Abaqus Crack Growth | Practical Examples
Abaqus Concrete Structure Modeling | Practical Examples (Part 4)
Abaqus Concrete Structure Modeling | Practical Examples (Part 3)
Abaqus Concrete Structure Modeling | Practical Examples (Part 2)
Abaqus Concrete Structure Modeling | Practical Examples (Part 1)
Abaqus steel material and structures | Practical examples
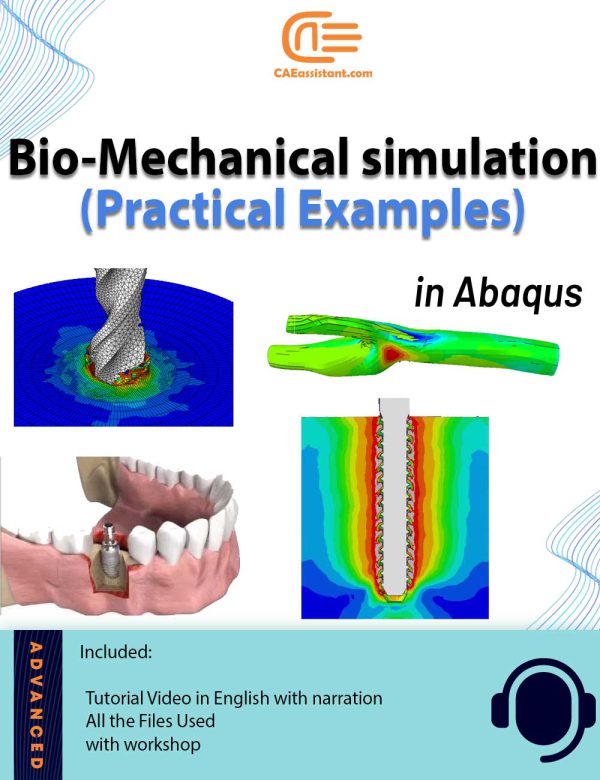
Bio-Mechanical Abaqus simulation | Practical Examples
This package offers multiple practical examples on biomechanical simulations using Abaqus, covering a range of applications from dental to orthopedic and cardiovascular analyses. The workshops delve into finite element method (FEM) simulations, exploring static loading on human teeth, crack growth in bones under bending, bone drilling, and the behavior of titanium foam implants. Each tutorial emphasizes the importance of precise modeling and meshing techniques, utilizing dynamic explicit procedures, Johnson-Cook material models, and various contact and boundary conditions to simulate realistic biomechanical behaviors. Additionally, the package includes fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulations for blood flow within coronary vessels, addressing both Newtonian and non-Newtonian models, and demonstrates the integration of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with structural analysis for enhanced accuracy. For more details on this topic, including explanatory videos covering the necessary formulation and theory in the form of a course, you can check out our full package on Abaqus Bio-mechanical simulation. The introduced package includes all the workshops within this package, along with several lessons in video format, to help you master the theory of biomedical simulation in Abaqus.
ADVANCED ABAQUS SUBROUTINE COURSE | FULL
ABAQUS PYTHON COURSE FOR SCRIPTING IN FEM SIMULATION | FULL
COMPREHENSIVE ABAQUS TUTORIAL FOR CIVIL ENGINEERS | FULL
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
Fatigue in composites refers to the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads or stress cycles over time. When a composite material is subjected to cyclic loading, small cracks or microdamage can form within the material, which may grow and lead to failure after a certain number of loading cycles. This is a significant consideration in the design and analysis of composite structures, especially in applications subjected to repeated stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering.
In one of our other packages, we have used the UMAT subroutine in Abaqus to simulate fatigue in composites in two-dimensional space. The current project is more comprehensive, as it addresses composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D spaces. So you can use it for the simulation of both shells and solids. In this project, you will first become familiar with simulating composite fatigue in 2D space using the Abaqus UMAT subroutine. Then, we will provide a complete UMAT code along with Abaqus files for extending the simulation to 3D space, enabling the 3D simulation of composite fatigue in Abaqus.
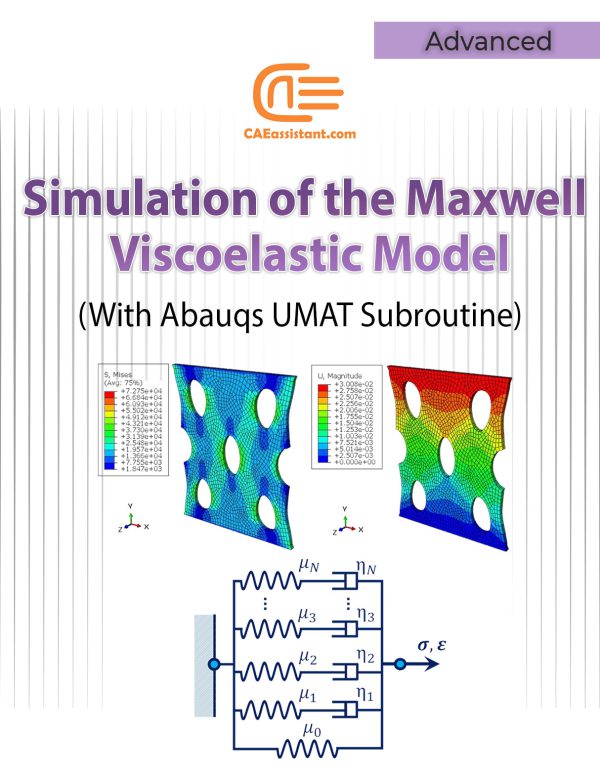
Simulation of the Generalized Maxwell Viscoelastic Model using UMAT Subroutine
This research presents a precise three-dimensional mechanical response of viscoelastic materials, such as polymers and elastomers, using the generalized rheological Maxwell viscoelastic model (considering the five Maxwell elements). That is to say, we implement the Maxwell model of viscoelasticity using the UMAT subroutine for the Abaqus standard solver. To clarify, using the concepts in this tutorial, you can implement the model for any N-Maxwell elements, using the viscoelastic Maxwell model.
The Maxwell viscoelastic model is appropriate for qualitative and conceptual analysis, but the single Maxwell element is not sufficient to describe the behavior of elastomers and polymers. For a more precise definition of these materials, the generalized Maxwell viscoelastic model is used. In the generalized Maxwell viscoelastic model, N piece of Maxwell elements and a single spring (the Hooke-element) are assembled in parallel. This tutorial, by customizing the UMAT subroutine to simulate flexible samples behavior, contributes to the advancement of viscoelastic materials design and analysis.
Essential Abaqus Training for Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Techniques
This beginner-friendly Abaqus course offers a complete guide to mastering finite element simulations through step-by-step tutorials and practical workshops. It covers essential topics such as Abaqus/CAE basics, finite element theory, composite material simulation, and thermal and impact analyses. Advanced sections delve into UMAT/VUMAT subroutines and Python scripting, equipping users with skills to automate workflows and solve complex engineering problems. Workshops include real-world examples like cantilever beams, forming processes, and fracture simulations. Perfect for engineering students and professionals, this course helps you build a solid foundation in Abaqus and expand your simulation capabilities.
Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation with Scripting in Abaqus
This Package offers a comprehensive tutorial on using Abaqus for Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation. To do so, it combines theoretical knowledge with practical application in Finite Element Method (FEM) simulations. The package guides users through both detailed lessons and interactive workshops. In fact, it focuses on developing 2D Fretting-Fatigue models in Abaqus with three core areas: model creation with exclusively designed meshing methodologies, the development of custom Field Outputs for detailed analysis, and automated parameter selection and post-processing through Python scripting.
Throughout the tutorial, participants master critical aspects of Fretting Fatigue Failure simulation. It includes basics from mesh refinement techniques and step control optimization to complete workflow automation. The program distinctively integrates command prompt operations for extracting Field Outputs and modifying simulation parameters. For example, we can refer to the Coefficient of Friction (CoF). Users gain practical experience in creating robust models while understanding the fundamental principles of the Fretting Fatigue Failure phenomenon.
Upon completion, participants will acquire the skills to independently develop and analyze Fretting Fatigue failure simulations. Moreover, they can automate post-processing tasks, and implement custom analysis parameters for precise fatigue prediction in mechanical systems.
Domino Effect Simulation in Abaqus | With a Review of Contact Definition Methods in Abaqus Explicit
This project focuses on the domino effect simulation with Abaqus CAE, a widely recognized finite element program. The domino effect refers to a chain reaction where one event triggers a series of similar events. It often leads to larger and unpredictable consequences. The project highlights the challenges of defining contact between components in Abaqus, a crucial aspect of domino effect simulation. The provided video explains the step-by-step modeling process. However, since one of the key challenges in this topic is defining contact, we have also attached a separate PDF. It covers defining contact in Abaqus Explicit. It includes its formulations and methods. The PDF will provide you with a better understanding of the modeling process. You can also apply it to model other problems.