CFD
Airfoil simulation with different angles of Attack | Ansys fluent
Airfoils are a vital and important part of many industrial units. For example, in many kinds of rotary equipment such as gas turbines and wind turbines or compressors, airfoils play a vital role. Another usage of airfoils is in the aviation industry, which they used in airplane wings. The crucial parameters that are important in airfoils are the drag and lift forces or drag and lift coefficients. By using these parameters, we can design better airfoils to achieve greater lift coefficients and lesser drag coefficients. With this package, you learn airfoil simulation; how to design, mesh, and simulate an airfoil. Also, you learn how to link MATLAB to Ansys Fluent to change the geometrical constraints and boundary conditions automatically (airfoil simulation Ansys). You can use this method for your own optimization.
Mixing tank simulation with Ansys fluent(2D and 3D)
The mixing process is crucial and highly effective in various industrial applications. It finds application in industries such as food and cement manufacturing, among others. This course focuses on the implementation of mixing processes in both 2D and 3D spaces.
This course begins with designing the geometry with complete details. Next, we learn how to use Ansys Meshing software to mesh the geometry in detail and assess the mesh quality. Following this, we apply appropriate two-phase and turbulence models to simulate the process, allowing us to analyze the results. Additionally, we create animations of the process to visualize how the mixing process occurs.
FSI analysis in Abaqus
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) refers to the interaction between a deformable or movable structure and an internal or surrounding fluid flow. FSI simulations are vital for understanding and predicting the behavior of systems where fluid and solid components interact. These simulations enable engineers and researchers to study the effects of fluid forces on structures and vice versa.
FSI simulations are crucial in various fields, including aerospace, civil engineering, biomechanics, and automotive industries. They provide valuable insights into the performance, safety, and reliability of engineering systems. By accurately modeling the complex interactions between fluids and structures, FSI simulations can identify potential issues such as vibrations, instabilities, and structural failures.
In this package, you’ll learn simulating FSI in Abaqus within 3 workshops.
Blood Flow Analysis in Abaqus
Human blood is a vital fluid that circulates through the body, carrying oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells. Simulation of human blood is crucial for understanding cardiovascular diseases, hemodynamics, and therapeutic interventions. It enables researchers to study the complex behavior of blood flow, investigate disease mechanisms, and develop improved diagnostic and treatment strategies. This package contains three workshops that would help you simulate blood flow in vessels: “Human blood with coronary vessel Fluid Structure Interaction simulation in Abaqus”, “Blood and vessel FSI simulation using Abaqus-Co Simulation process”, and “Non-Newtonian blood flow Simulation in Abaqus”.
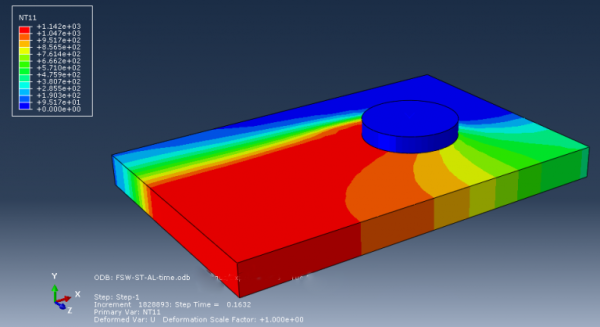
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Simulation in Abaqus
Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state joining process that utilizes a rotating tool to generate frictional heat, enabling the consolidation of materials without melting. FSW offers numerous benefits and is particularly valuable for welding challenging materials like aluminum alloys. It finds widespread applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and construction, providing enhanced strength, weight reduction, and structural integrity. FSW minimizes distortion, reduces the need for post-weld machining, and eliminates issues related to solidification and cooling. Simulations using Abaqus, a popular finite element analysis software, play a crucial role in optimizing FSW processes. Engineers can investigate process parameters, evaluate weld quality, predict residual stresses and distortions, and optimize weld designs through Abaqus simulations. These simulations enable cost-effective development, improved weld quality, reduced material waste, and enhanced productivity in industrial applications. In this package, you will learn how to simulate FSW simulations in a variety of examples with different methods.
Script to transfer load from CFD to structural model in Abaqus
FEA offers various loading types, such as force, pressure, and temperature, which can be applied to different parts of an object, such as points, surfaces, edges, nodes, and elements. Therefore, applying accurate loading conditions on these features is necessary for reliable simulation results and the safe design of structures. Sometimes, the loading conditions are obtained by another analysis, such as CFD, and need to be transferred and applied to the structural model for the structural analysis; during this transfer, the loads might not be appropriately applied to the model, especially when the loads are complicated like the pressure profile of a space rocket. So in this package, a Python script is presented to solve this issue and transfer the loads properly to the structural model.
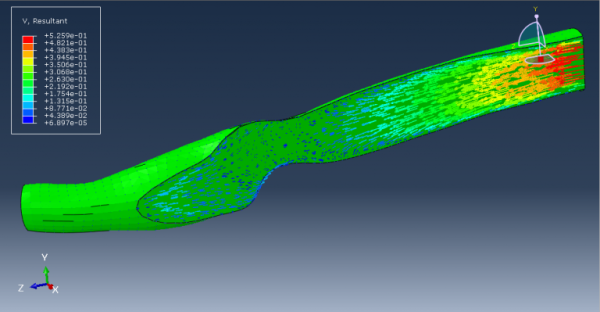
Abaqus CFD Analysis
Fluid-Structure Interaction also known as FSI is a multiphysics problem where the fluid and structure are coupled. The fluid flow can cause the structure to deform, and the deformation of the structure can affect the flow. So when you want to design something, you need to know how the structure will deform and how that deformation affects the flow. Common examples of FSI analysis are airplanes, cars, spacecrafts, and buildings. Other examples like junctions in piping systems, or the human circulatory system. CFD is a branch of research that uses numerical methods to solve the mathematical equations governing fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena. In Abaqus, you can model both methods. In this package, we present to you three workshops to get you started with Abaqus CFD and FSI: “Using Abaqus CFD methods, examining heat mixing and reverse flow characteristics in a T-junction”, “impact of air velocity over the short column”, “simulate fluid structure interaction on an aluminum body with a flexible tail in Abaqus”.