LPBF Printing Introduction
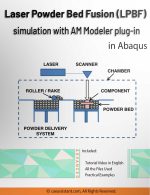
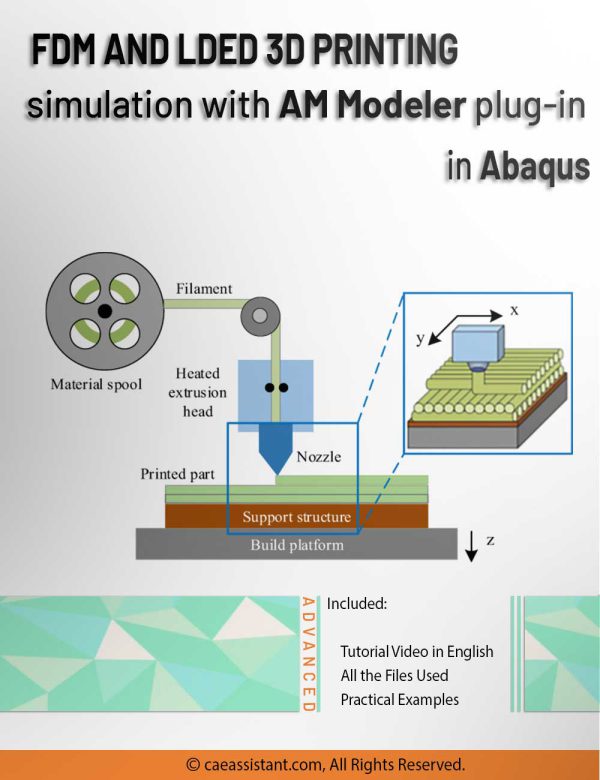
The Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) method is a 3D printing technique that utilizes a high-powered laser to melt and fuse metal powders layer by layer. In LPBF Printing, a layer of metal powder is spread over a build platform using a roller, and a laser scans the powder, melting and fusing it according to the 3D model. The platform is then lowered, and this layer-by-layer process continues until the object is fully formed.
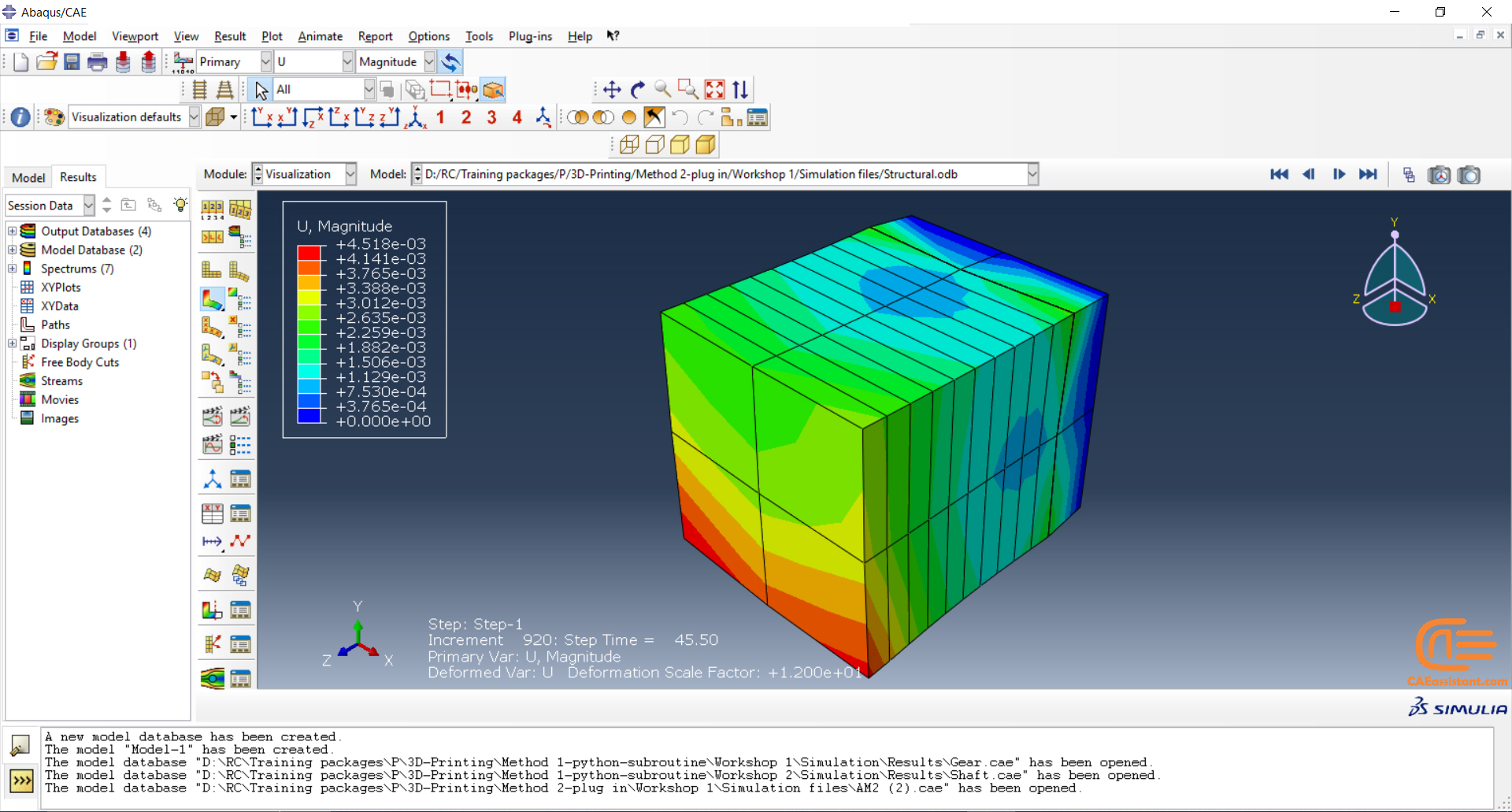
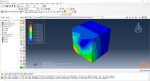
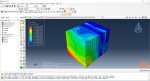
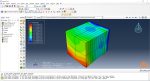
Workshop: Sequential thermomechanical analysis of a simple cube using the trajectory-based method with the AM plug-in for Laser Powder Bed Fusion 3D printing
In this workshop, the laser powder bed fusion simulation will be taught. the geometry of the model and layer details are discussed. Following that, the required material properties and information about the roller and laser beam, including their speeds and “Event series” data, are presented. Boundary conditions are explained, and the modeling process in Abaqus begins. First, modeling is performed using Abaqus/CAE, and then the necessary inputs for the simulation, such as “Event series” data, are added via the AM Modeler plug-in. Two analyses must be conducted: thermal analysis and structural analysis. Finally, the results are analyzed and discussed. This simulation is conducted using an older version of the AM Modeler plug-in.
What is additive manufacturing or 3D printing?
Additive manufacturing or 3D printing refers to the process of creating a three-dimensional object using a computer-aided design (CAD) model or digital 3D model. This process involves adding layers of material on top of each other until the final product is formed. It can be accomplished through various methods where materials are joined, deposited, and solidified under computer control. The materials used can include plastics, liquids, or powdered substances that are fused together. A comprehensive description of 3D printing and its modeling in Abaqus is provided in this training package.
Simulation of 3D printing in Abaqus
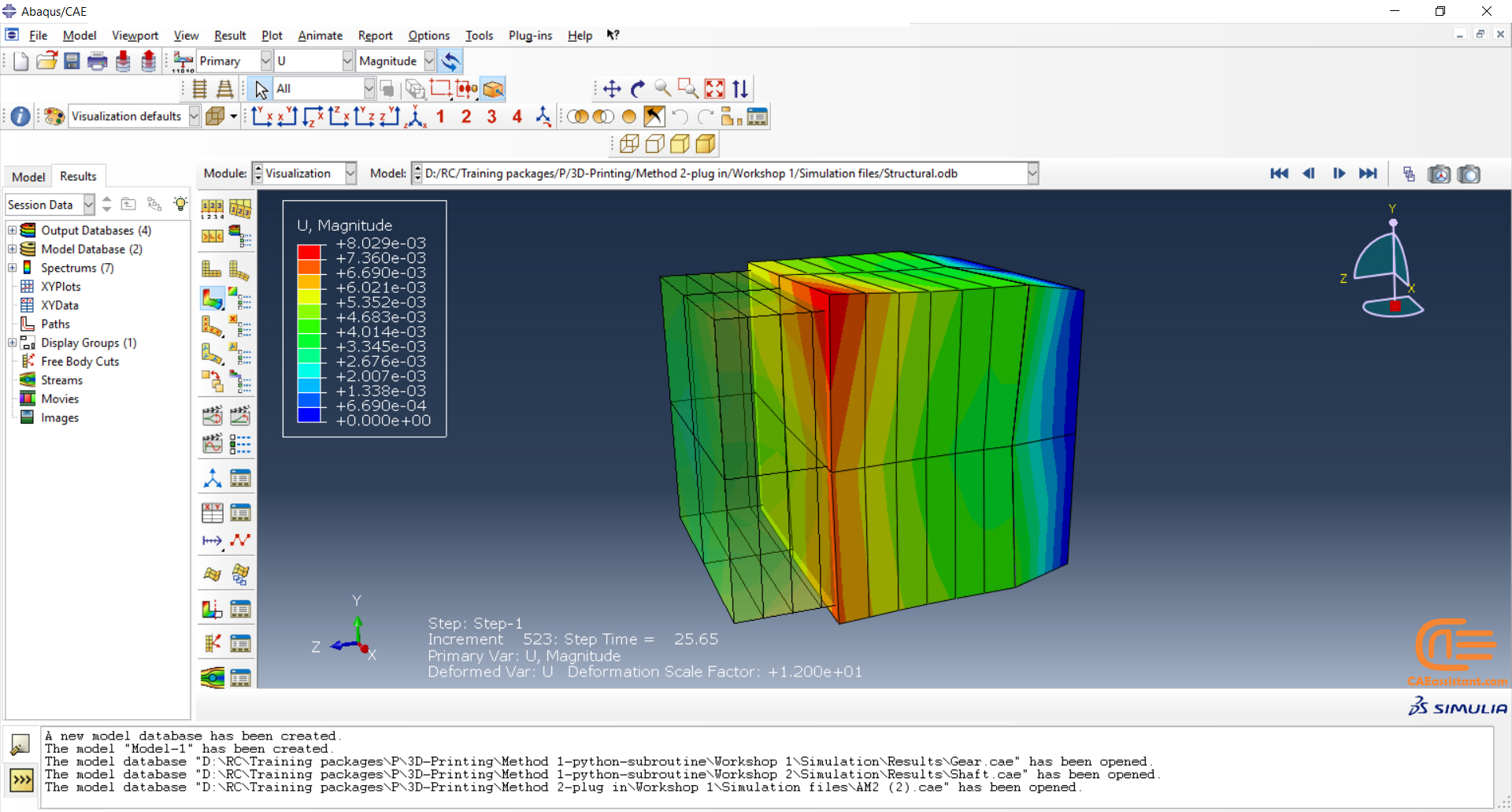
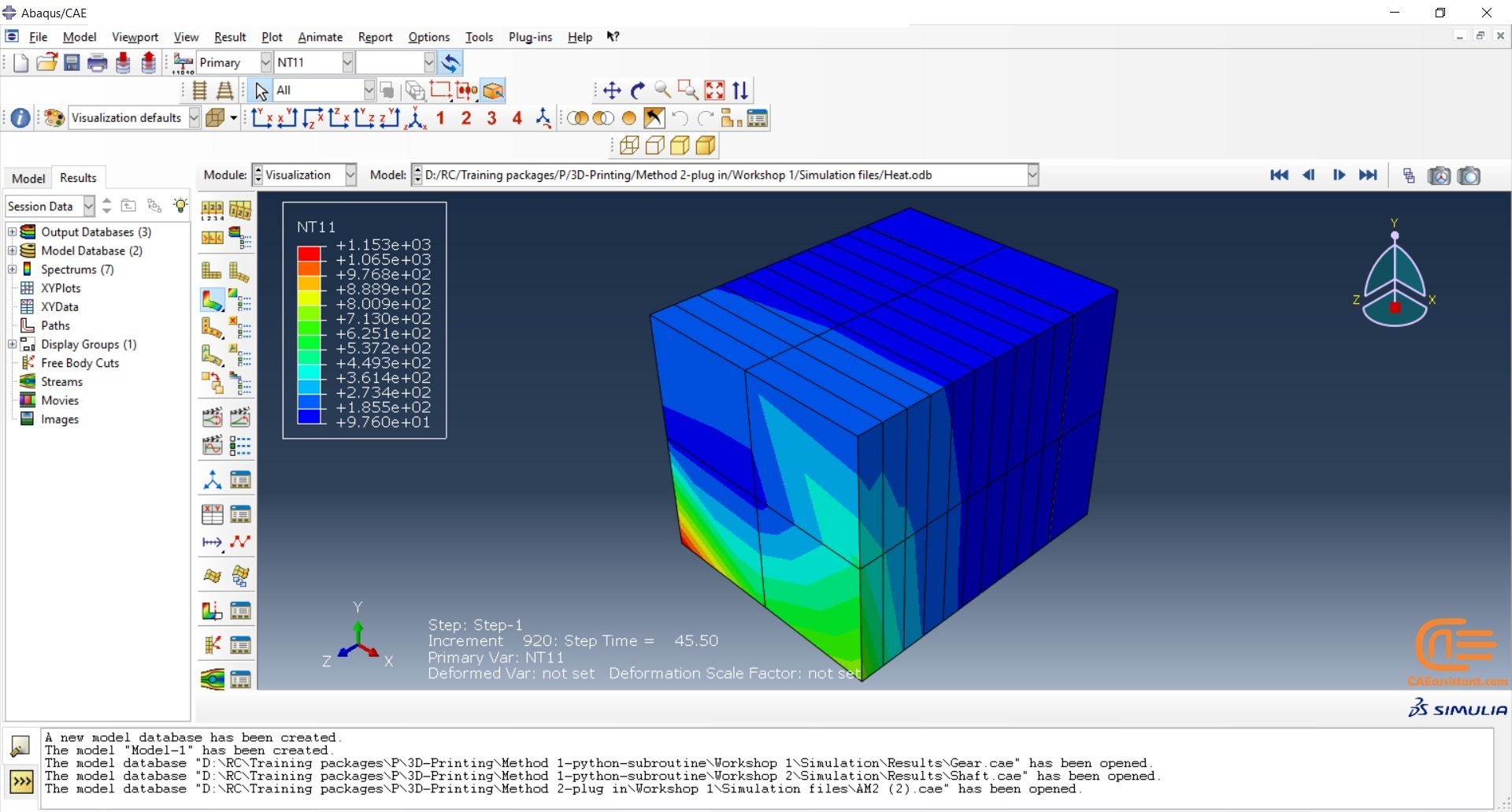
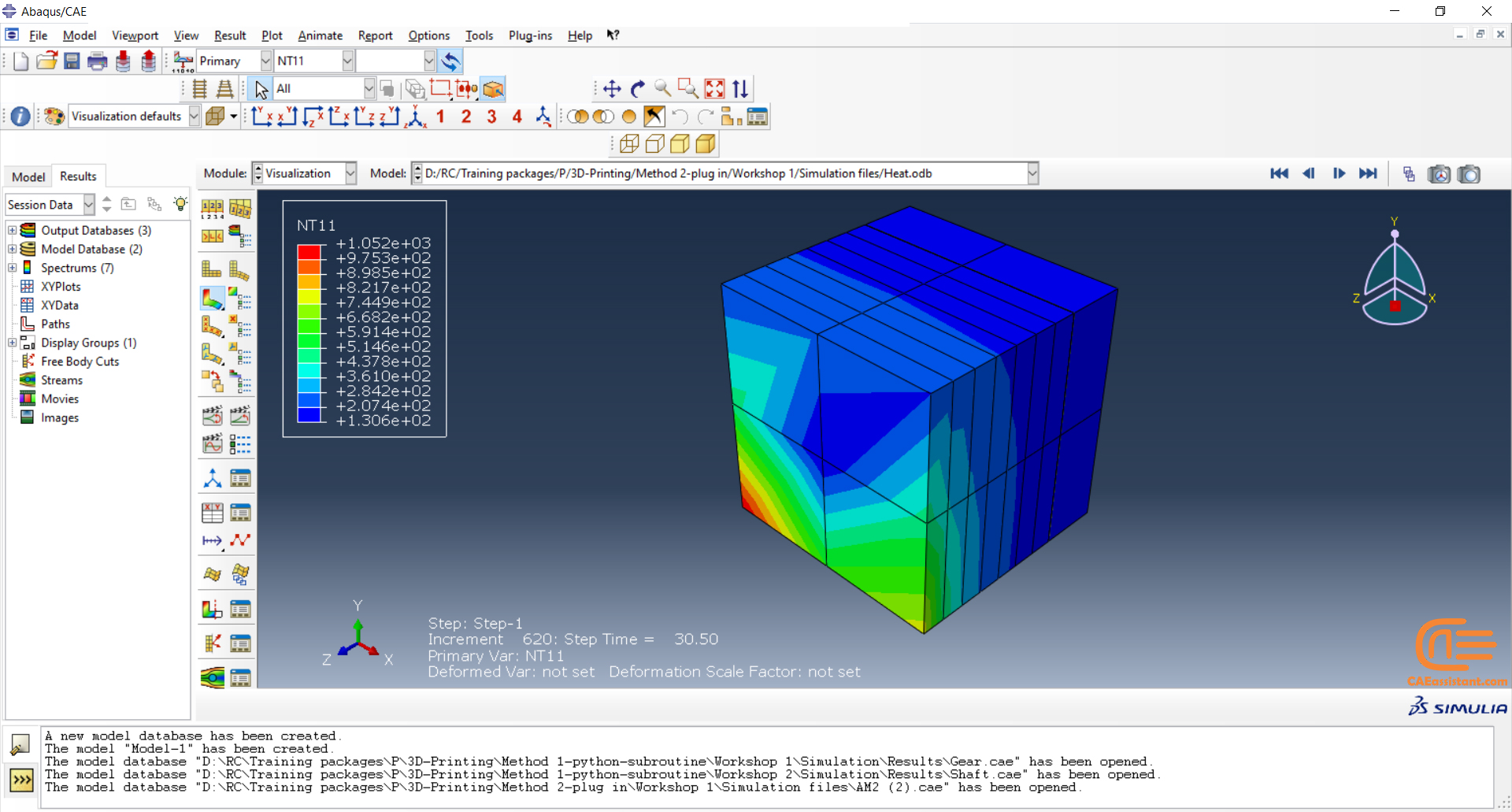
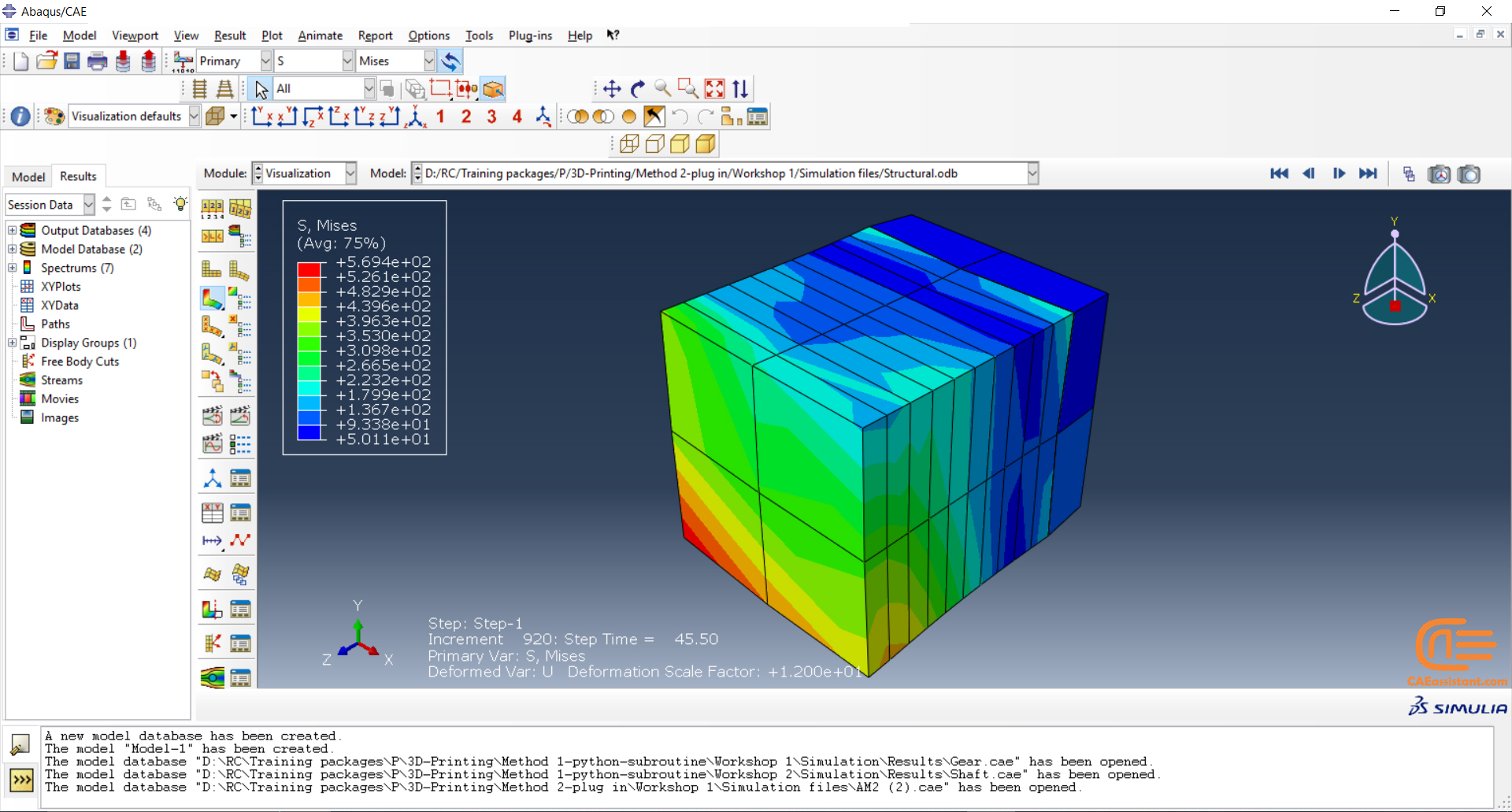
Why do we need to simulate 3D printing in Abaqus? The reasons are similar to other simulations. It allows us to examine residual stresses, temperature and thermal conditions, deflection in the model, and more. Additionally, it helps us determine if the machine settings are suitable for our model’s conditions before printing, thus avoiding unnecessary costs. Factors such as material properties and temperature need to be considered.
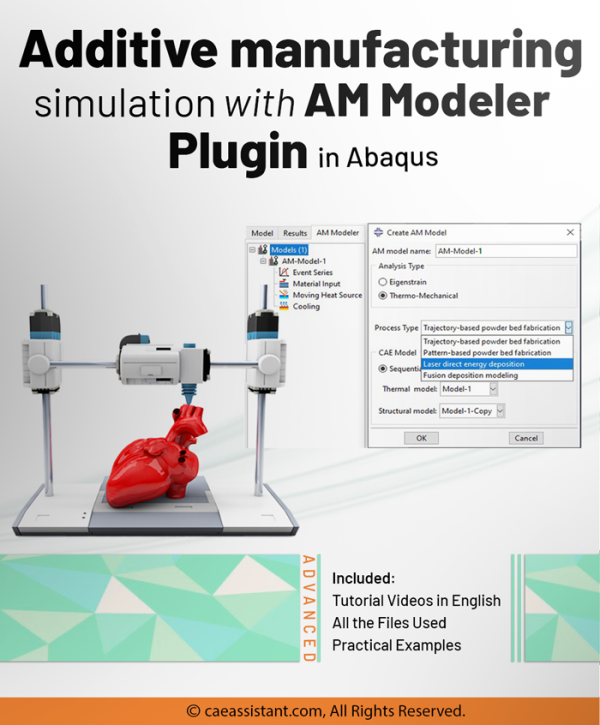
This training package on 3D printing in Abaqus will teach you how to perform this simulation using AM Modeler plug-in (old version). The method utilizes the ADM plug-in developed by Dassault Systemes to simulate the 3D printing process.

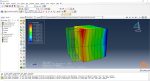
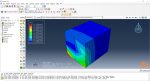













Miller –
The training package follows a logical structure, starting with an introduction to additive manufacturing and gradually progressing to the specific simulation methods in Abaqus. The inclusion of a workshop towards the end helps consolidate the knowledge gained from the previous sections. The flow of information is clear and coherent. thanks CAEassistant group.