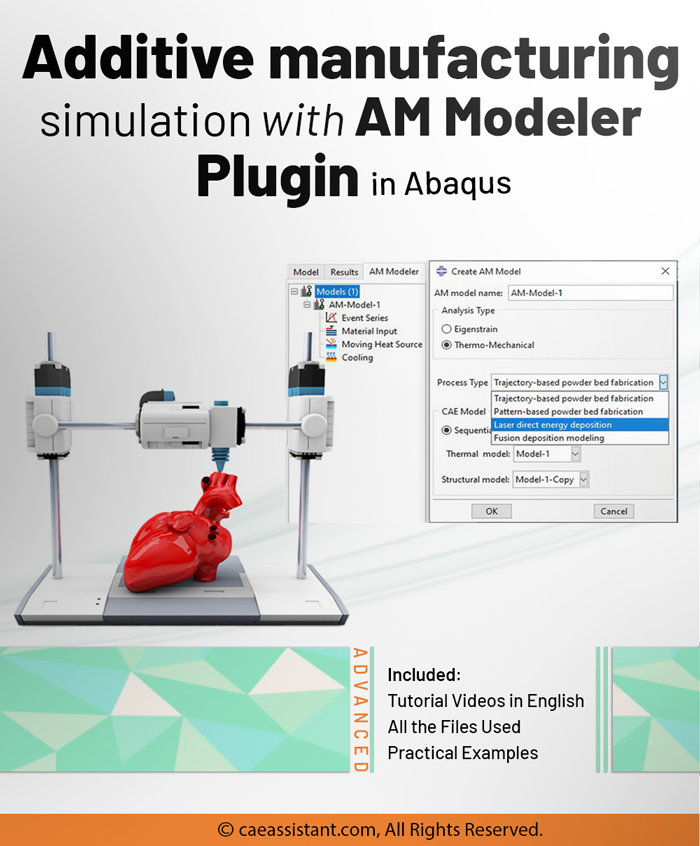
The Abaqus AM Modeler plug-in offers a streamlined, user-friendly approach for simulating additive manufacturing processes, minimizing errors and complexities. Unlike the challenges of coding or Python scripting, this plug-in simplifies simulation setup. Users only need to input data, create the job, and initiate the simulation.
The Abaqus AM Modeler utilizes two primary 3D printing simulation methods: eigenstrain and thermomechanical. Each approach supports specific process types to suit varied user needs. The eigenstrain method includes two process types: trajectory-based and pattern-based, ideal for users needing fast, efficient setups. The thermomechanical method expands this with four process types: trajectory-based powder bed fabrication, pattern-based powder bed fabrication, laser direct energy deposition, and fusion deposition modeling.
Workshops of the Abaqus AM Modeler plug-in
This method involves three primary workshops: “Sequential thermomechanical analysis of simple cube one-direction LPBF 3D printing using the trajectory-based method with AM plug-in,” “3D printing simulation with Fusion deposition modeling and Laser direct energy deposition method with AM plug-in,” and “Material Removing with AM plug-in.” The first two workshops are done with two versions of the Abaqus AM Modeler: an older and a newer version. The first workshop, which involves LPBF, is carried out using the older version, while the second workshop uses the newer version. The reason for using two versions is to familiarize the participants with both versions, in case they encounter either one.
Note: 3D printing can be used to produce complex components quickly and cost-effectively, allowing for more customization and reduced lead times, right? SO, it can be a great help in Smart manufacturing! But what is smart manufacturing anyway? Do not worry because we have a complete course of it: “Smart Manufacturing Course.”
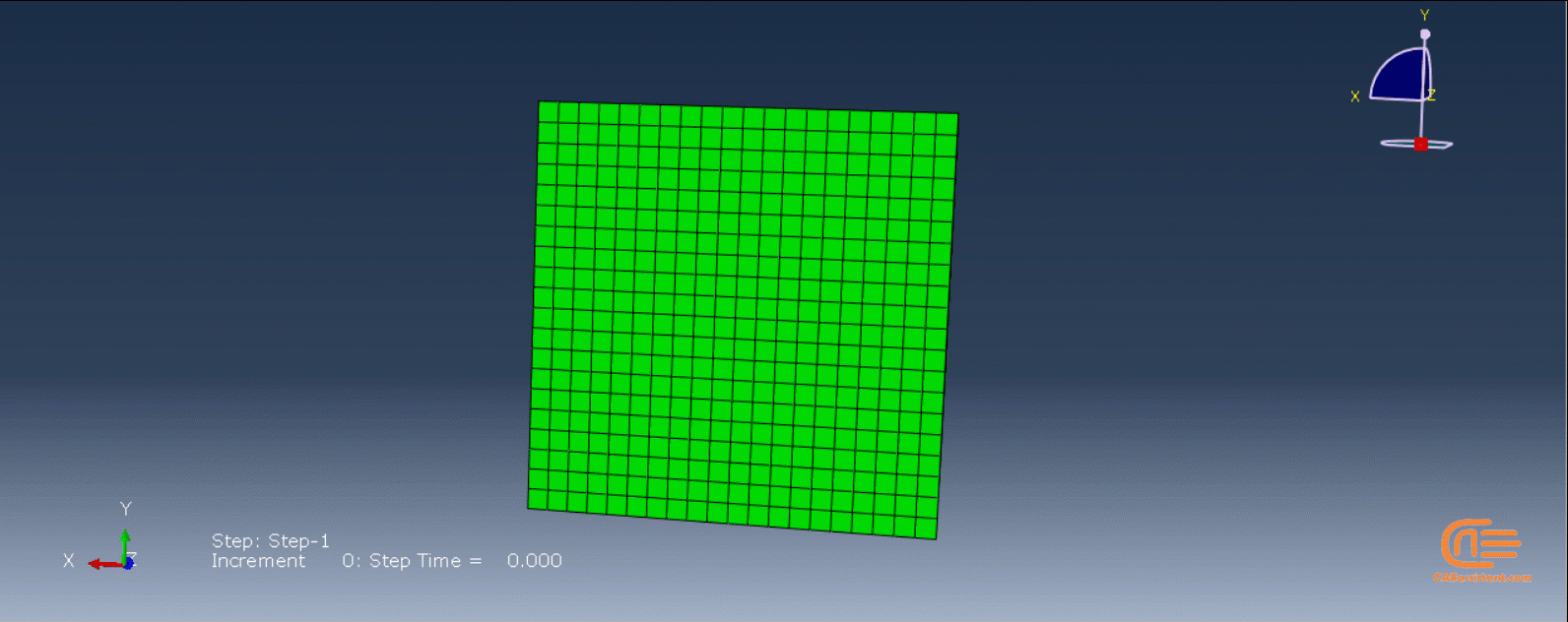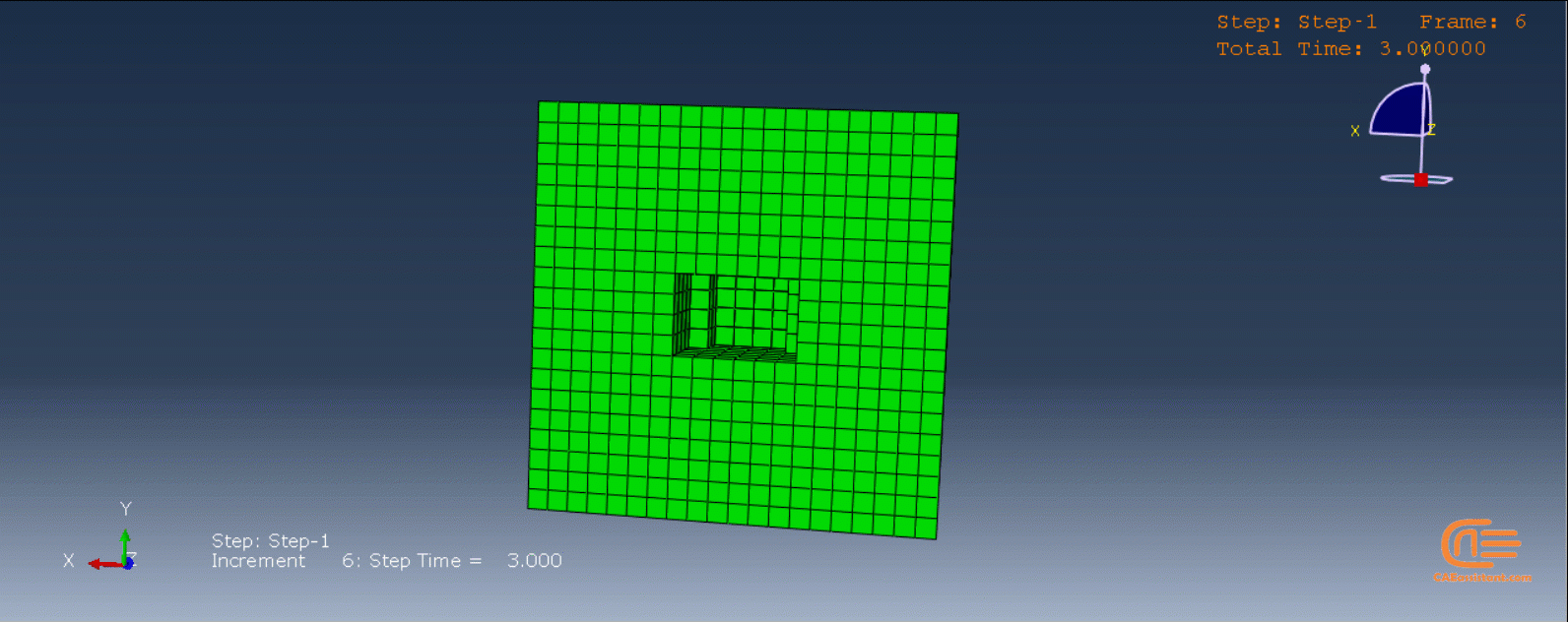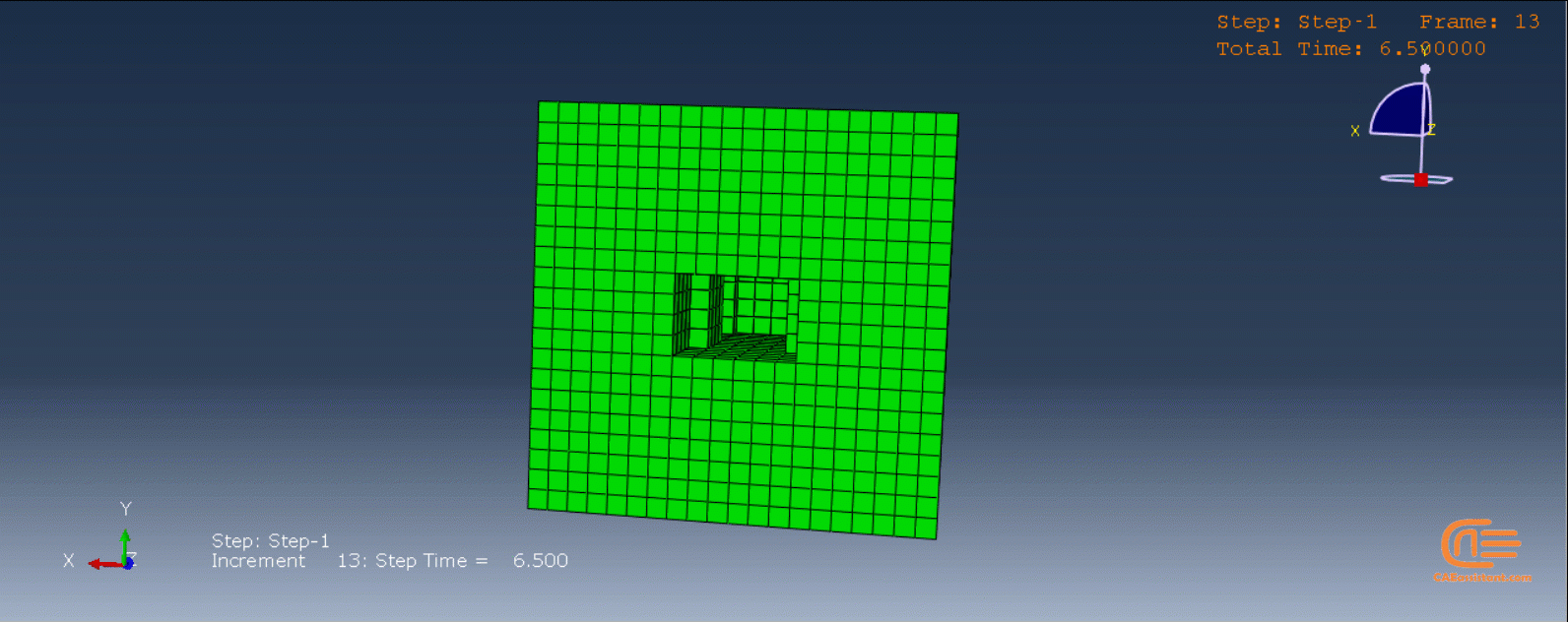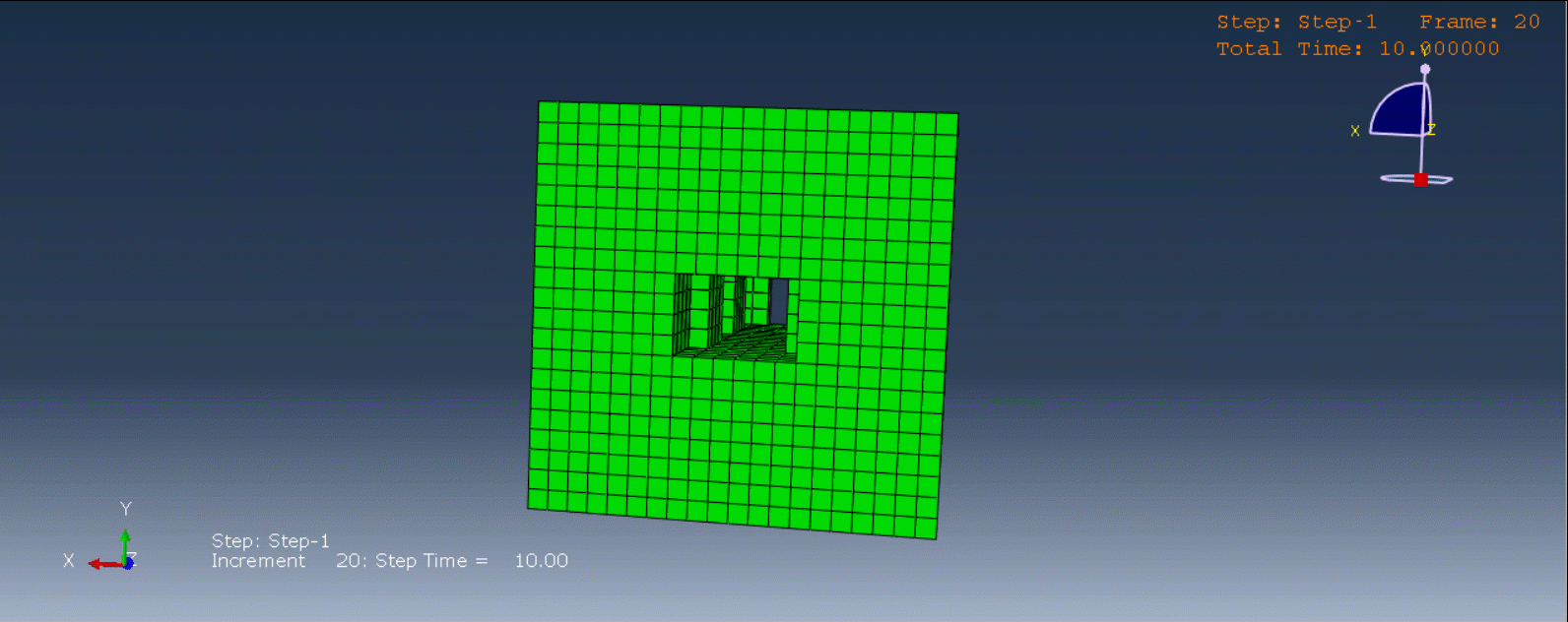
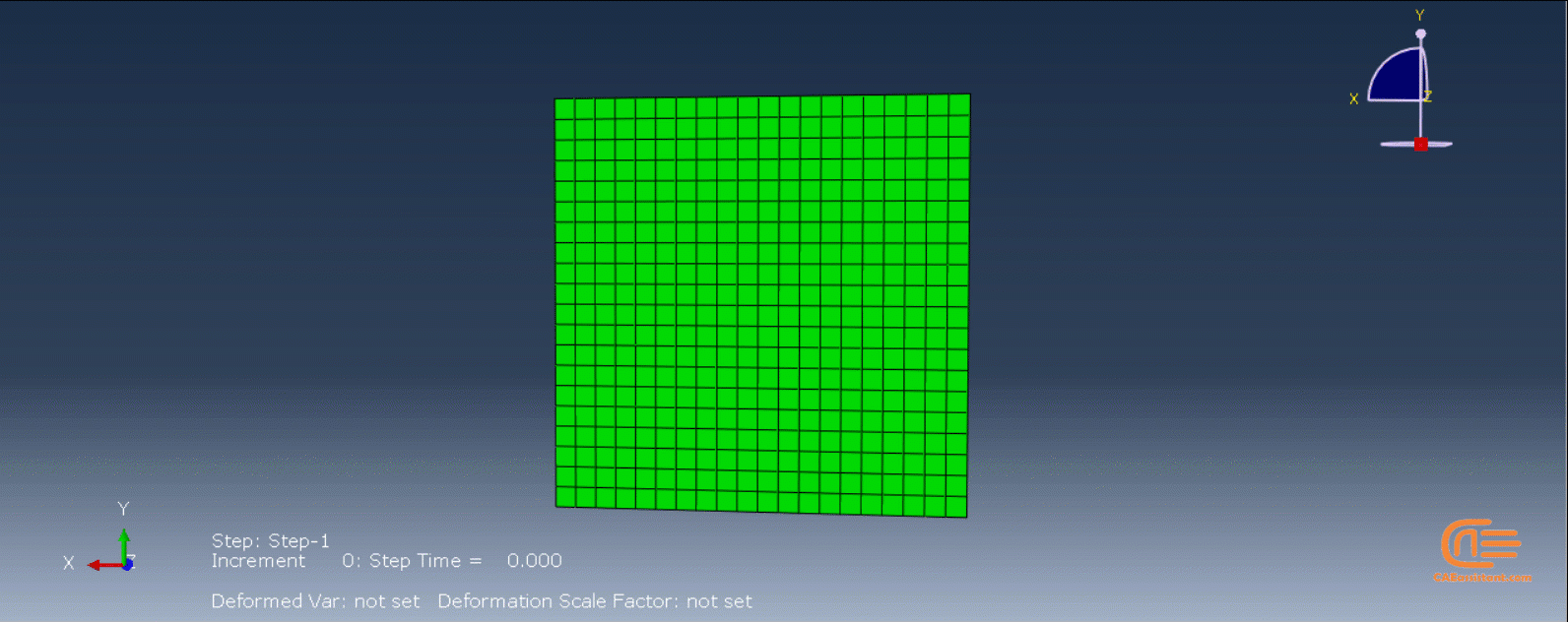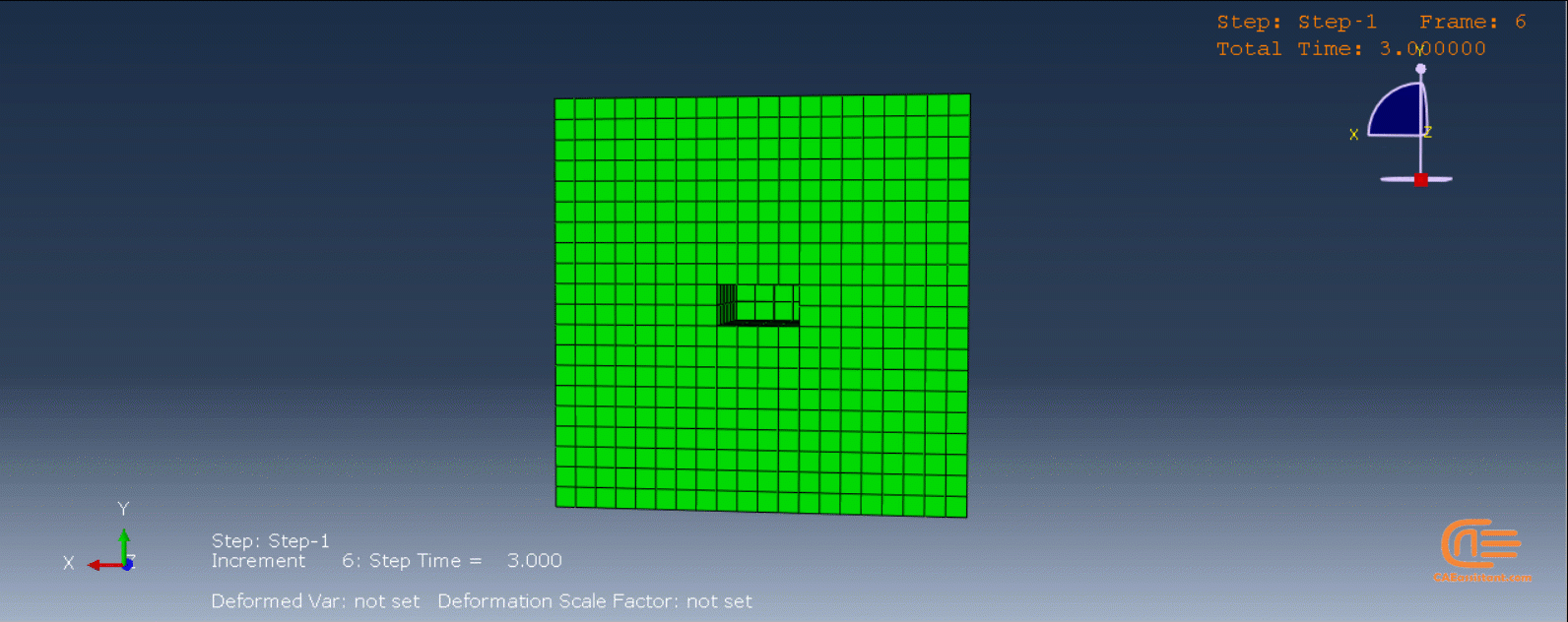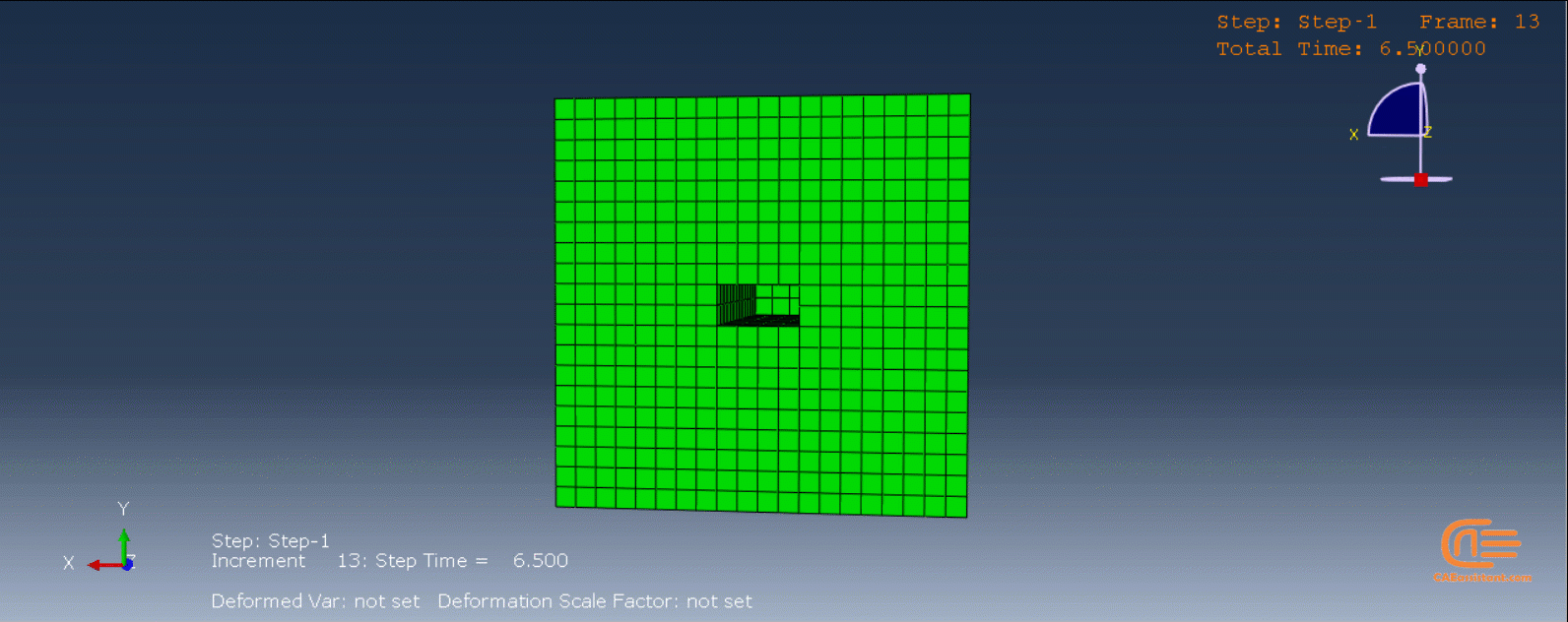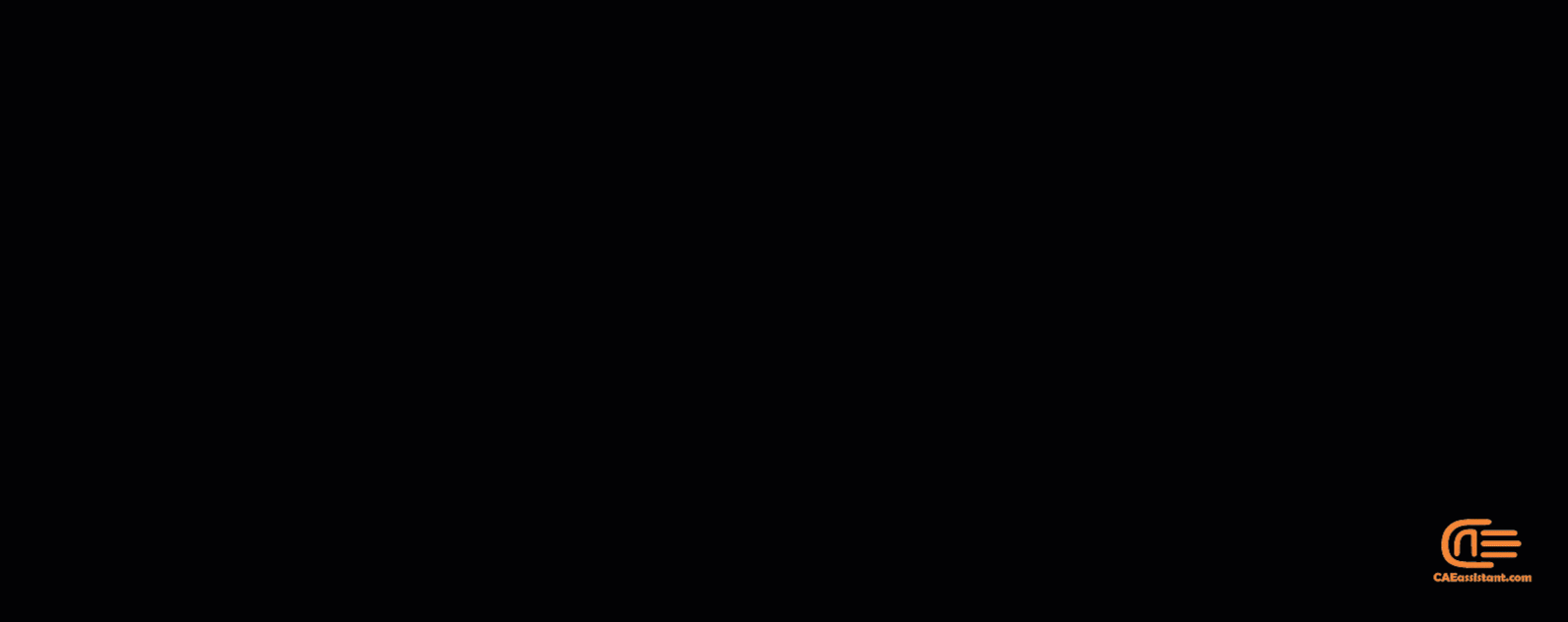
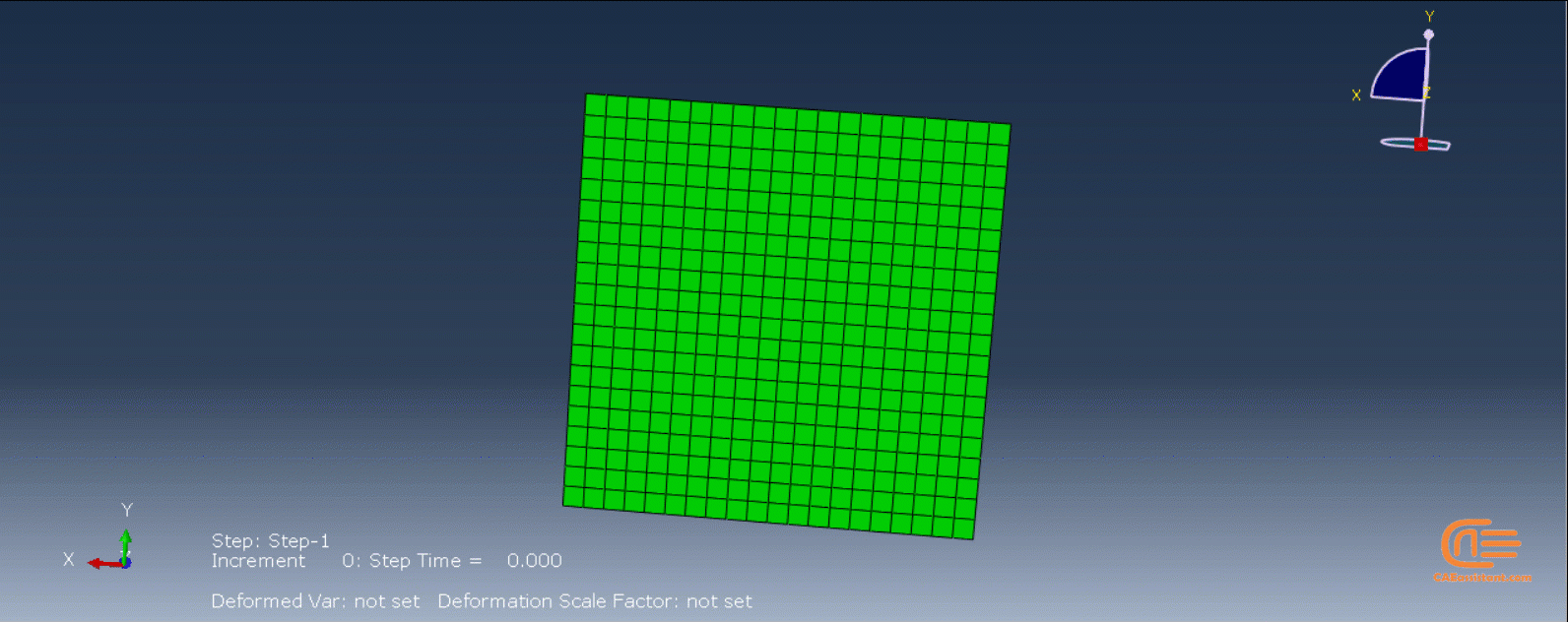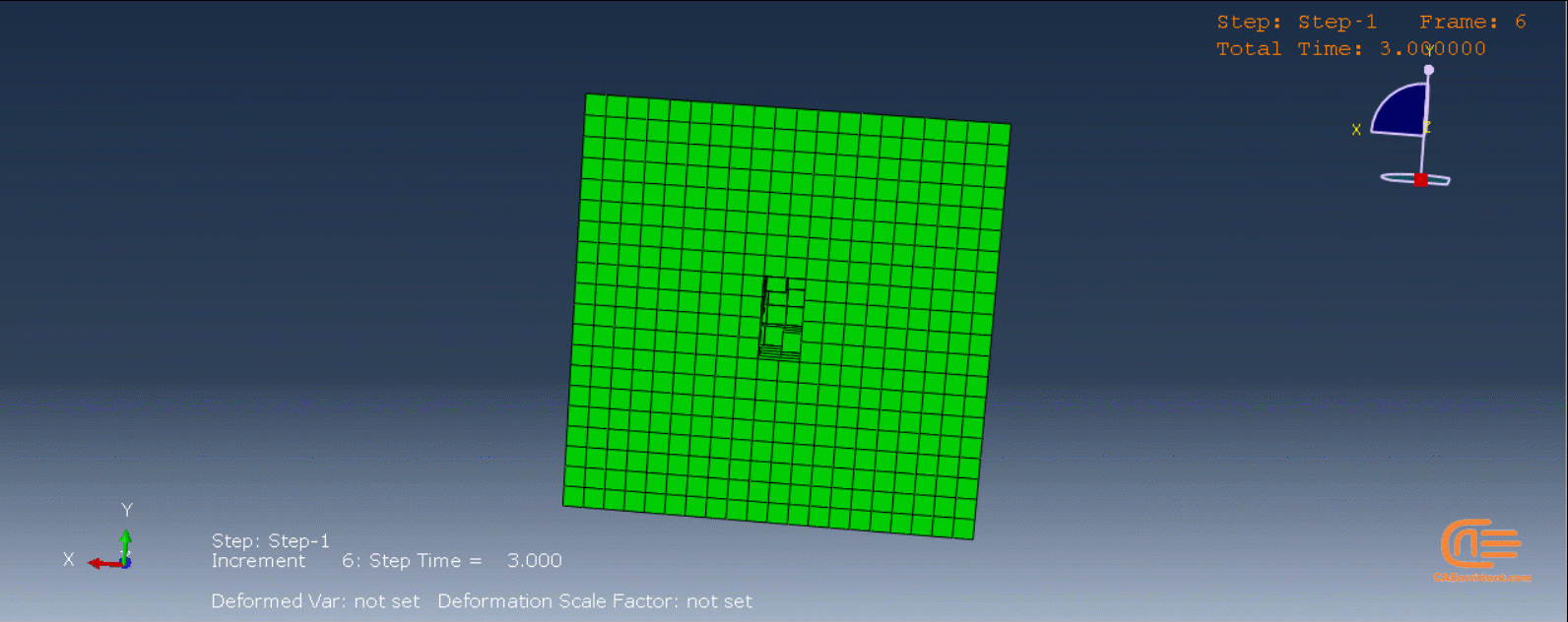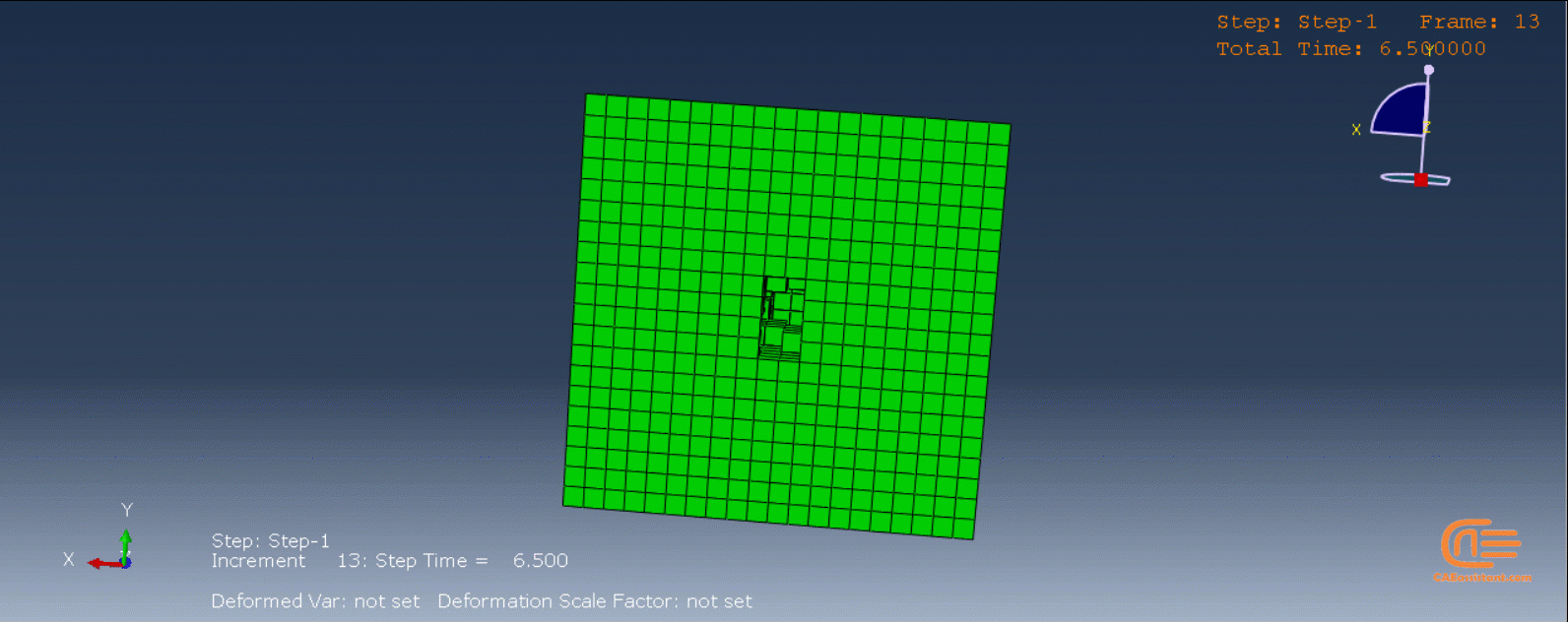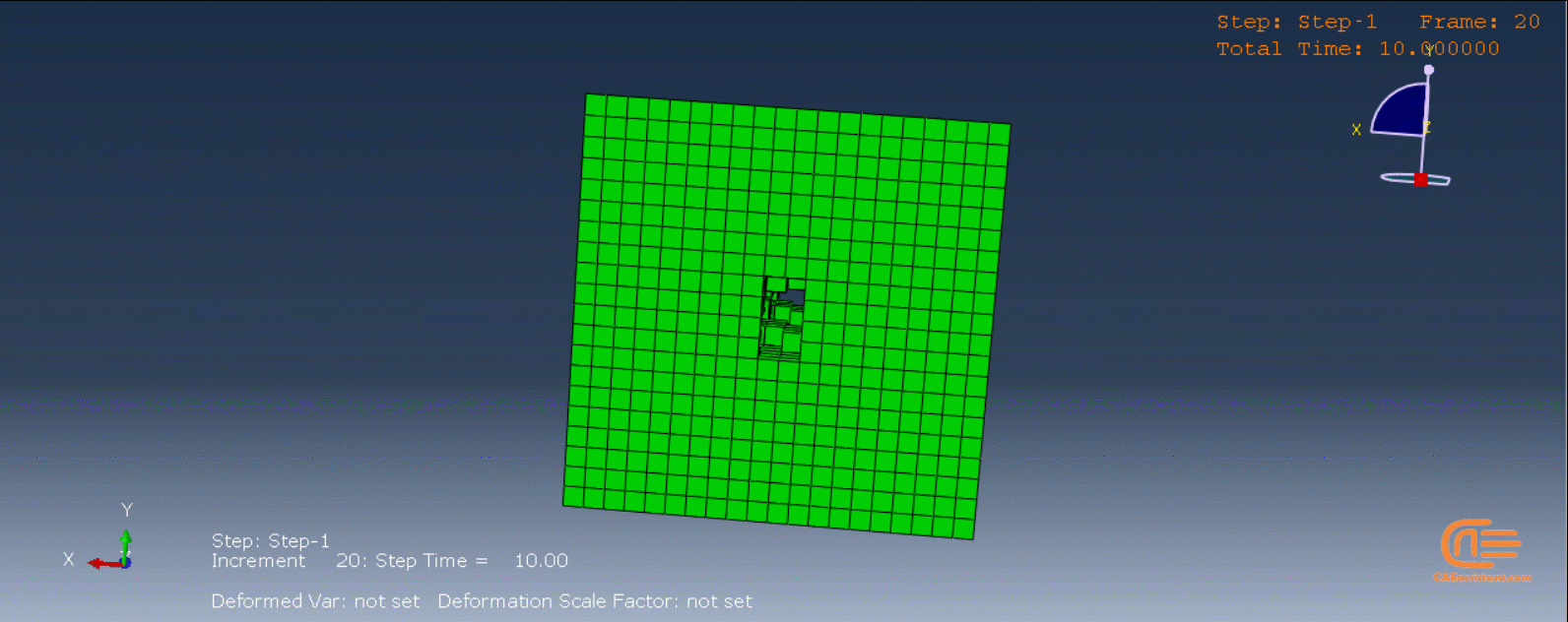
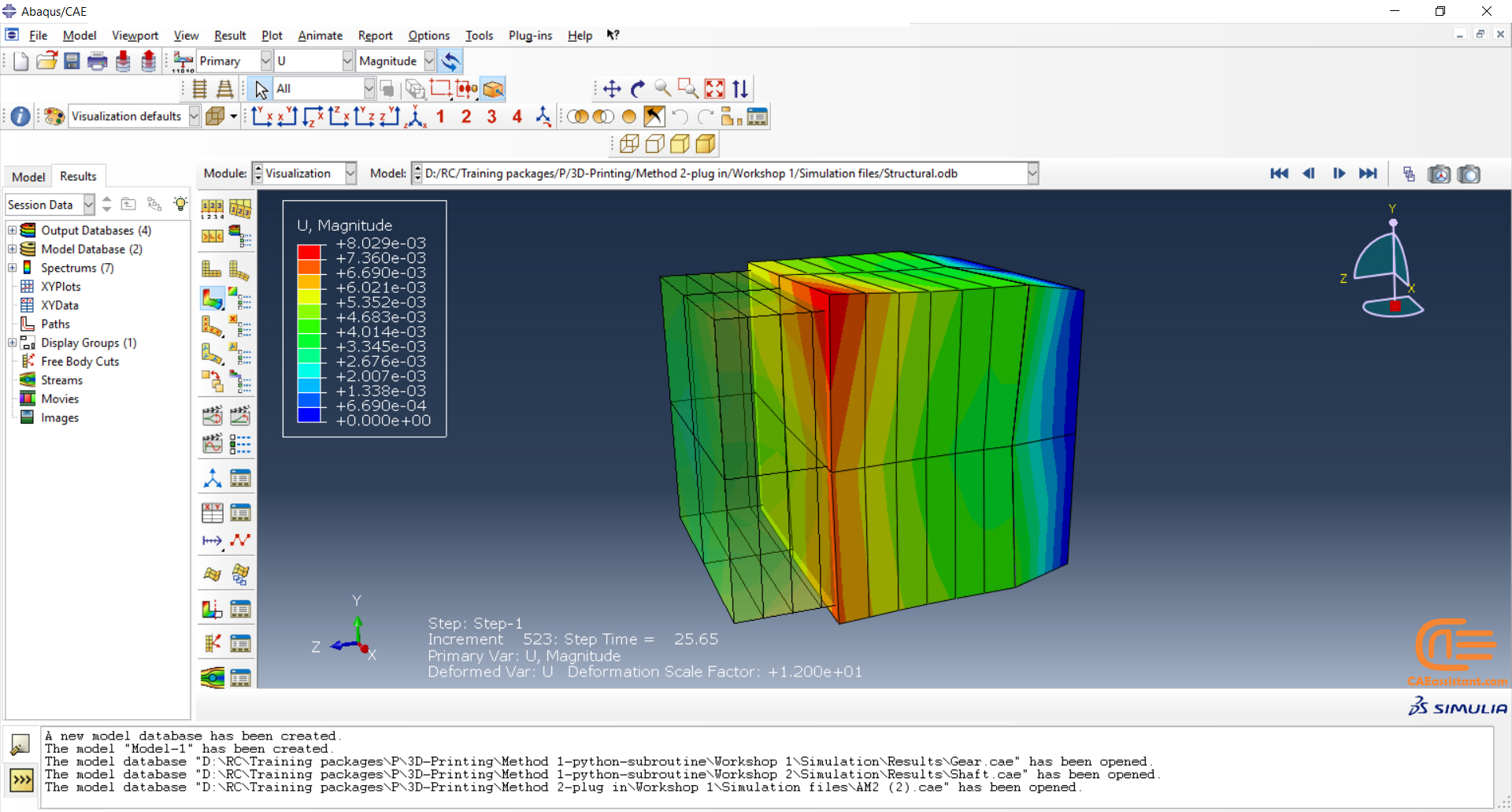
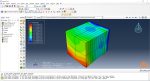
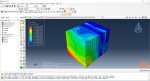
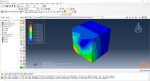
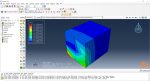
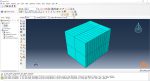
Workshop 1: Sequential thermomechanical analysis of simple cube one-direction LPBF 3D printing using trajectory-based method with AM plug-in
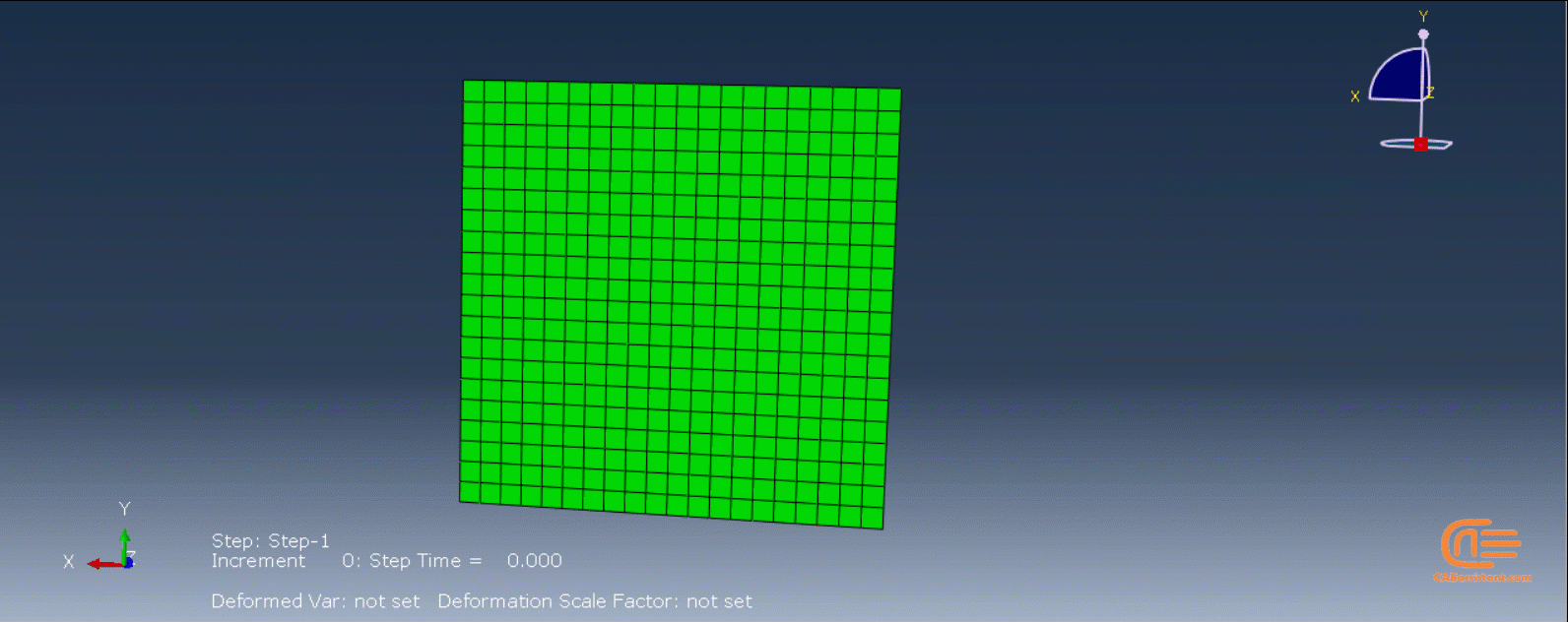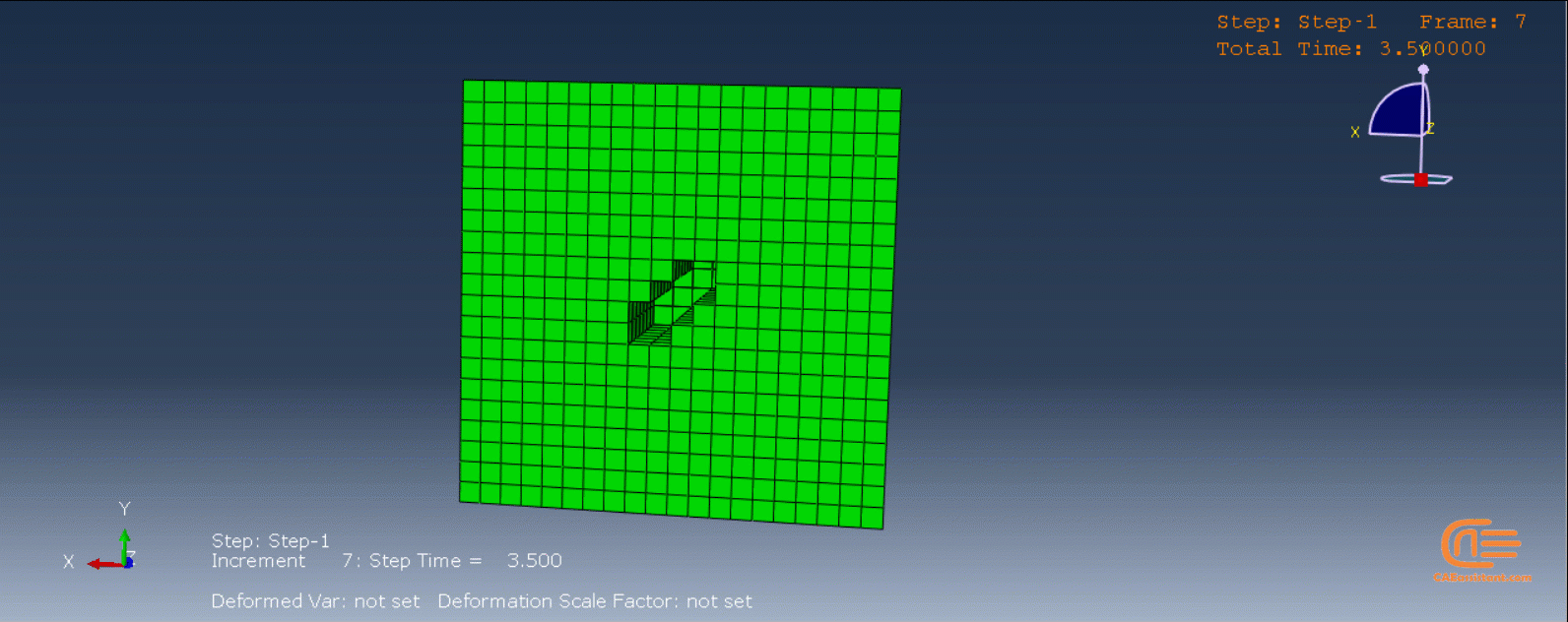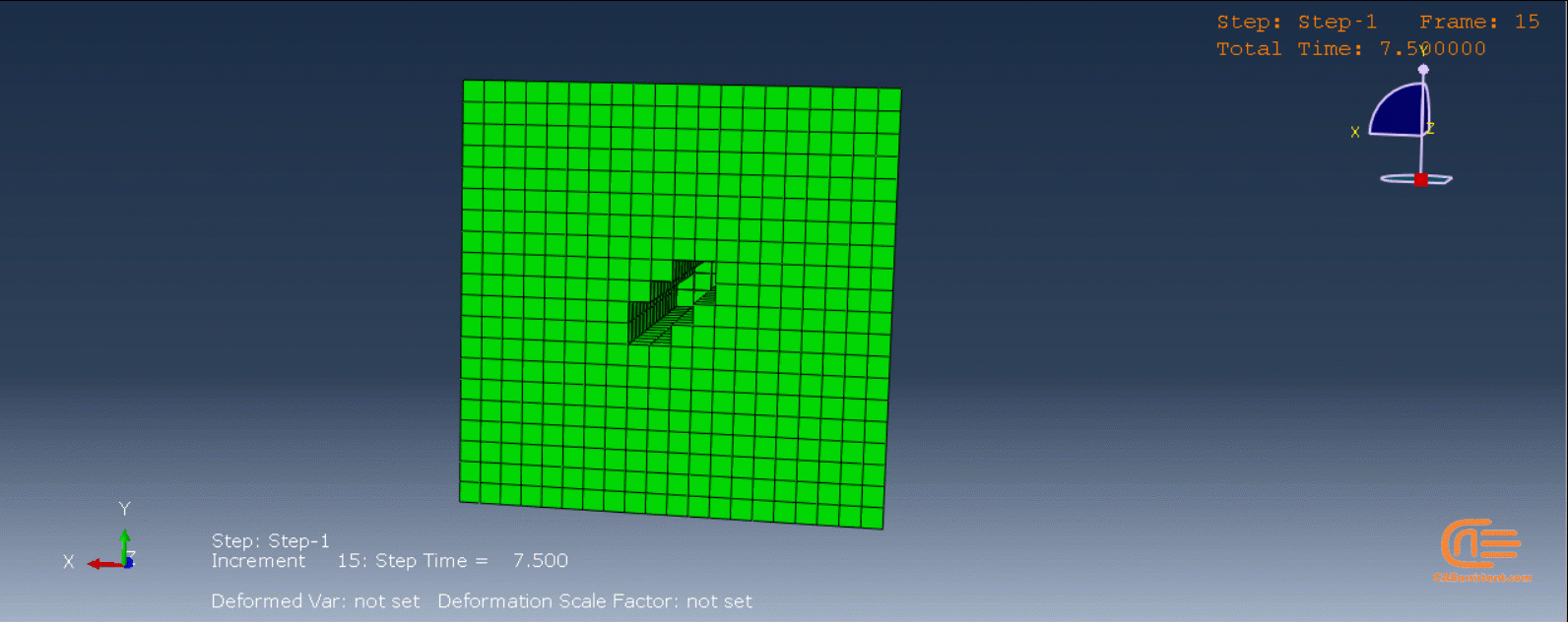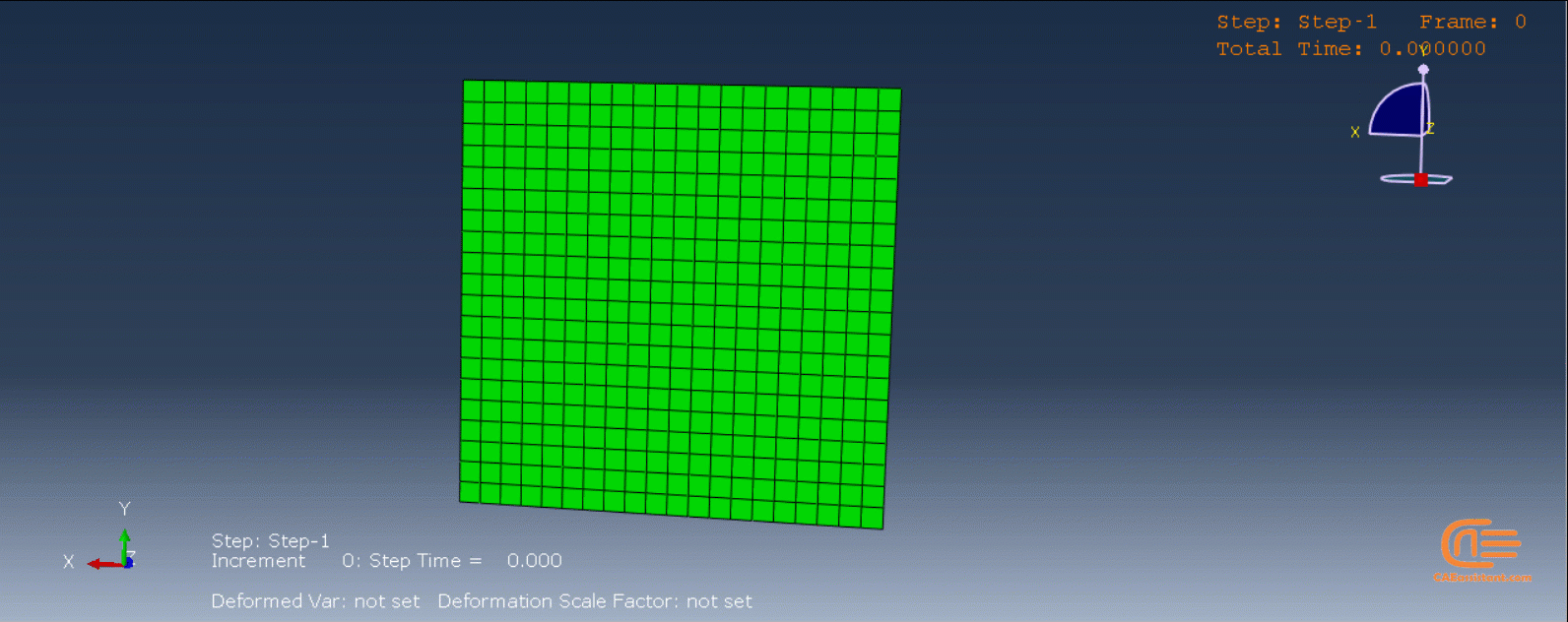
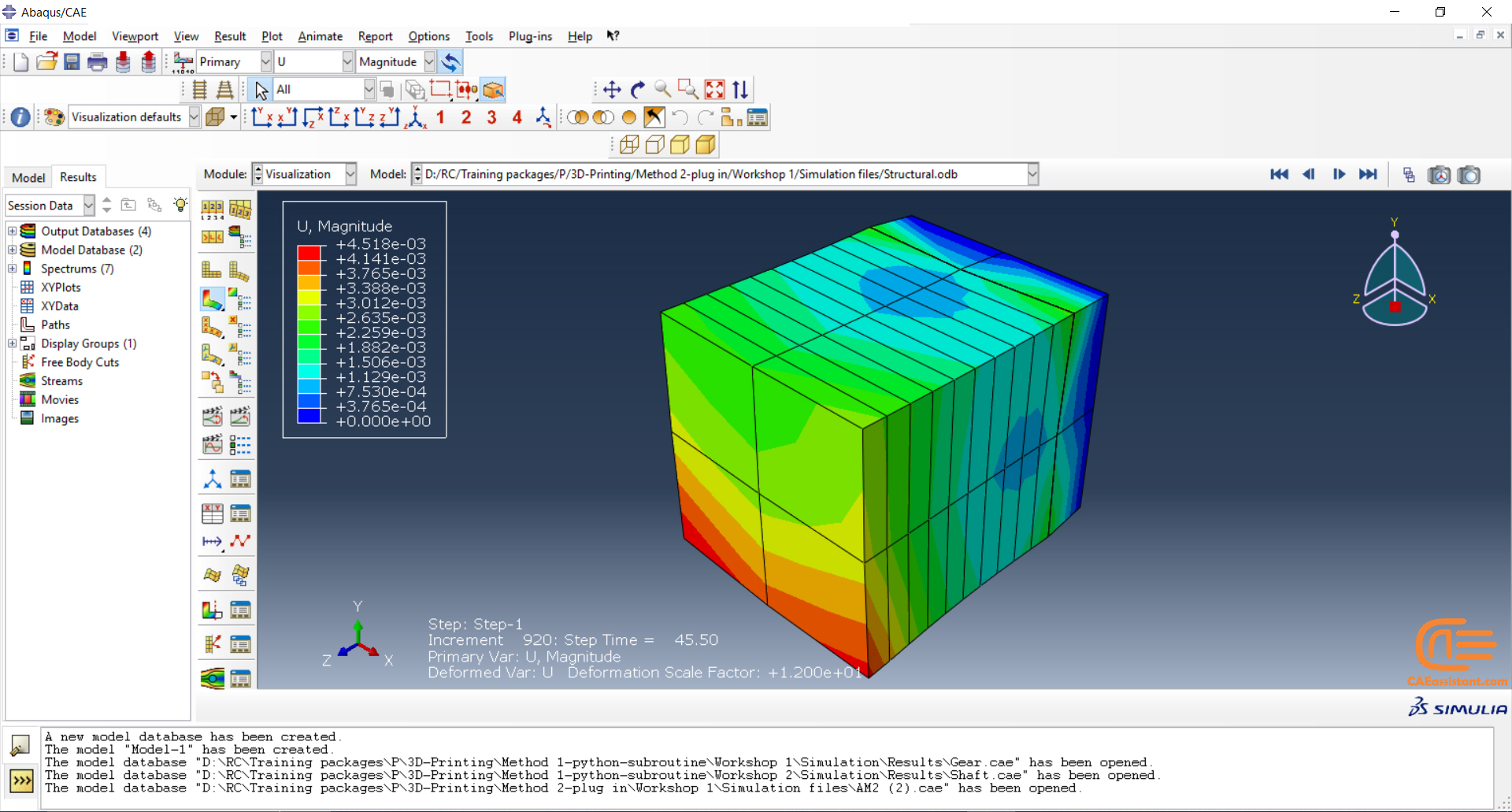
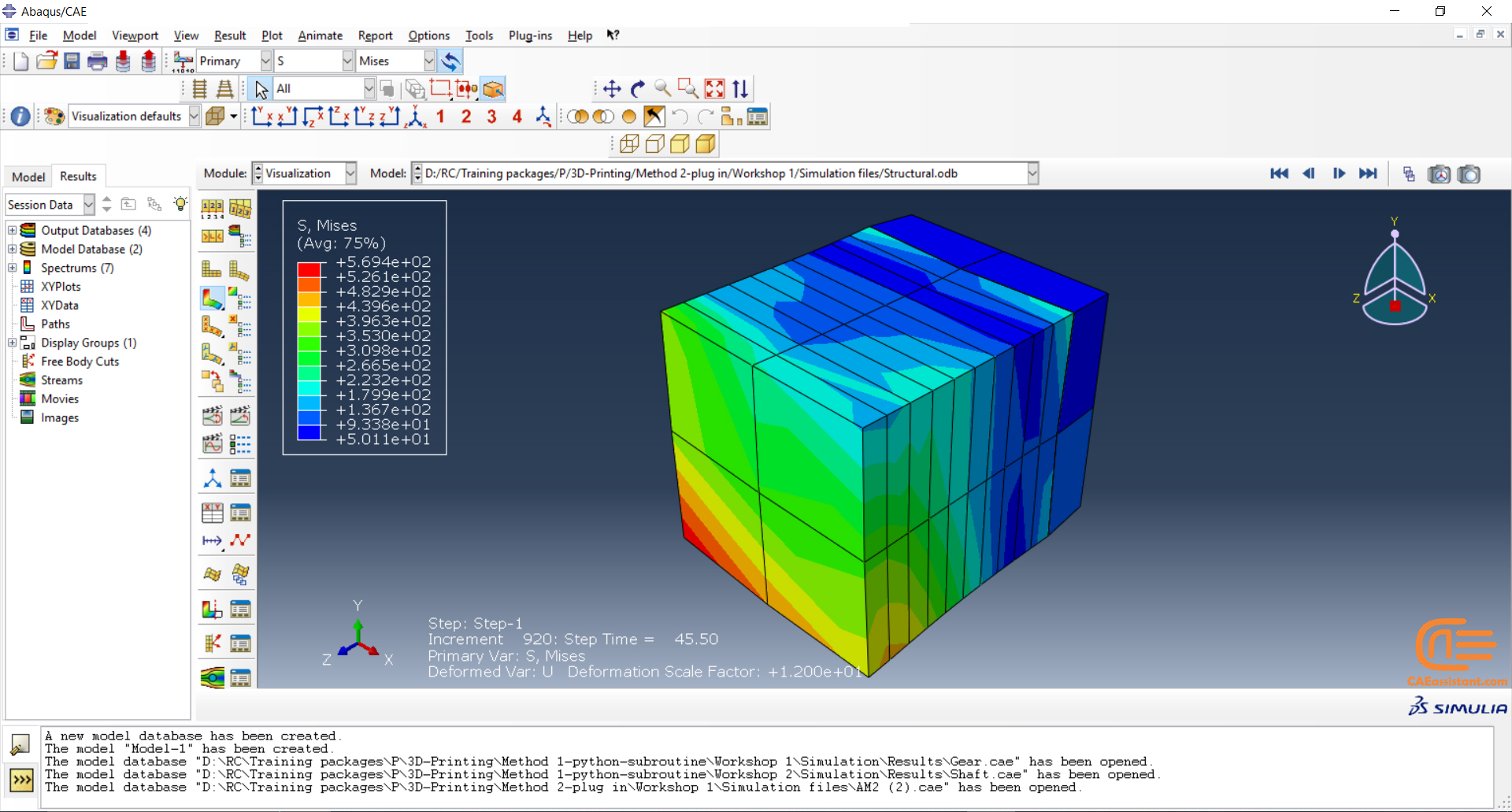
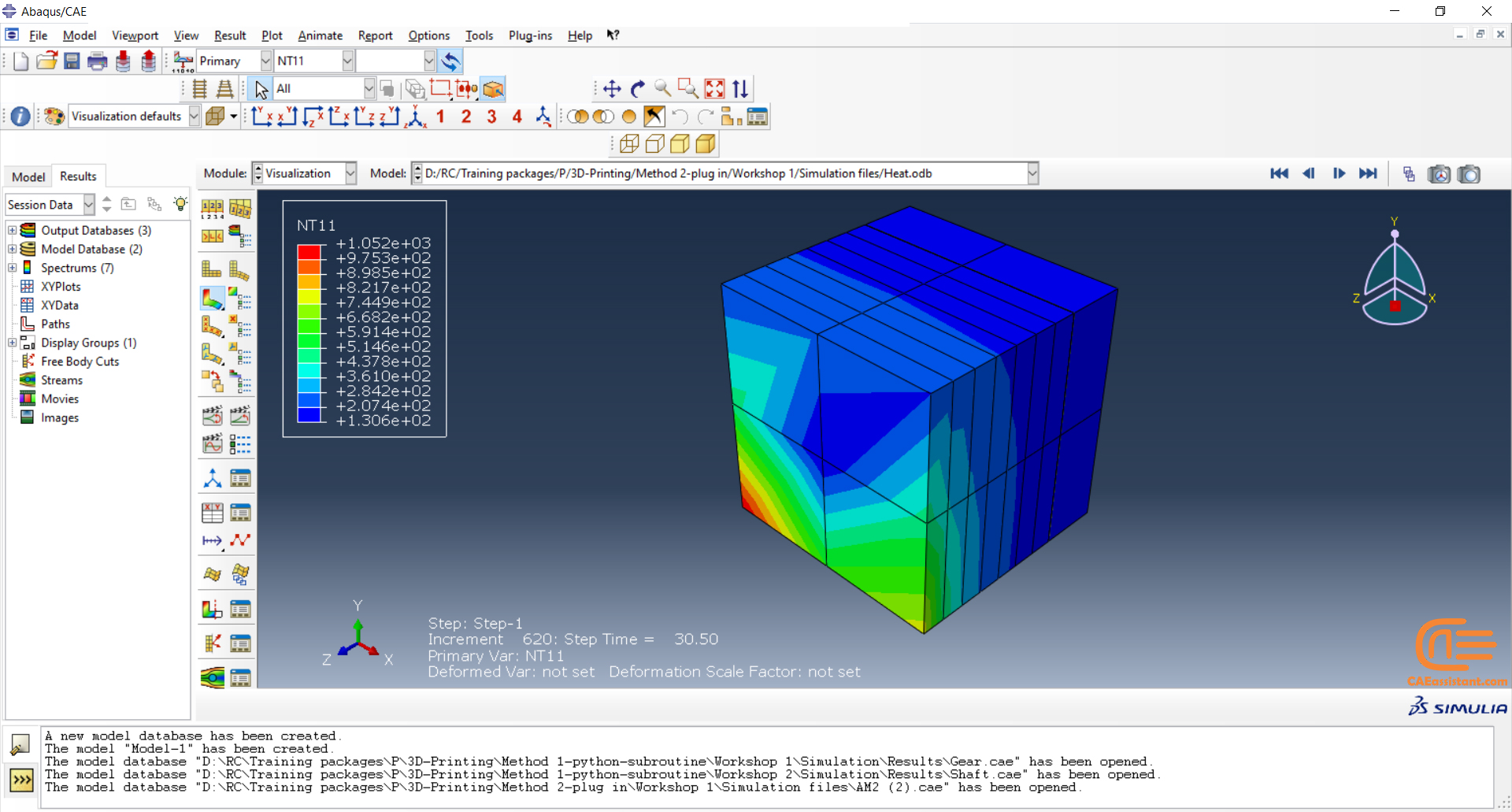
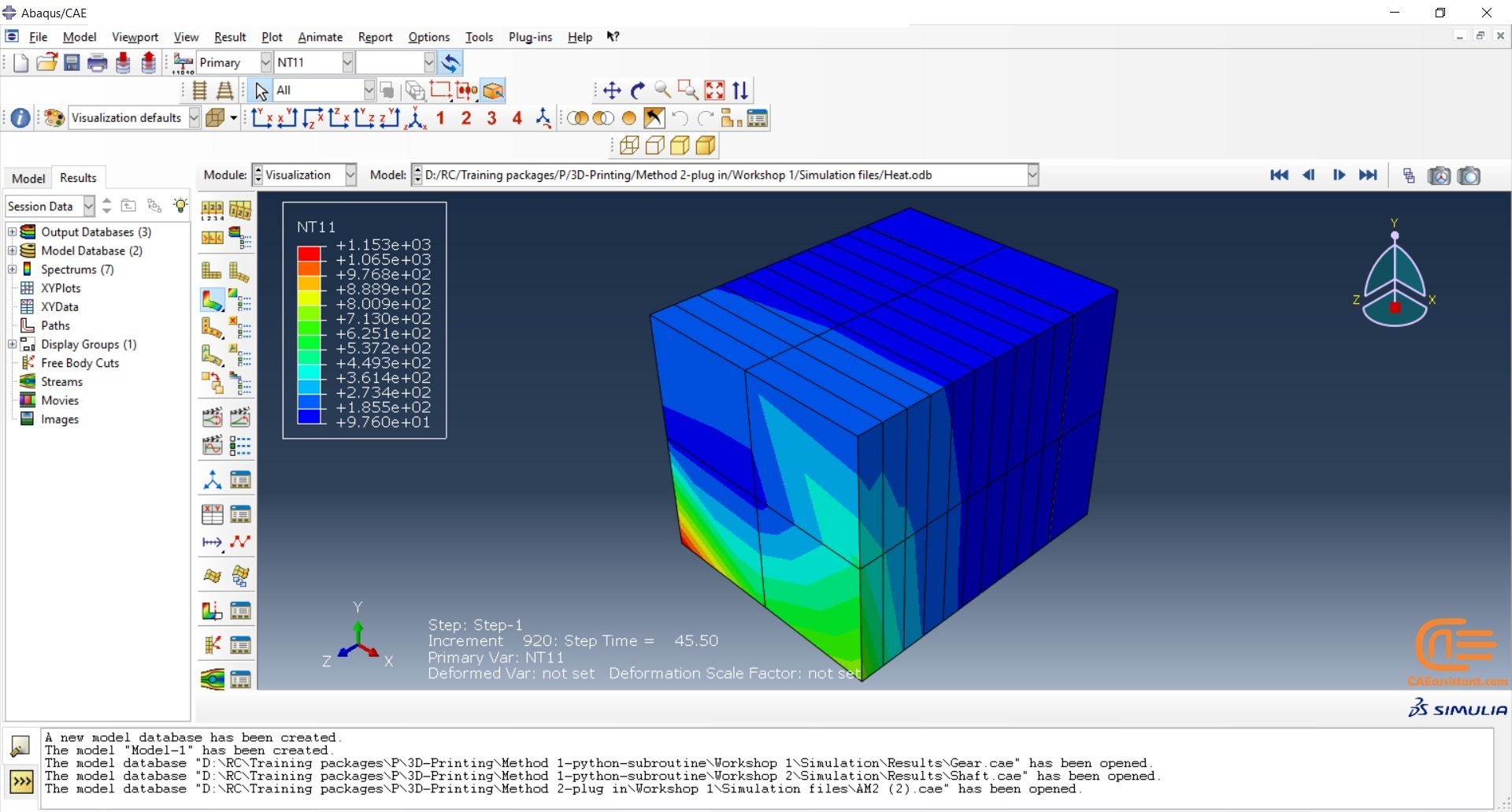
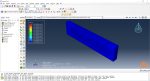
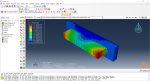
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) is a 3D printing method that utilizes a high-powered laser to melt and fuse metal powders together layer by layer. The process involves spreading a layer of metal powder over a build platform using a roller, followed by scanning the powder with a high-powered laser to melt and fuse it together based on the 3D model. The platform is lowered, and the process is repeated layer by layer until the object is complete.
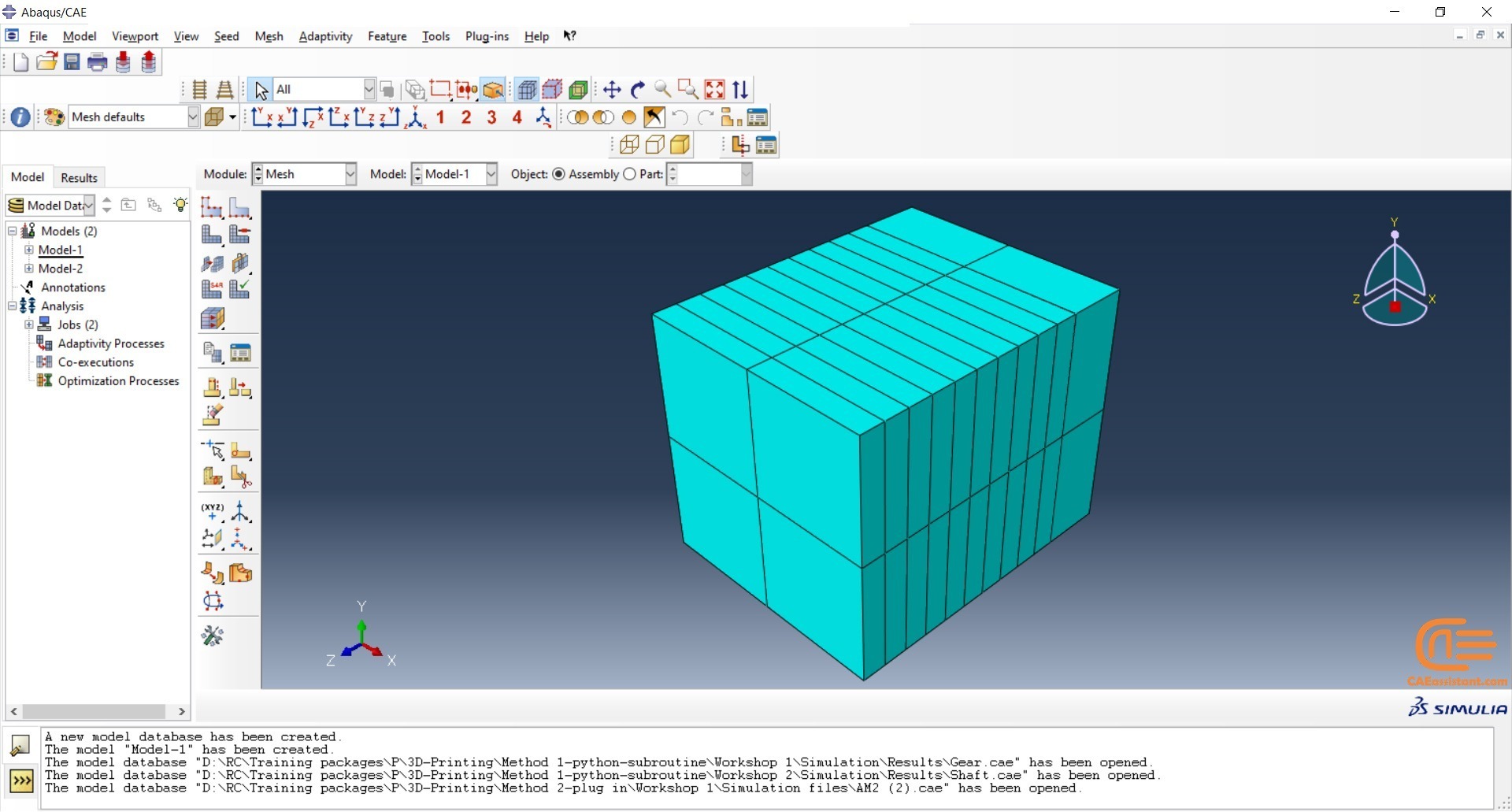
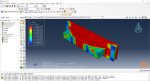
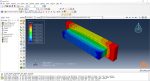
During the workshop, the model’s geometry and layer details are discussed, followed by presenting the required material properties. The necessary information and inputs for the roller and laser beam, including their speeds and “Event series” data, are provided. The boundary conditions are explained, and the modeling process in Abaqus begins. The simulation involves two analyses: a thermal analysis followed by a structural analysis. The required inputs, such as “Event series” data, are added via the Abaqus AM Modeler plug-in. The simulation is performed using the older version of the plug-in, and the results are discussed in the end.
Note: Did you know you can use topology optimization in for a 3D printing part? Interesting, isn’t it? Lucky for you we have course for that called: “Advanced Space–Time Topology Optimization in Multi-Axis Additive Manufacturing“.
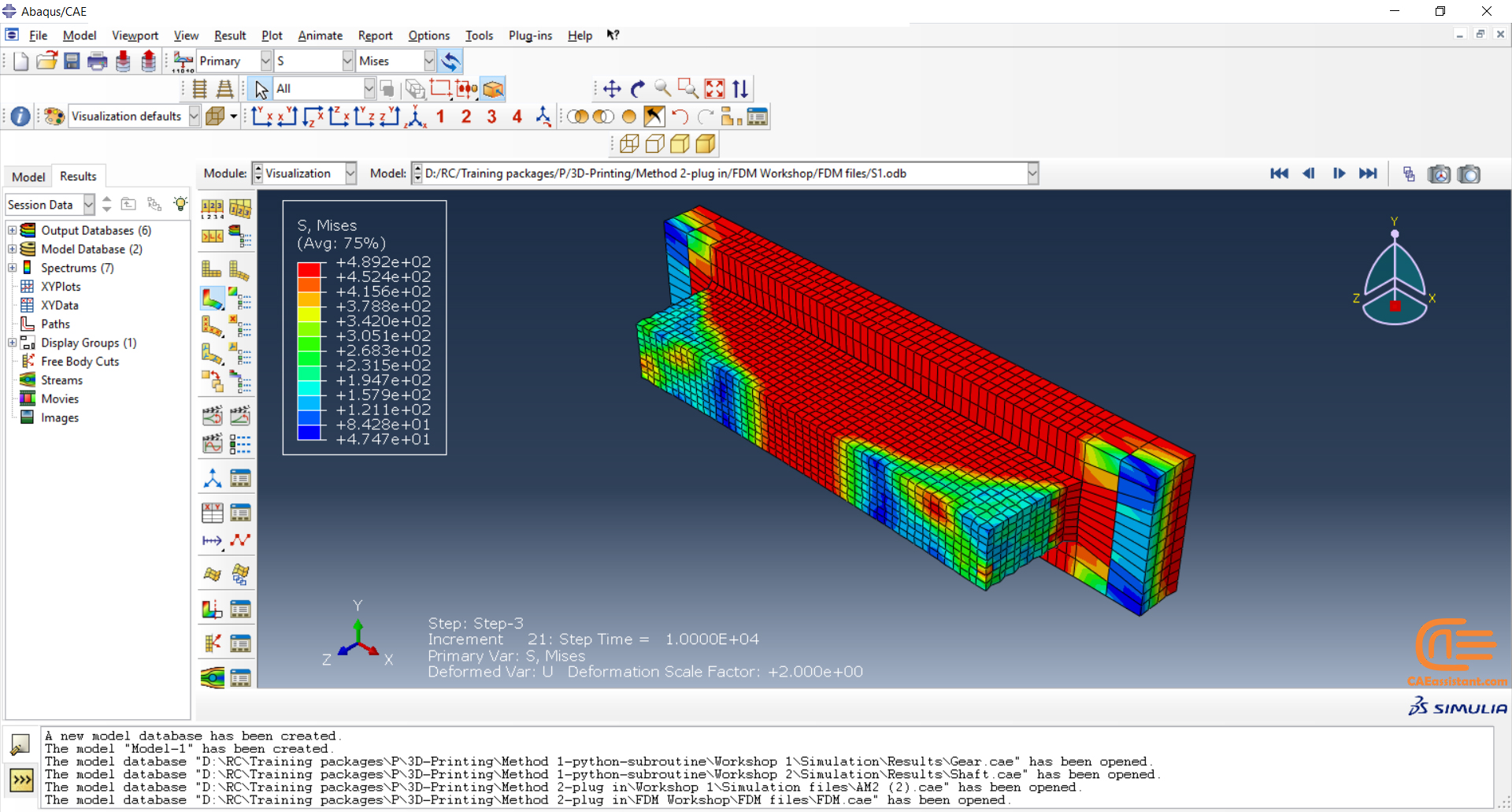
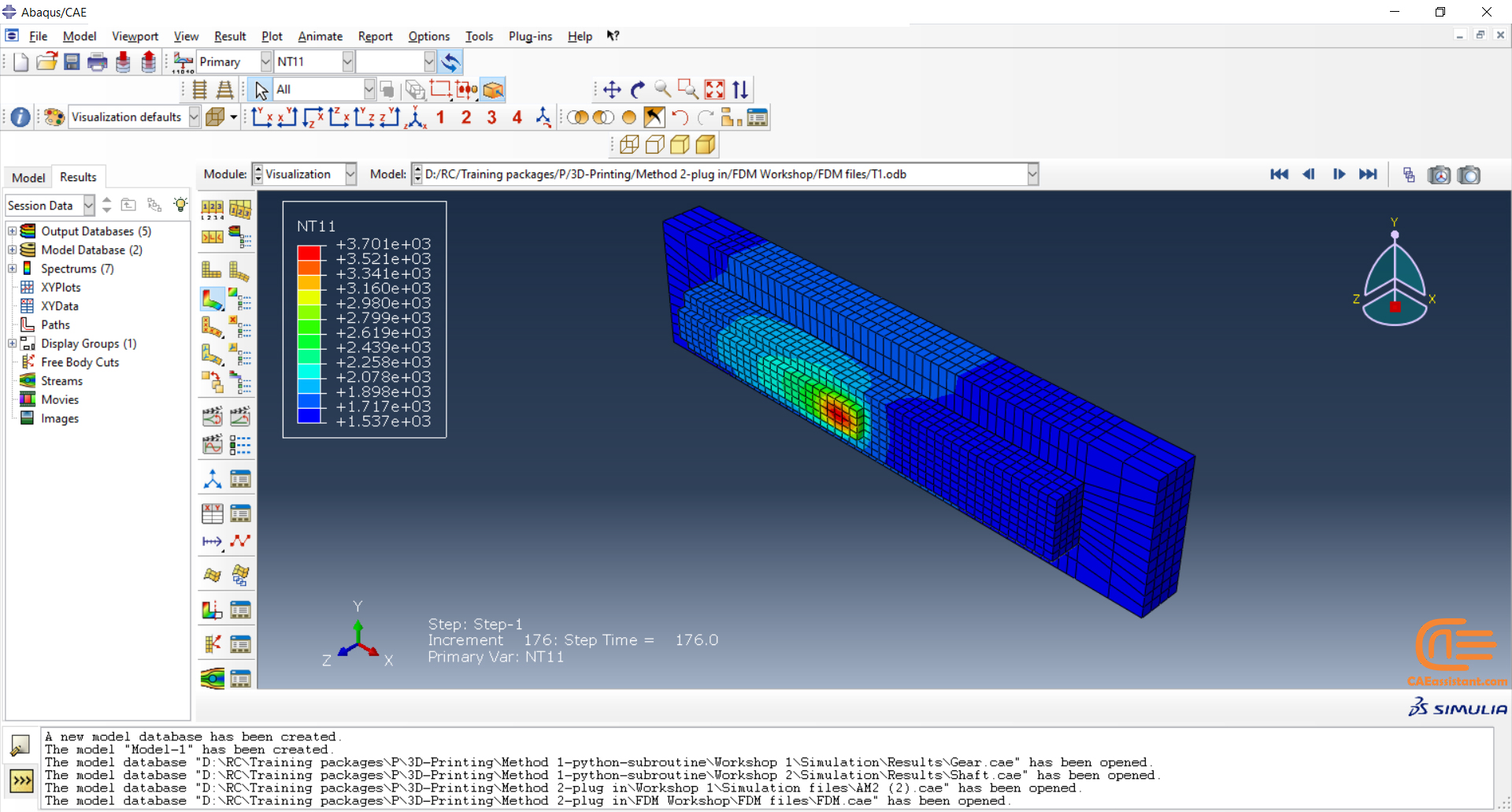
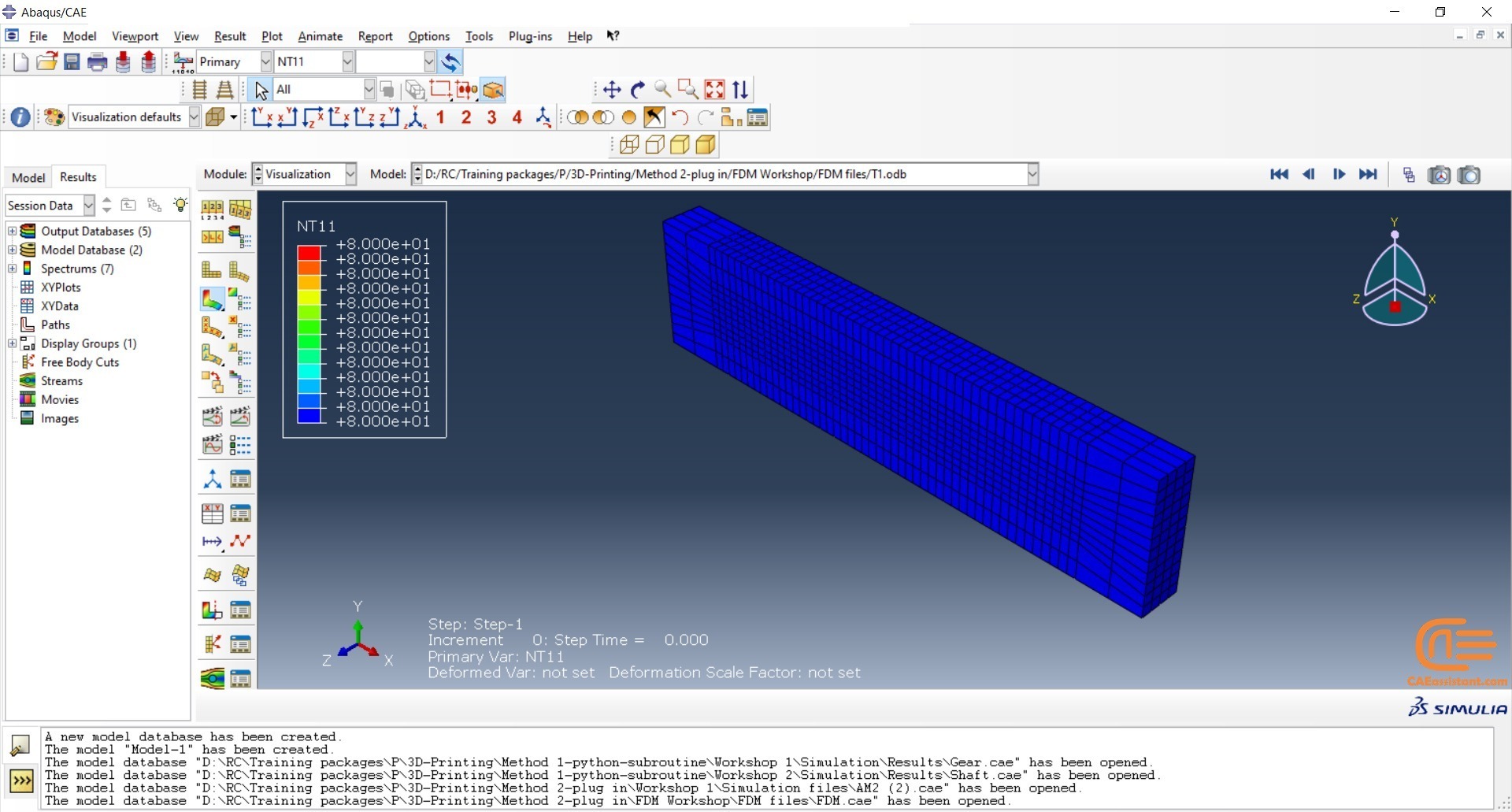
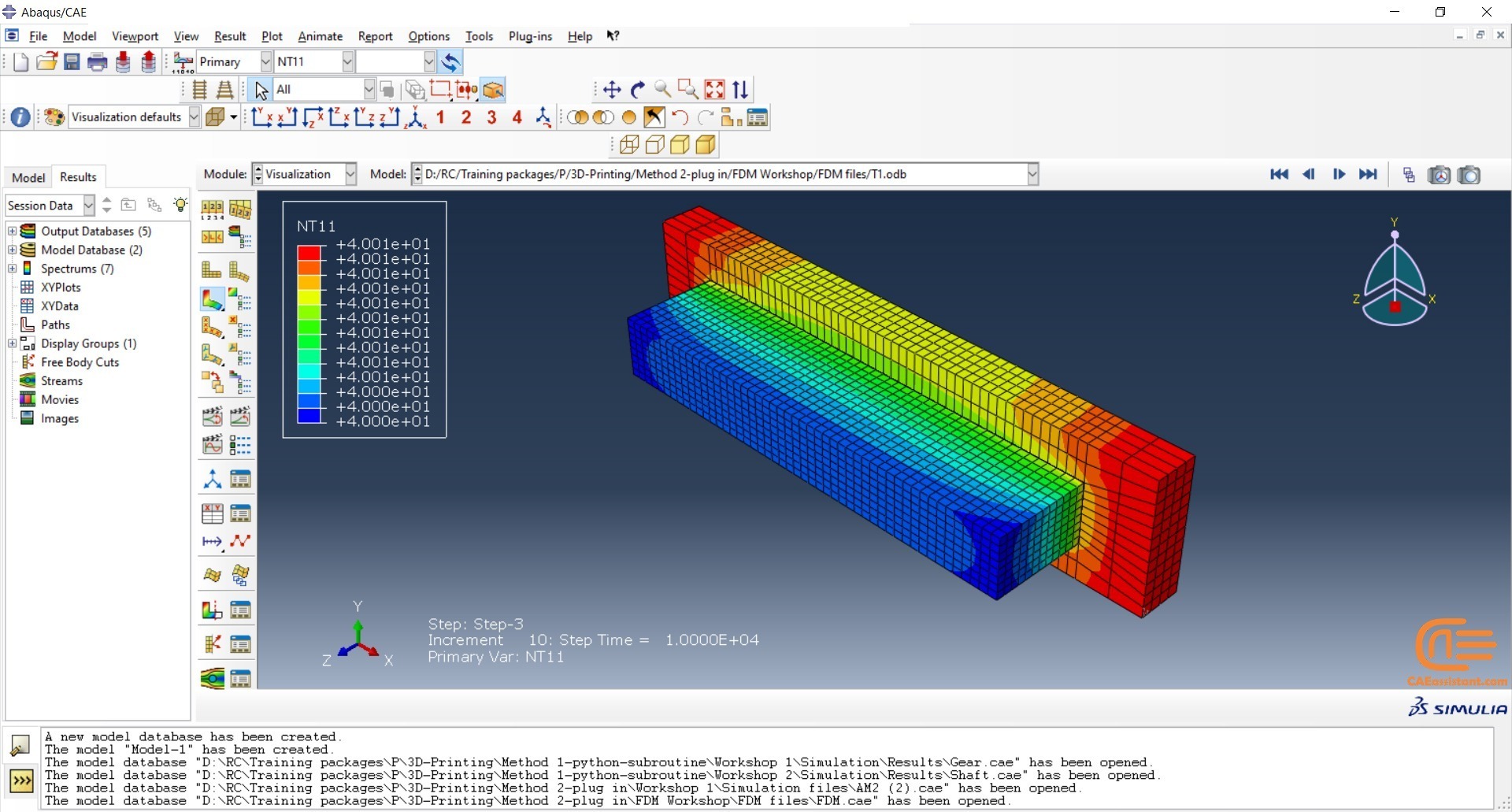
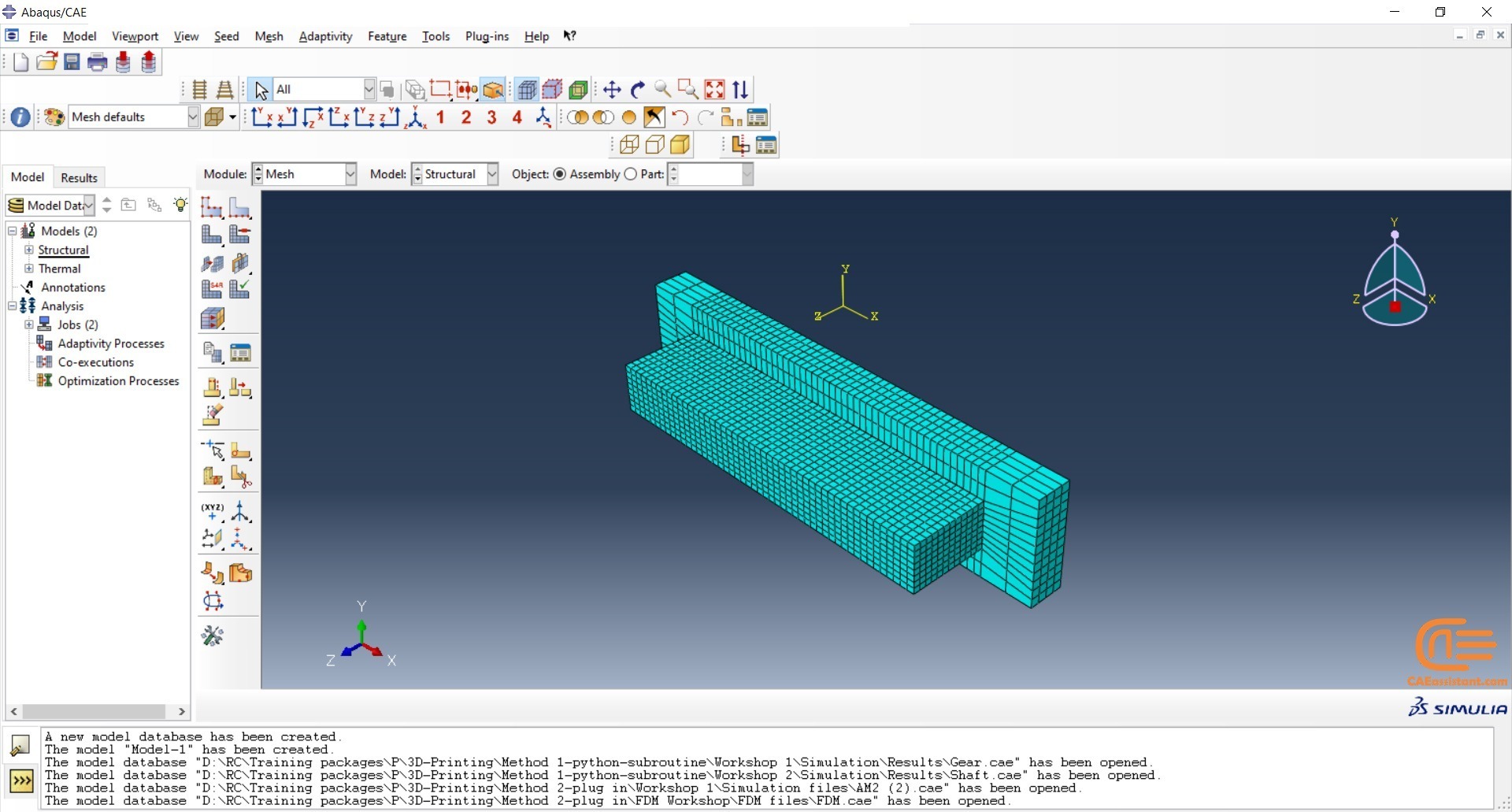
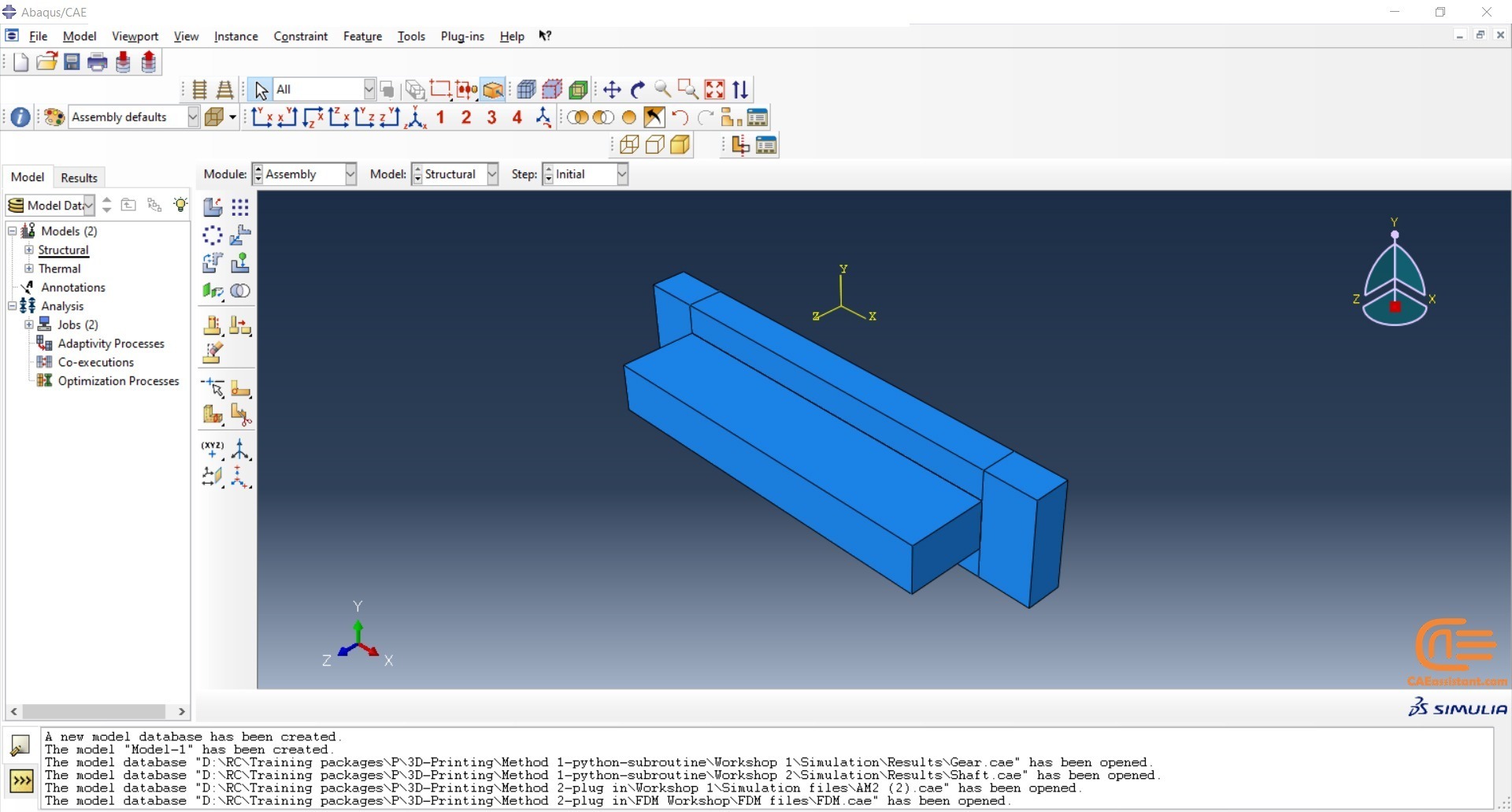
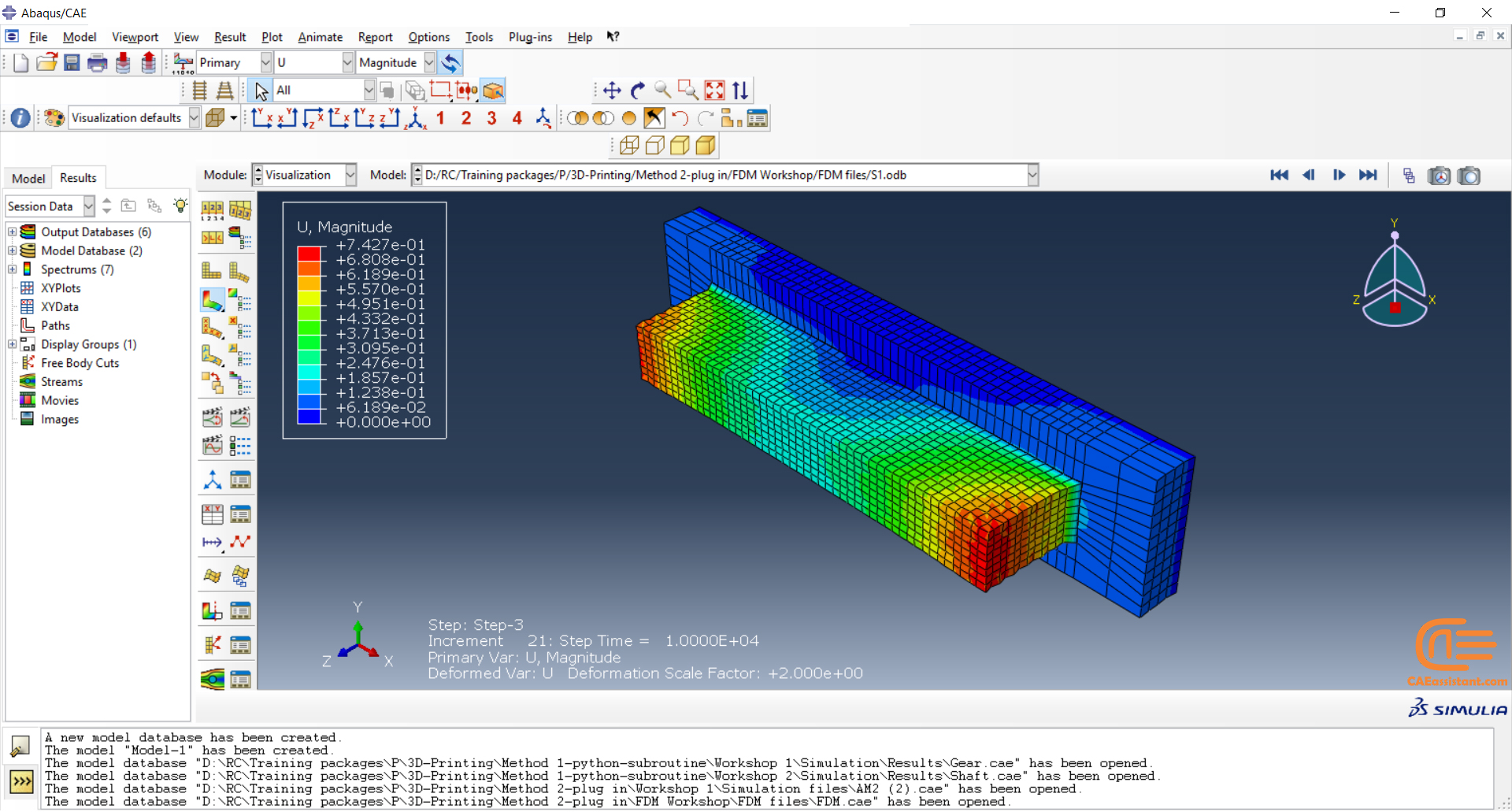
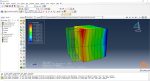
Workshop 2: 3D printing simulation with Fusion deposition modeling (FDM) and Laser direct energy deposition (LDED) method with AM plug-in
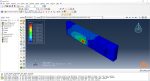
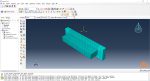
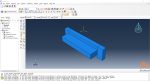
The Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a 3D printing technique that involves extruding melted filament layer by layer to create a 3D object. The process includes feeding a filament into a heated extruder (nozzle), which melts the filament and deposits it layer by layer onto a build platform based on the 3D model. The material cools and solidifies, creating the final object.
During the workshop, the model’s geometry, layering, and details such as bead dimensions are presented. Material properties are introduced, followed by the representation of nozzle data, including speed. All simulation steps are similar to the previous workshop, except for the Abaqus AM Modeler part, which uses the newer plug-in version.
In both workshops, element progressive activation technique (Material Deposition) is used for material deposition, and a moving heat source is employed for heating. Both material deposition and moving heat source have several types in Abaqus AM Modeler, which are explained during the workshops.










locas.mij –
This was a great course, great implementation and motivation was provided which has definitely increased my enthusiasm and I am really looking forward to other courses to increase my skills.
Daniel –
This package helped me successfully implement 3D printing simulation in my projects. Is there a possibility of receiving guidance for the development and improvement of these projects?
pawal.tin –
Excellent course!
It gave me a new perspective in 3D specialized software I did not know.
dani-lie –
As someone who works in the aerospace industry, I was looking for a training package that could help me simulate additive manufacturing accurately. The Additive Manufacturing Simulation with Abaqus AM modeler package was exactly what I needed. The package covers everything from residual stress and temperature to machine settings and material properties. It’s a must-have for anyone interested in 3D printing simulation.
Skylar.fil –
The Abaqus AM modeler plugin is a powerful tool for simulating 3D printing, and this training package does an excellent job of explaining how to use it. I found it to be an invaluable resource for my work.
Lorenzo –
Does this training package cover concepts such as topology optimization and parametric design?
Thomas –
After using this package, I was able to perform 3D printing simulations more effectively. Is it possible to receive guidance for the production of 3D printed products based on these simulations?
Sophia –
I am truly satisfied with this educational package. Is it possible to receive guidance for my future 3D printing projects as well?
Joshua –
The videos and educational content of this package were very comprehensive and practical. Is there a possibility of accessing any future updates?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Yes. Buy purchasing the package you can access the package in new updates
Liam –
After completing this course, I was able to perform more complex 3D printing simulations using the AM Modeler. Is it possible to receive guidance on the application of this plugin in my industrial projects?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Use our consulting service
Oliver –
Thanks to this educational package, I gained a better understanding of 3D printing process simulation. Is there a possibility of receiving additional training in this area?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
contact us +17409661814
Hannah –
The educational materials provided in this package were very comprehensive and understandable. Is there a possibility of receiving technical support to resolve any potential issues in the future?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
Yes . it is possible
Henry –
The educational content provided in this package was excellent and helped me learn to use the AM Modeler plugin. Is there a possibility of receiving a discount for purchasing future educational packages?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
It depends on your total amount and other parameters. Contact us via whatsapp
Charlotte –
The quality of the videos and educational content in this package was excellent. Is there a possibility of receiving guidance for the selection of other educational packages related to Abaqus?”
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
All you need to learn Abaqus are avaialble on this website. Enjoy it!