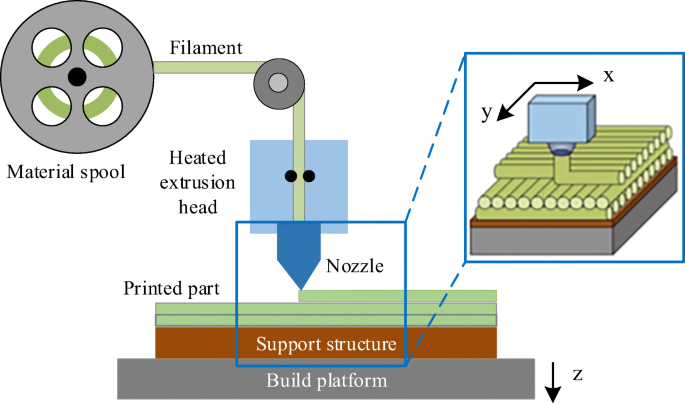
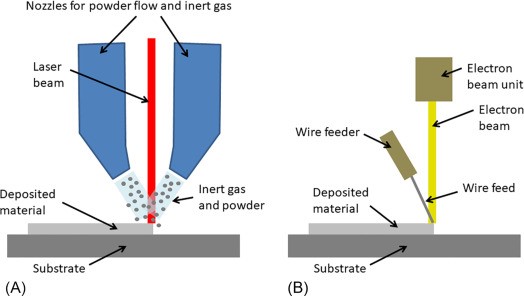
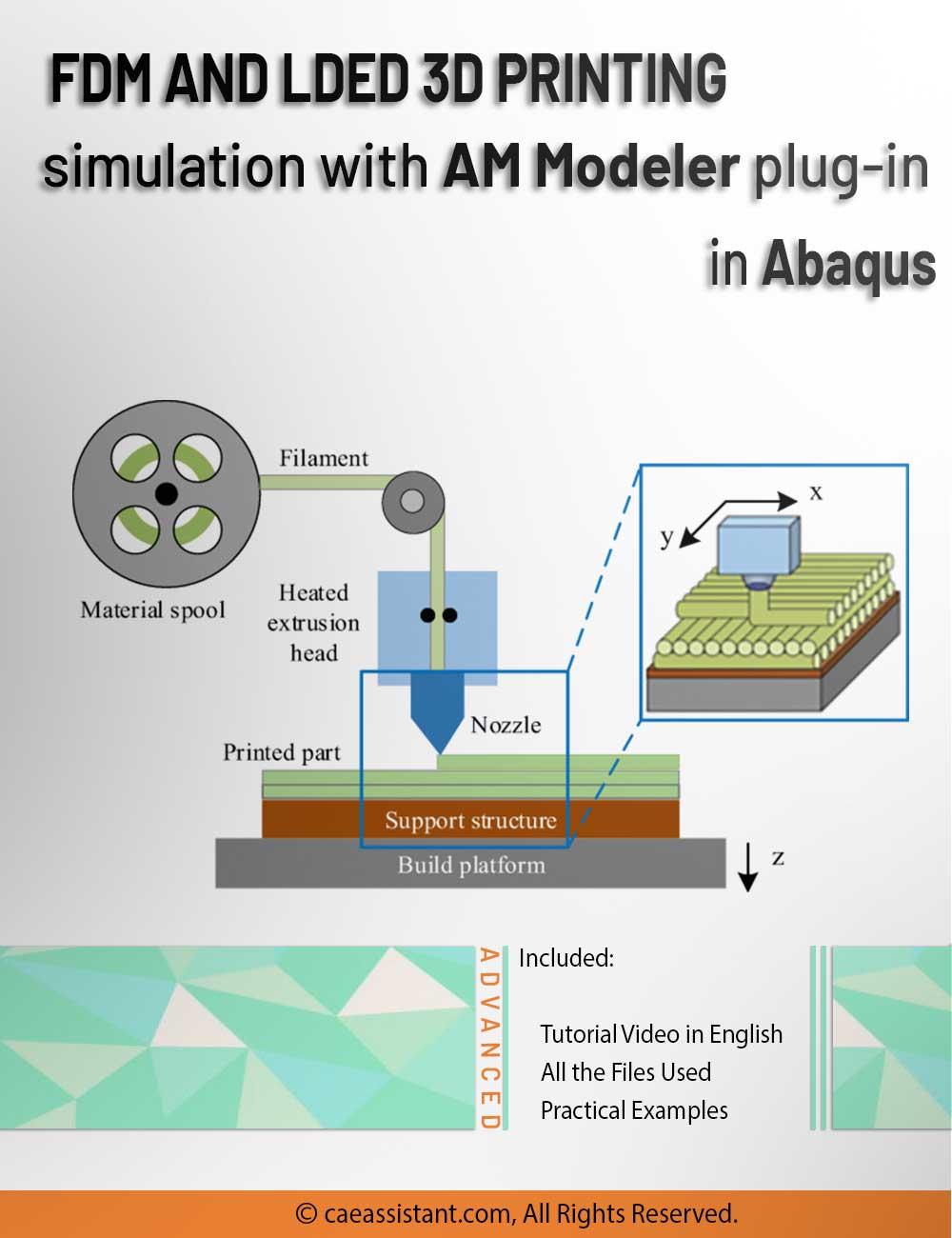
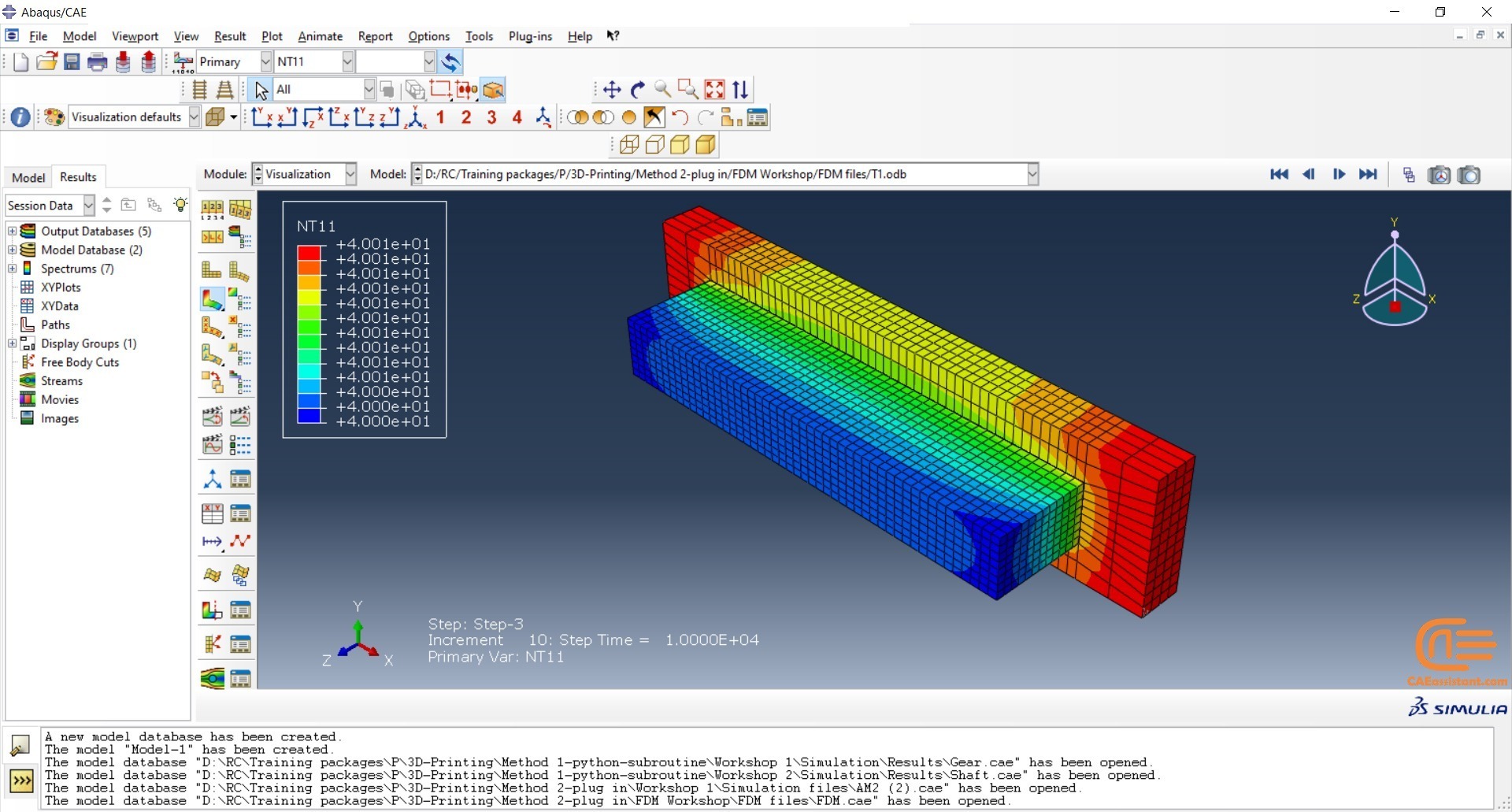
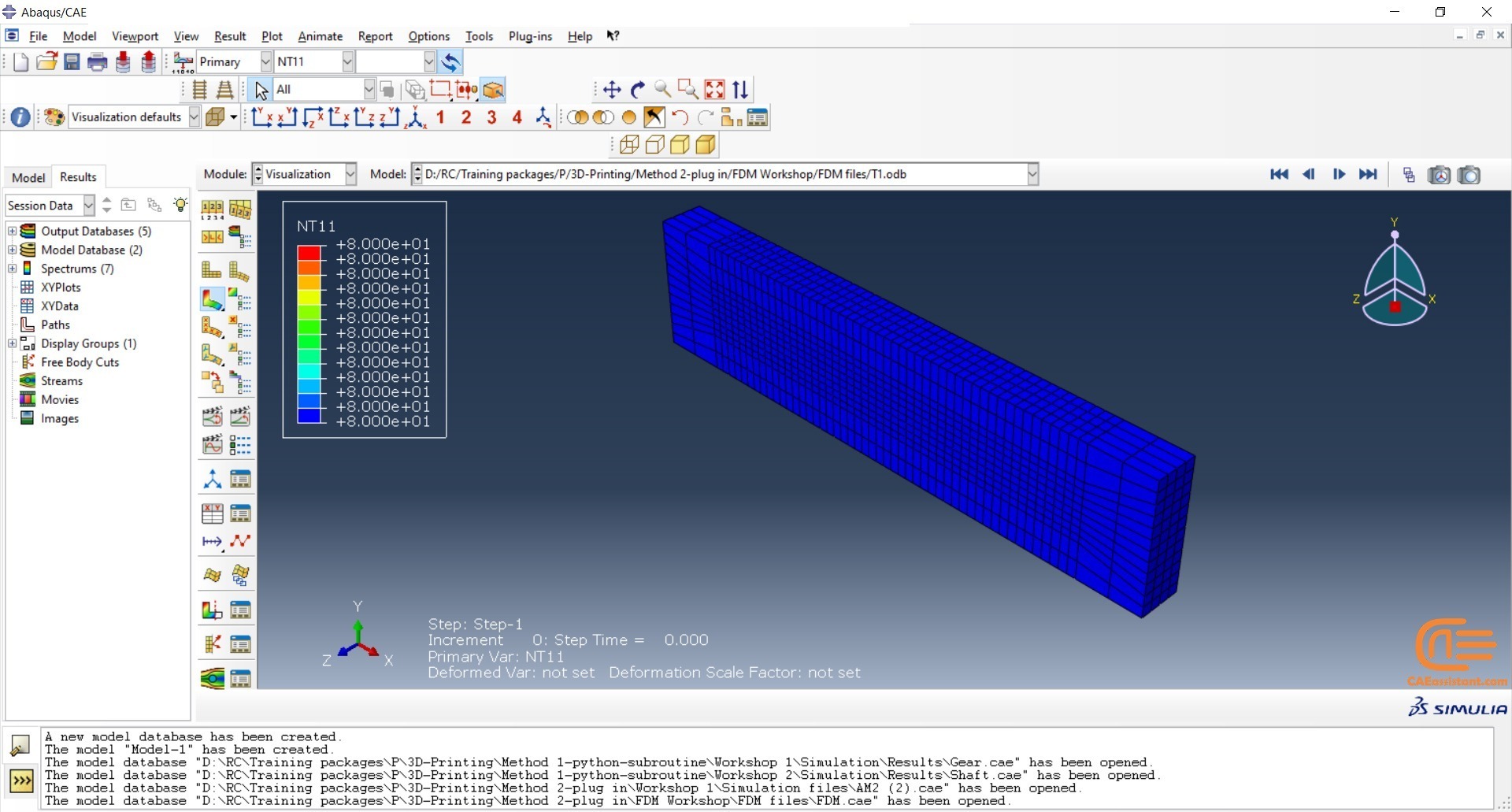
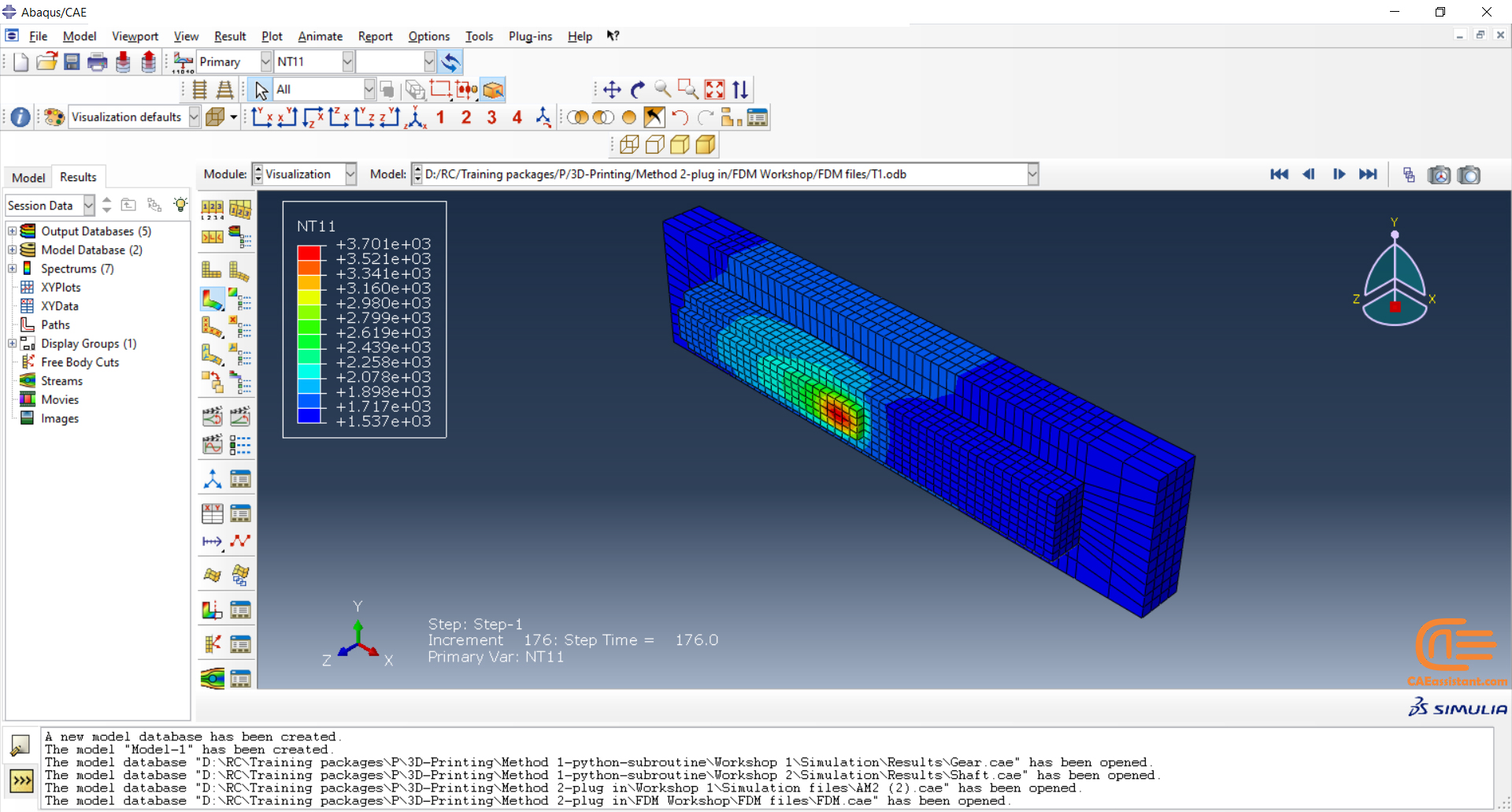
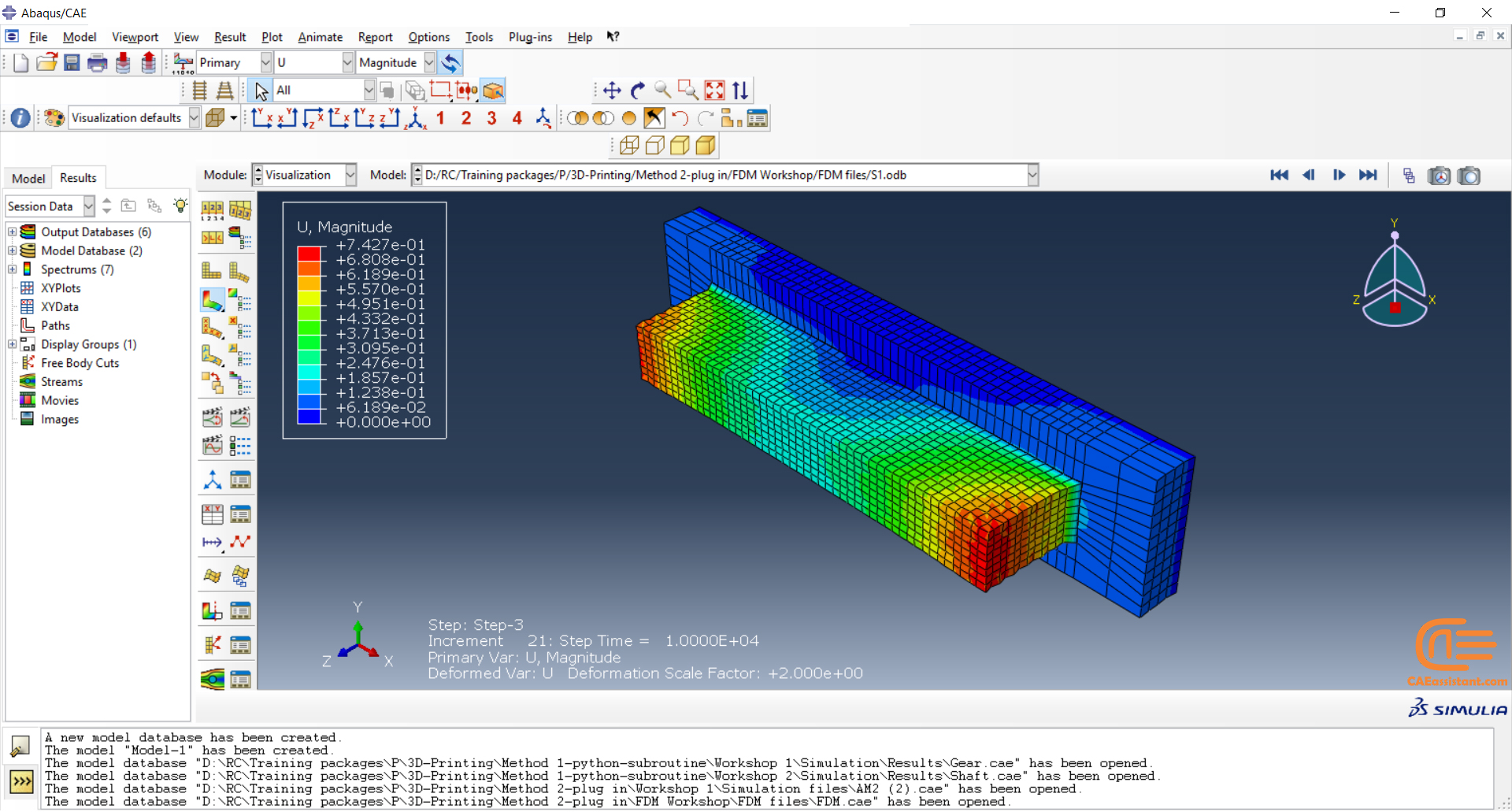
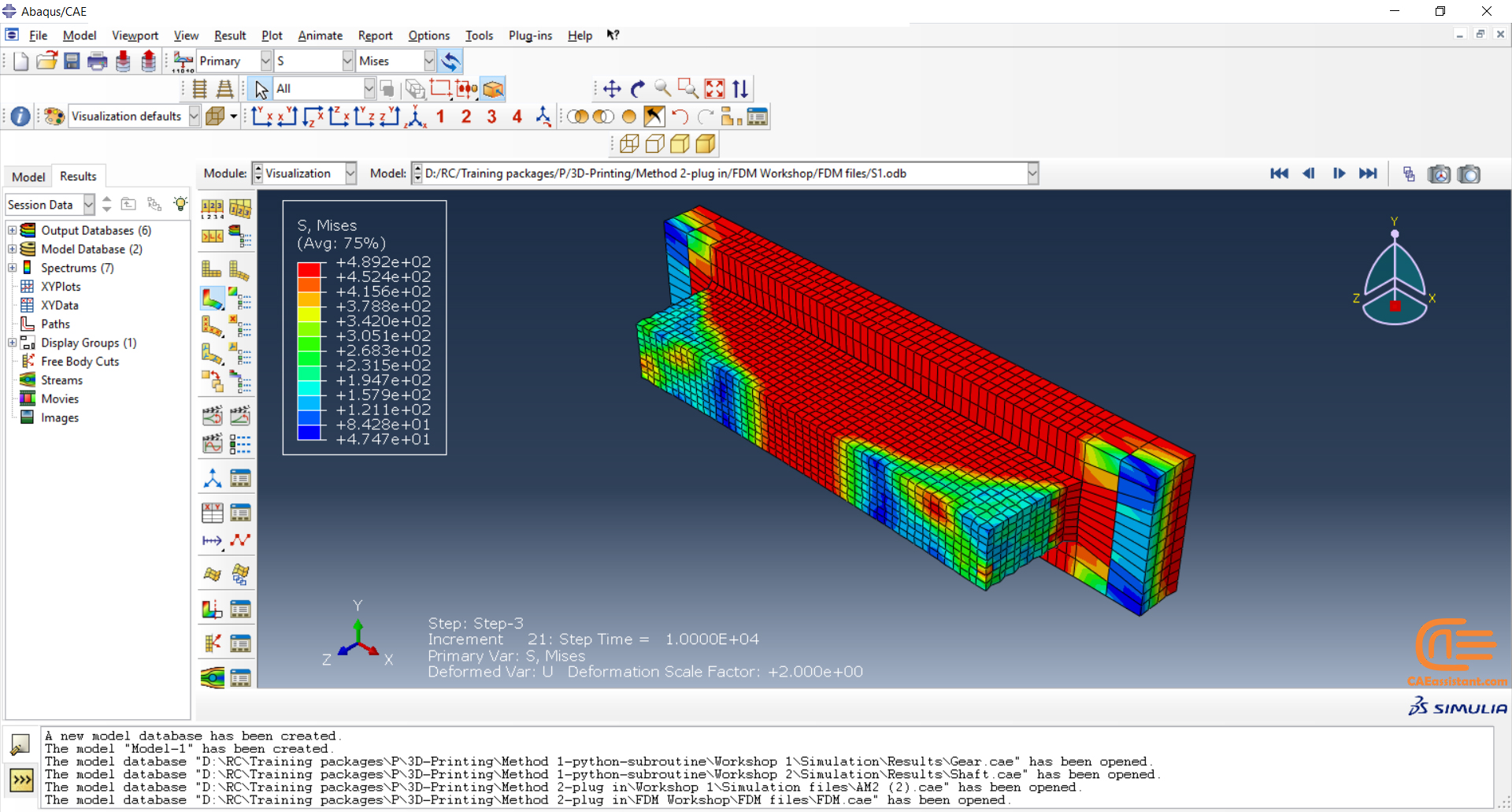
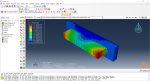
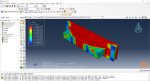
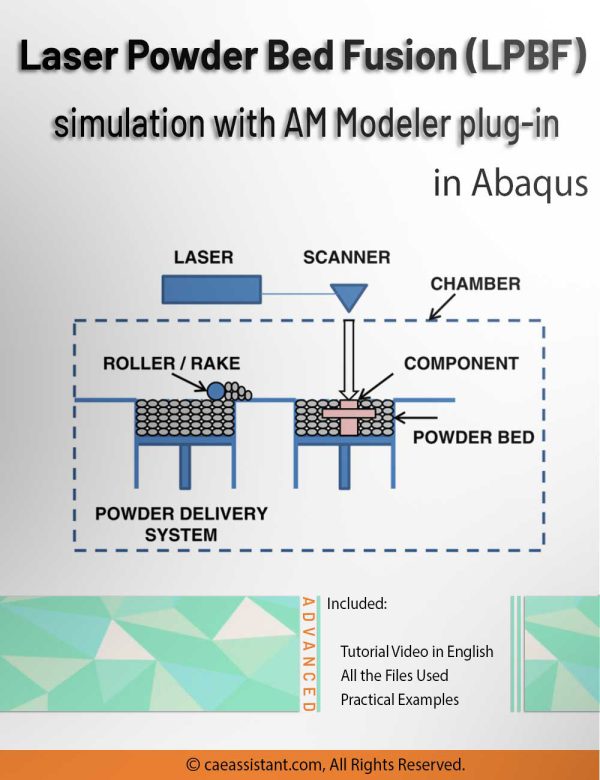
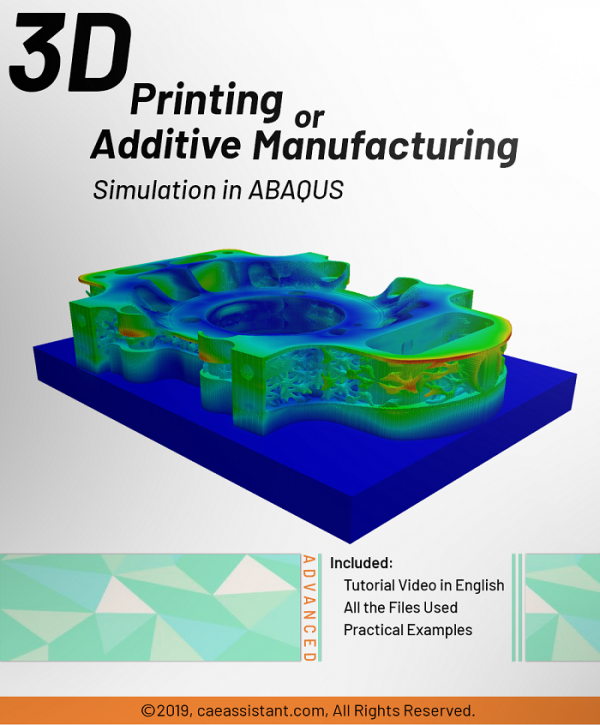
Fused Deposition Modeling process (FDM) is one of the most common methods in 3D printing, where thermoplastic material is melted and deposited layer by layer to create an object. FDM simulation is valuable for predicting how printed parts will behave under different conditions, allowing engineers to detect issues early and improve designs efficiently before production.
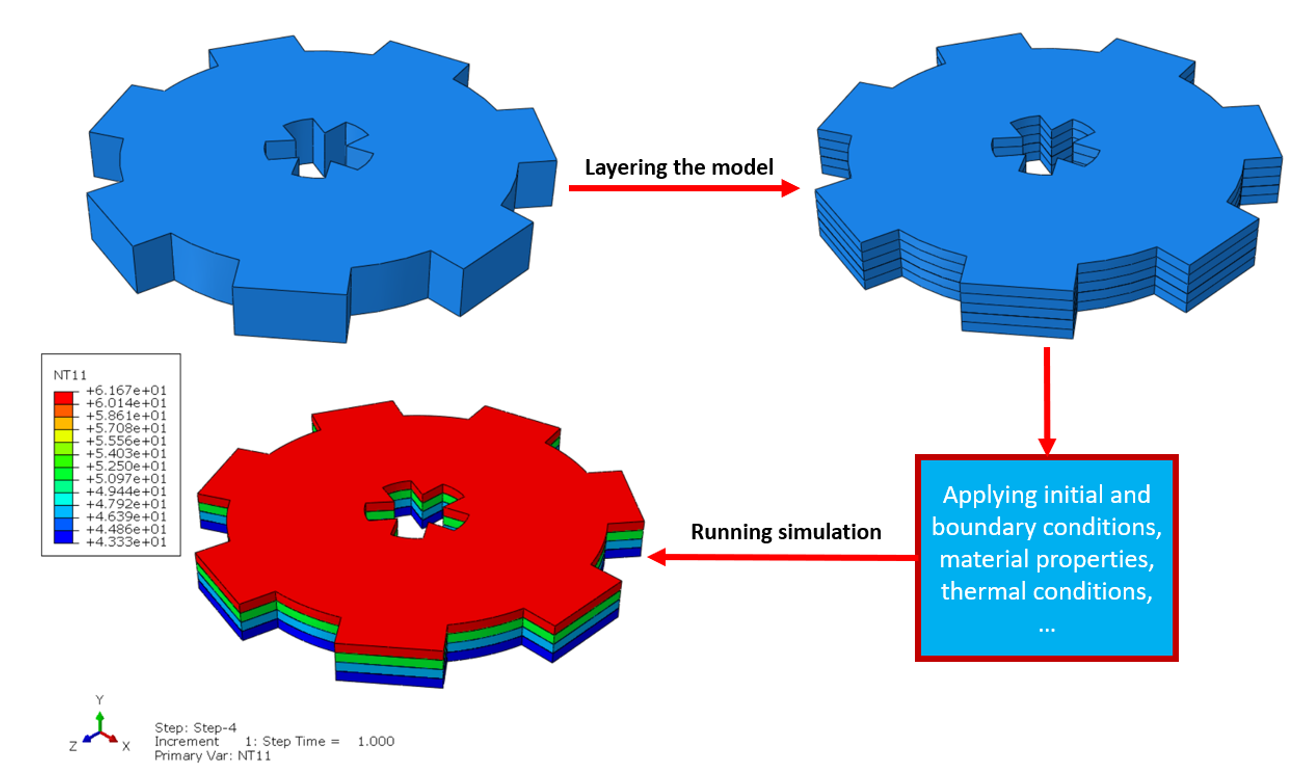
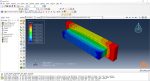
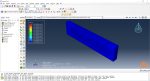
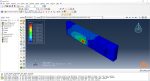
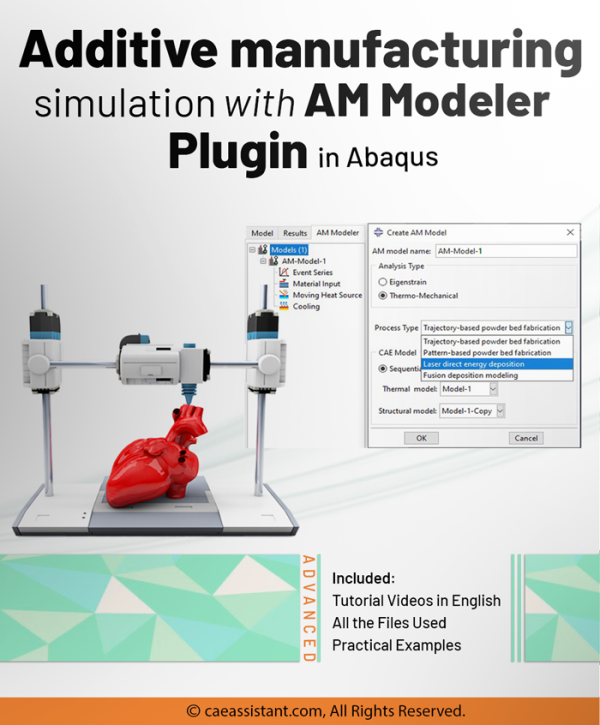
In Abaqus, FDM simulation involves creating a detailed virtual model that replicates the printing process, layer by layer. The AM Modeler plug-in in Abaqus helps streamline this by offering tools to define key aspects like event series, material inputs, and heat sources. With features for precise control over material deposition and element activation, users can simulate the heat and mechanical behaviors as each new layer cools and stabilizes. This level of control provides a realistic view of the printing process and helps refine designs to match physical performance.
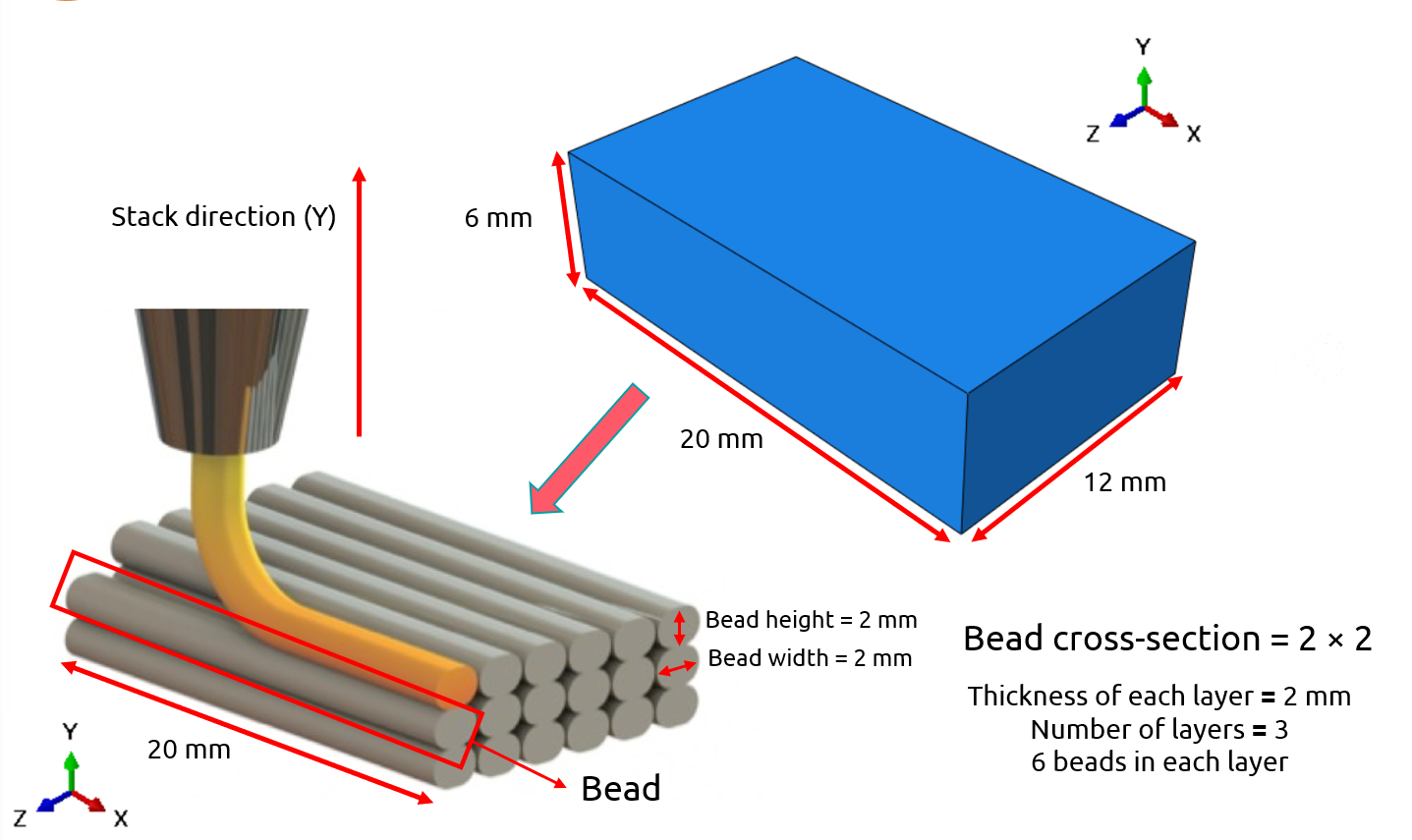
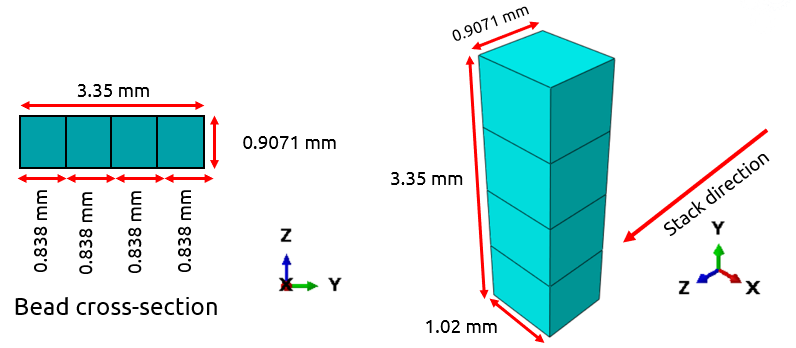
This blog will guide you through the essentials of setting up FDM simulation in Abaqus, covering topics like mesh size, bead dimensions, and event series configuration. You’ll learn how to define nozzle speed, select heat sources, and apply cooling settings for accurate temperature and material flow control. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to perform reliable FDM simulations for complex 3D printing projects in Abaqus.





Ishita –
This training package provides a concise and practical introduction to simulating 3D printing in Abaqus. One question that comes to mind is: Does the package cover any specific considerations or techniques for optimizing the printing process to improve the quality and accuracy of the printed objects?
Experts Of CAE Assistant Group –
I’m so glad we could meet your expectations! Thank you for your kind words. We’re dedicated to providing excellent service, and it means a lot to know that we succeeded in making you happy