Abaqus Crack Growth | Practical Examples
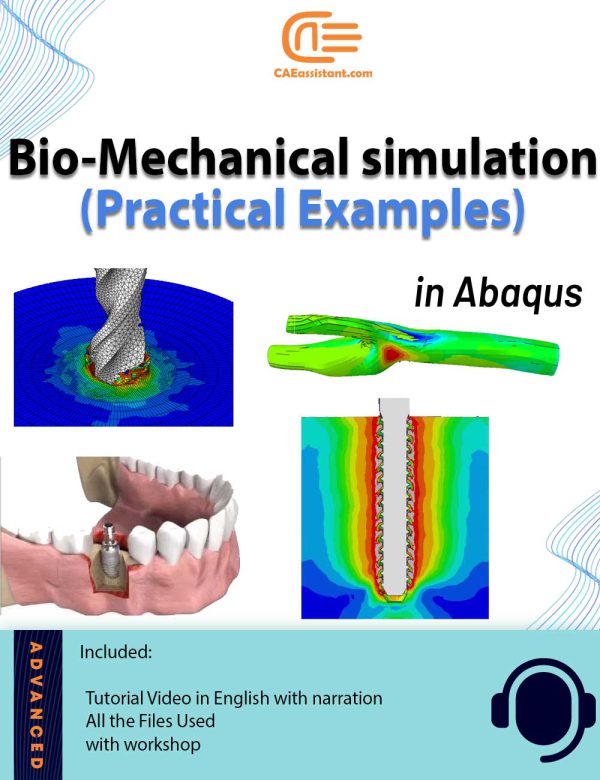
Bio-Mechanical Abaqus simulation | Practical Examples
This package offers multiple practical examples on biomechanical simulations using Abaqus, covering a range of applications from dental to orthopedic and cardiovascular analyses. The workshops delve into finite element method (FEM) simulations, exploring static loading on human teeth, crack growth in bones under bending, bone drilling, and the behavior of titanium foam implants. Each tutorial emphasizes the importance of precise modeling and meshing techniques, utilizing dynamic explicit procedures, Johnson-Cook material models, and various contact and boundary conditions to simulate realistic biomechanical behaviors. Additionally, the package includes fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulations for blood flow within coronary vessels, addressing both Newtonian and non-Newtonian models, and demonstrates the integration of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with structural analysis for enhanced accuracy. For more details on this topic, including explanatory videos covering the necessary formulation and theory in the form of a course, you can check out our full package on Abaqus Bio-mechanical simulation. The introduced package includes all the workshops within this package, along with several lessons in video format, to help you master the theory of biomedical simulation in Abaqus.
ABAQUS PYTHON COURSE FOR SCRIPTING IN FEM SIMULATION | FULL
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
Fatigue in composites refers to the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads or stress cycles over time. When a composite material is subjected to cyclic loading, small cracks or microdamage can form within the material, which may grow and lead to failure after a certain number of loading cycles. This is a significant consideration in the design and analysis of composite structures, especially in applications subjected to repeated stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering.
In one of our other packages, we have used the UMAT subroutine in Abaqus to simulate fatigue in composites in two-dimensional space. The current project is more comprehensive, as it addresses composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D spaces. So you can use it for the simulation of both shells and solids. In this project, you will first become familiar with simulating composite fatigue in 2D space using the Abaqus UMAT subroutine. Then, we will provide a complete UMAT code along with Abaqus files for extending the simulation to 3D space, enabling the 3D simulation of composite fatigue in Abaqus.
Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation with Scripting in Abaqus
This Package offers a comprehensive tutorial on using Abaqus for Fretting Fatigue Failure Simulation. To do so, it combines theoretical knowledge with practical application in Finite Element Method (FEM) simulations. The package guides users through both detailed lessons and interactive workshops. In fact, it focuses on developing 2D Fretting-Fatigue models in Abaqus with three core areas: model creation with exclusively designed meshing methodologies, the development of custom Field Outputs for detailed analysis, and automated parameter selection and post-processing through Python scripting.
Throughout the tutorial, participants master critical aspects of Fretting Fatigue Failure simulation. It includes basics from mesh refinement techniques and step control optimization to complete workflow automation. The program distinctively integrates command prompt operations for extracting Field Outputs and modifying simulation parameters. For example, we can refer to the Coefficient of Friction (CoF). Users gain practical experience in creating robust models while understanding the fundamental principles of the Fretting Fatigue Failure phenomenon.
Upon completion, participants will acquire the skills to independently develop and analyze Fretting Fatigue failure simulations. Moreover, they can automate post-processing tasks, and implement custom analysis parameters for precise fatigue prediction in mechanical systems.
Inherent strain method in Metal Additive Manufacturing simulation (using subroutines and Python scripting in Abaqus)
This tutorial package focuses on the Inherent Strain method in Abaqus, an efficient numerical approach to simulate Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) in metal additive manufacturing.
It addresses the high computational cost of detailed thermo-mechanical LPBF simulations by utilizing an agglomeration approach to transfer inherent strain from micro to macro-scale models. Through theoretical explanations and practical workshops, users will learn to implement the ISM method, including Dflux and USDFLD subroutine coding and Python scripting, for improved LPBF process simulation control. This product does not utilize AM plugins, making it ideal for users who prioritize transparency in calculation methods and flexibility in variable modification for similar models.Laser Assisted Machining (LAM): Modeling and Simulation in Abaqus/CAE
In this tutorial, a comprehensive discussion on modeling and simulation of laser assisted machining is presented. It includes building FEM-based models of machining, laser heating, and laser-assisted machining models in Abaqus/CAE. The finite element method (FEM) simulation is based on the coupled thermo-mechanical behavior. The package walks learners through building models that simulate the impact of laser heating on the workpiece. Detailed lessons cover constructing basic machining and laser heating models, setting boundary conditions like cutting speed and laser power, and writing subroutines such as DFLUX and VDFLUX to simulate laser heat sources. Additionally, learners will perform analyses to study temperature distribution, and stress-strain behavior. Through parametric analysis and comprehensive result evaluation, learners will gain a deep understanding of temperature distribution, stress behavior, and how laser heating can improve the machining process.
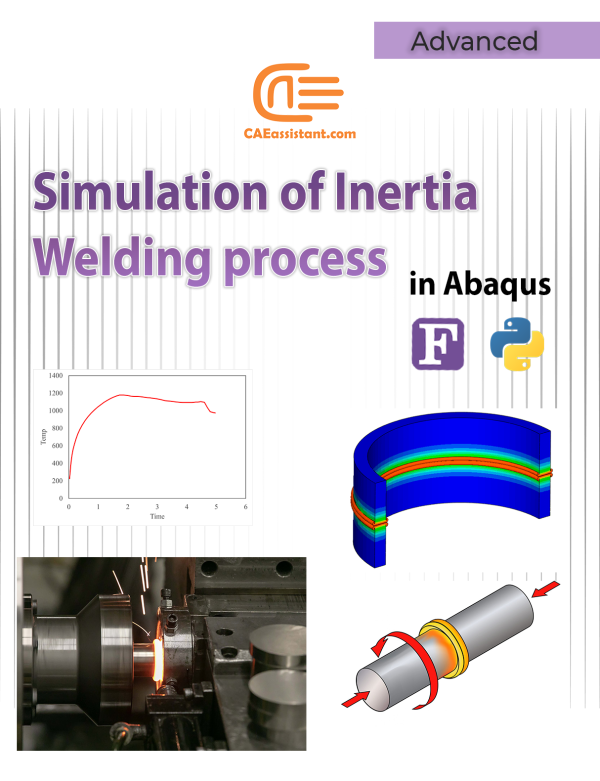
Simulation of Inertia Welding process in Abaqus | Fortran Subroutines and Python Scripts
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to simulating inertia friction welding process using Abaqus, a powerful Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tool. Inertia welding process, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, is a solid-state process that joins metal parts using kinetic energy. The simulation focuses on modeling frictional heating, temperature distribution, and material behavior through integrated Fortran subroutines and Python scripts. These scripts automate tasks such as remeshing and model generation, enhancing efficiency. Key steps include defining axisymmetric models, applying material properties, and simulating thermal and mechanical interactions during the inertia welding process. This guide equips researchers and engineers with a robust methodology for inertia welding simulation, to optimize welding parameters and analyze weld quality.
Brittle Damage in Abaqus | Brittle Cracking Abaqus
Brittle materials, such as ceramics, glass, and concrete, break or fracture easily under stress without extensive deformation. Unlike ductile materials, brittle materials snap suddenly, lacking the flexibility to rearrange their atomic structure under strain. These materials have low tensile strength but strong compressive resistance, making them vulnerable to brittle cracking Abaqus simulations when stretched or pulled.
Understanding brittle material damage is crucial in safety-critical fields like civil engineering, aerospace, and manufacturing, where unexpected fractures can lead to catastrophic failures. Simulations help engineers predict when and how brittle materials may break, guiding safer design choices. Brittle cracking Abaqus can be modeled using various methods, including the Johnson-Holmquist (JH) model, XFEM, and energy-based approaches, each suited to different types of loading conditions.
For dynamic, high-strain applications like impacts, the JH model is effective, particularly in Abaqus/Explicit with specific damage parameters. For general crack modeling, XFEM is versatile, allowing cracks to form naturally without predefined paths. The energy-based method is useful for slow-loading scenarios, defining an energy threshold for fracture initiation. Each method requires careful input of material properties, mesh refinement, and load conditions to reveal potential failure points and improve material performance in real applications.
A Comprehensive Tutorial for Soft Body Impact Composites Simulation
This comprehensive tutorial package focuses on simulating soft body impact composites on laminated composite materials using the Finite Element Method (FEM) in Abaqus. The course covers key topics such as soft body modeling, metal material modeling, composite material modeling, composite to composite interface modeling, metal to composite interface modeling, interaction between soft bodies and FML, interaction between layers, and Python scripting for parametric studies. Users will explore different material models and learn about impact failure mechanisms, including matrix failure, fiber failure, shear failure, and delamination. The course is structured into lessons that cover theoretical aspects, followed by hands-on workshops to model soft body impacts, apply material properties, and analyze post-processing results such as forces, displacements, and energy dissipation. It also includes an advanced section on Python scripting, enabling users to automate parametric studies for complex simulations. This package is ideal for engineers, researchers, and students looking to deepen their understanding of soft body impact phenomena and composite material behavior.
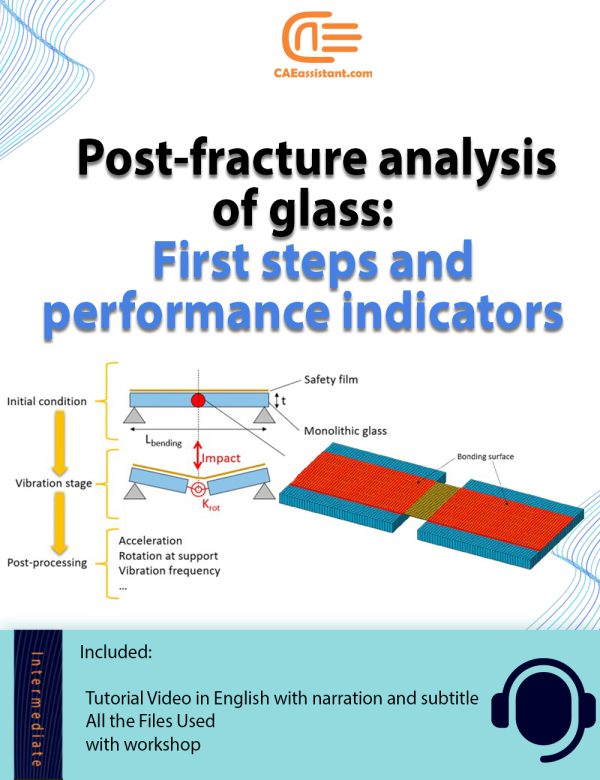
Glass Fracture Analysis with Abaqus | Post-Fracture
This tutorial explores a finite element method (FEM) simulation using Abaqus to analyze the post-fracture behavior of structural glass members retrofitted with anti-shatter safety films. In particular, it focuses on simulating and calibrating the vibration response of cracked glass elements under repeated impacts and temperature gradients, contributing to a comprehensive analysis of critical phenomena that take place in the post-fracture stage. This tutorial follows the methodology outlined in the research article “Effects of post-fracture repeated impacts and short-term temperature gradients on monolithic glass elements bonded by safety films”.
Key aspects include modeling glass fracture, assigning material properties, and defining boundary conditions to assess the vibration frequency and load-bearing capacity of cracked monolithic glass members. Additional topics cover basic concepts of dynamic identification techniques, definition of performance indicators for glass retrofit efficiency, and frequency sensitivity analysis of monolothic retrofitted glass elements under various operational and ambient conditions. The simulation results help quantify the expected contribution and residual strength of safety films in post-fracture scenarios, providing a robust framework for structural engineers to extend this investigation to other glass configurations.
This tutorial is ideal for users who want to understand FEM modeling in Abaqus and perform detailed simulations involving complex material interactions, with a focus on practical applications in glass retrofit technology.
ABAQUS PYTHON COURSE FOR SCRIPTING IN FEM SIMULATION
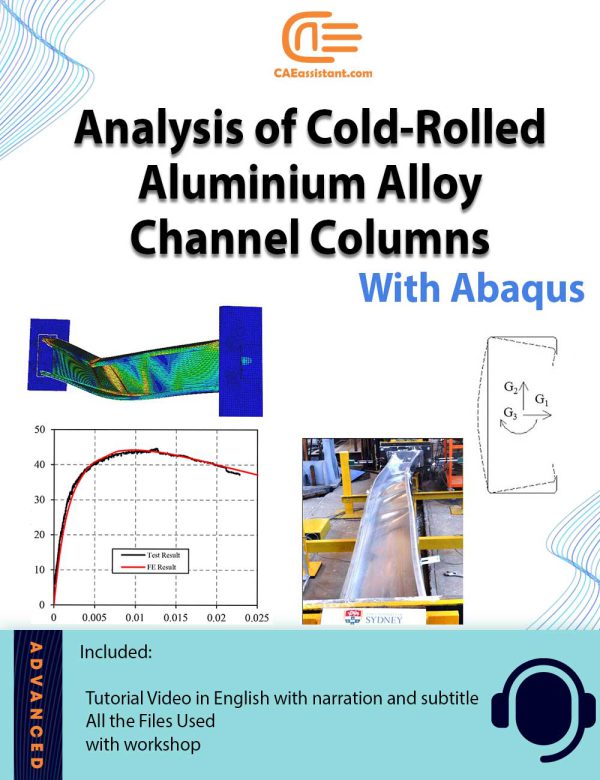
Analysis of Cold Rolled Aluminium Alloy Channel Columns With Abaqus CAE
Abaqus shaft slip ring simulation | Using Python scripts for parametric analysis
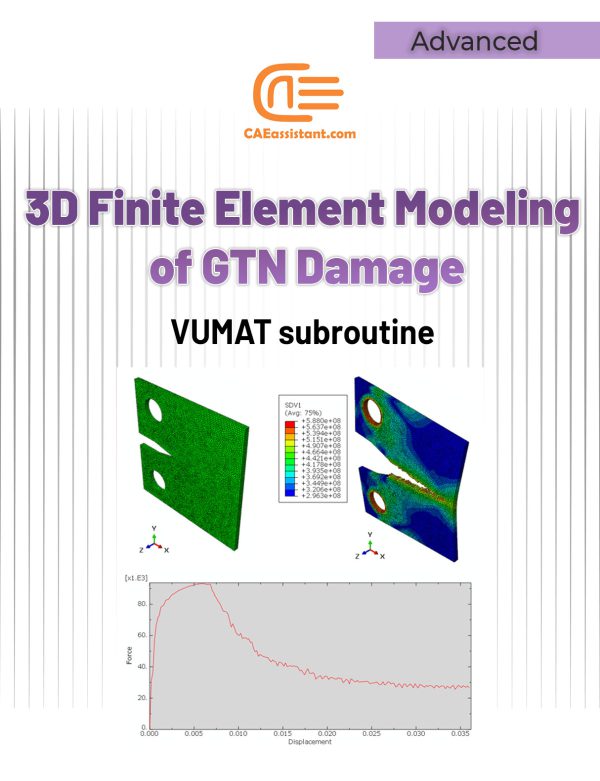
3D Simulation of Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) Damage Model
Abaqus User element tutorial | UEL advanced level
Theta Protection Creep Model | Turbine Blade Creep Life Accurate Prediction | Creep Failure in Turbine Blades
Creep is one of the most significant failure modes in many components where the working temperature and stresses are high for a prolonged period of time. Existing creep models in commercial analysis software like Abaqus are not adequate to model all stages of creep namely – primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. Theta projection method is a convenient method proven to predict all stages of creep, especially the tertiary stage where strain rates are high leading to internal damage and fracture. The aim of the project is to develop a user subroutine for Abaqus to model creep in components using the Theta projection method. The constitutive model for the Theta projection method based on the accumulation of internal state variables such as hardening, recovery, and damage developed by (R.W.Evans, 1984) is adopted to compile a Fortran code for the user subroutine. The user subroutine is validated through test cases and comparing the results with experimental creep data. Creep analysis of a sample gas turbine blade (Turbine Blade Creep) is then performed in Abaqus through the user subroutine and the results are interpreted.
Results of test cases validate the accuracy of the Theta Projection Method in predicting all primary, secondary, and tertiary stages of creep than existing creep models in Abaqus (Creep Failure in Turbine Blades). Results at interpolated & extrapolated stress & temperature conditions with robust weighted least square regression material constants show the convenience in creep modeling with less input data than existing models. The results of creep analysis not only predicted the creep life but also indicated the internal damage accumulation. Thus, creep modeling of components through the user subroutine at different load conditions could lead us to more reliable creep life predictions and also indicate the regions of high creep strain for improvements in the early stages of design.
Simulation of Pitting Corrosion Mechanism with Scripting in Abaqus
Dynamic Response of Rail Track Analysis Under a Moving Load
Railway tracks are subjected to moving loads of trains and this causes vibration and degradation of the track. The judgment of these vibrations is important to design the railway tracks. Therefore, the rail track analysis become important. The design involves the permissible speed of trains and the maximum axle load of the train. The model given here creates a 3D geometry of a railway track and applies a moving load in the form of a wheel. A user can change the speeds and the properties of the material including geometry as per their needs.