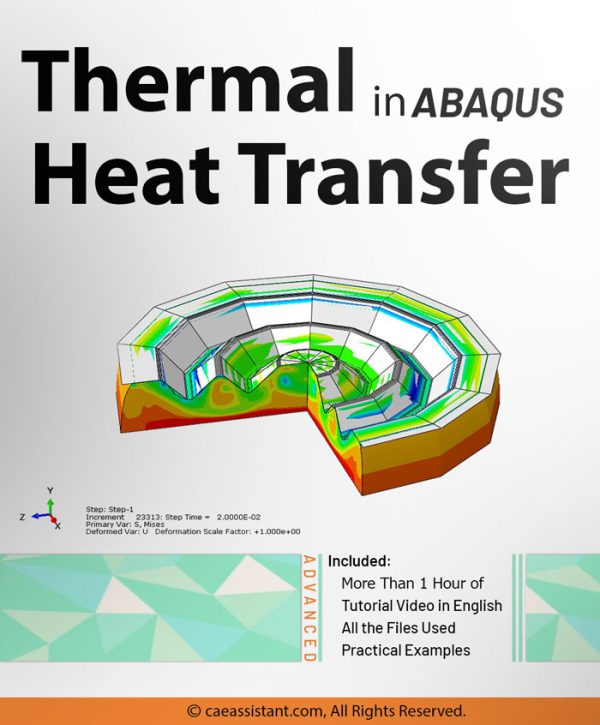
Heat Transfer
Thermal Heat Transfer in Abaqus
This package is related to Thermal Analysis in Abaqus. This package helps Abaqus users to simulate professionally.
In general, Abaqus can solve the following types of heat transfer problems (For thermal and thermo-mechanical problems):
- Uncoupled heat transfer analysis
- Sequentially coupled thermal-stress analysis
- Fully coupled thermal-stress analysis
- Adiabatic analysis
Analysis of Heat Transfer in Abaqus
This Product Is No Available. Go to the below product: