Abaqus Crack Growth | Practical Examples
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
Fatigue in composites refers to the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads or stress cycles over time. When a composite material is subjected to cyclic loading, small cracks or microdamage can form within the material, which may grow and lead to failure after a certain number of loading cycles. This is a significant consideration in the design and analysis of composite structures, especially in applications subjected to repeated stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering.
In one of our other packages, we have used the UMAT subroutine in Abaqus to simulate fatigue in composites in two-dimensional space. The current project is more comprehensive, as it addresses composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D spaces. So you can use it for the simulation of both shells and solids. In this project, you will first become familiar with simulating composite fatigue in 2D space using the Abaqus UMAT subroutine. Then, we will provide a complete UMAT code along with Abaqus files for extending the simulation to 3D space, enabling the 3D simulation of composite fatigue in Abaqus.
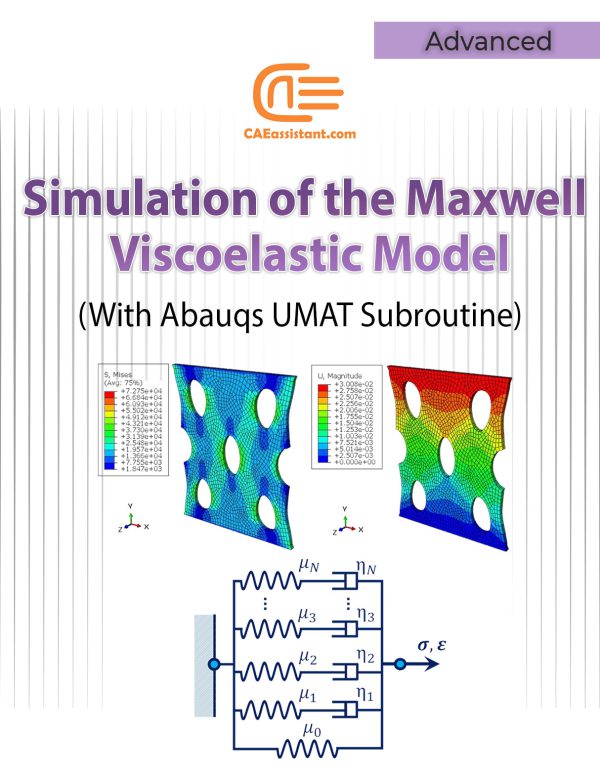
Simulation of the Generalized Maxwell Viscoelastic Model using UMAT Subroutine
This research presents a precise three-dimensional mechanical response of viscoelastic materials, such as polymers and elastomers, using the generalized rheological Maxwell viscoelastic model (considering the five Maxwell elements). That is to say, we implement the Maxwell model of viscoelasticity using the UMAT subroutine for the Abaqus standard solver. To clarify, using the concepts in this tutorial, you can implement the model for any N-Maxwell elements, using the viscoelastic Maxwell model.
The Maxwell viscoelastic model is appropriate for qualitative and conceptual analysis, but the single Maxwell element is not sufficient to describe the behavior of elastomers and polymers. For a more precise definition of these materials, the generalized Maxwell viscoelastic model is used. In the generalized Maxwell viscoelastic model, N piece of Maxwell elements and a single spring (the Hooke-element) are assembled in parallel. This tutorial, by customizing the UMAT subroutine to simulate flexible samples behavior, contributes to the advancement of viscoelastic materials design and analysis.
Essential Abaqus Training for Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Techniques
This beginner-friendly Abaqus course offers a complete guide to mastering finite element simulations through step-by-step tutorials and practical workshops. It covers essential topics such as Abaqus/CAE basics, finite element theory, composite material simulation, and thermal and impact analyses. Advanced sections delve into UMAT/VUMAT subroutines and Python scripting, equipping users with skills to automate workflows and solve complex engineering problems. Workshops include real-world examples like cantilever beams, forming processes, and fracture simulations. Perfect for engineering students and professionals, this course helps you build a solid foundation in Abaqus and expand your simulation capabilities.
Laser Assisted Machining (LAM): Modeling and Simulation in Abaqus/CAE
In this tutorial, a comprehensive discussion on modeling and simulation of laser assisted machining is presented. It includes building FEM-based models of machining, laser heating, and laser-assisted machining models in Abaqus/CAE. The finite element method (FEM) simulation is based on the coupled thermo-mechanical behavior. The package walks learners through building models that simulate the impact of laser heating on the workpiece. Detailed lessons cover constructing basic machining and laser heating models, setting boundary conditions like cutting speed and laser power, and writing subroutines such as DFLUX and VDFLUX to simulate laser heat sources. Additionally, learners will perform analyses to study temperature distribution, and stress-strain behavior. Through parametric analysis and comprehensive result evaluation, learners will gain a deep understanding of temperature distribution, stress behavior, and how laser heating can improve the machining process.
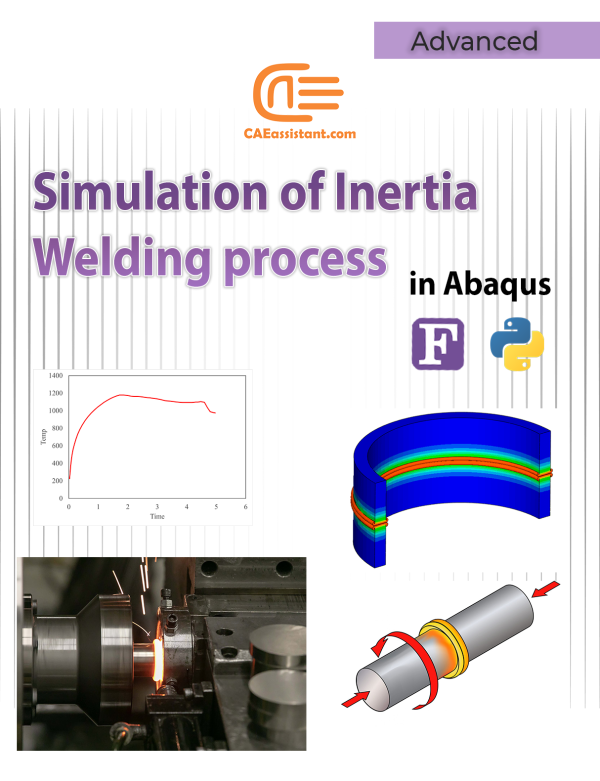
Simulation of Inertia Welding process in Abaqus | Fortran Subroutines and Python Scripts
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to simulating inertia friction welding process using Abaqus, a powerful Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tool. Inertia welding process, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, is a solid-state process that joins metal parts using kinetic energy. The simulation focuses on modeling frictional heating, temperature distribution, and material behavior through integrated Fortran subroutines and Python scripts. These scripts automate tasks such as remeshing and model generation, enhancing efficiency. Key steps include defining axisymmetric models, applying material properties, and simulating thermal and mechanical interactions during the inertia welding process. This guide equips researchers and engineers with a robust methodology for inertia welding simulation, to optimize welding parameters and analyze weld quality.
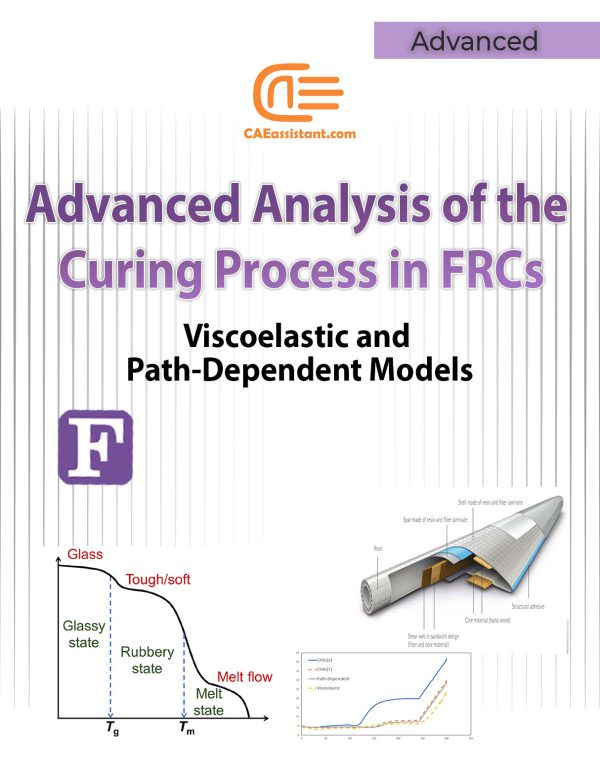
Using Viscoelastic and Path-Dependent Models for Analyzing the Curing Process in Fiber-Reinforced Composites With Abaqus subroutines
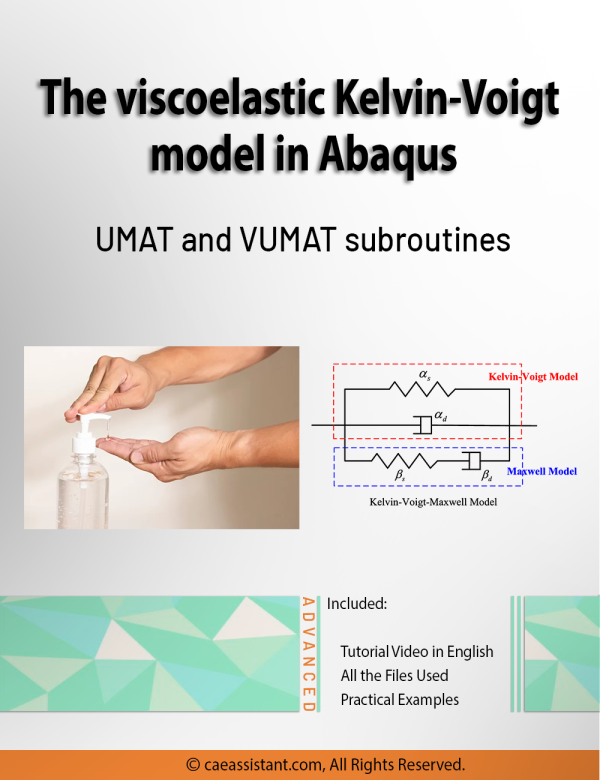
Abaqus Kelvin Voigt Model (Viscoelastic) Simulation Using UMAT and VUMAT Subroutines
This research presents a precise three-dimensional mechanical response of viscoelastic materials using Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model. We performed this kelvin voigt model Abaqus simulation using both UMAT and VUMAT subroutines for standard and explicit solvers.
The behavior of viscoelastic materials is a state between the behavior of a liquid and a solid. In other words, they behave both like liquids and solids. That is to say, there are many natural and synthetic materials that are classified as viscoelastic materials; From the biological structures of the body such as skin, cartilage and tissue to concrete, foams, rubbers, and synthetic polymers. Due to these unique properties, viscoelastic materials have many applications.
In this regard, the primary goals of this study include the development and implementation of an accurate three-dimensional Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model, and the integration of viscoelastic properties into the analysis, which can improve the prediction of viscoelastic materials response under different boundary and loading conditions.
This tutorial, by customizing the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines to simulate flexible samples behavior, contributes to the advancement of viscoelastic materials design and analysis.
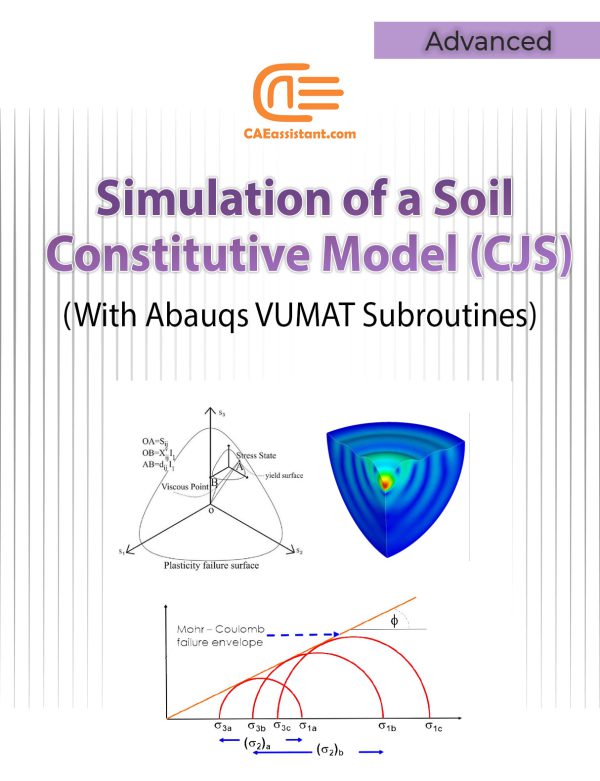
Implementation of Soil Constitutive Models in Abaqus | With a Special Focus on CJS Models
Constitutive model implemented in calculation code, play an important role in the material behaviors prediction. In the field of geotechnical engineering there are numerous soil constitutive models. By installing these models in a finite element code such as Abaqus, their development, efficiency and advancement can be increased. Also, more and more complex engineering problems can be solved by this method. But to do this, you need a proper understanding of the mathematical and programming basics of these models. This tutorial focuses on implementing advanced constitutive models in Abaqus, particularly for simulating soil behavior. Focusing on the CJS model, this tutorial tries to teach how to work and how to program these models in Abaqus code. It includes detailed explanations of VUMAT and UMAT subroutines and practical examples of implementing the CJS model.
Note: In this project, we have discussed the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines, their specifications, and features. You will become familiar with the implementation of both UMAT and VUMAT subroutines. However, the specific focus of this project, for which we have provided the necessary files and run the analysis, is on using the VUMAT model. If you need to use Abaqus for this project with the standard solver, you will need to write the UMAT subroutine yourself.
Concrete Damage Plasticity Simulation of FRP-Confined Concrete Columns in Abaqus
This tutorial package provides a comprehensive guide to implementing USDFLD subroutine in the context of Concrete Damage Plasticity Material Model. The tutorial focuses on key modeling aspects such as definition of concrete material properties using Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) Model. A theoretical background of the model will be presented and detailed explanation of the definition of all material properties will be given. The package will also explain the usage of the USDFLD subroutine to modify concrete material properties dynamically during simulation. Examples of implementing USDFLD in the context of CDP will be presented with focus on material properties that vary in function of pressure and axial strain defined as field variables.
All other modeling details will also be explained including boundary conditions, meshing, loading, and interactions.
By following the detailed steps in this tutorial, you will be able to create and analyze advanced FEM simulations in Abaqus with a focus on concrete having properties that vary during simulation.
Hygrothermal effects on composite materials | Degradation in Fiber Reinforced Composites Abaqus Simulation: Python & Subroutines
In this tutorial, we explore the hygrothermal degradation composites using ABAQUS, a powerful tool for parallel finite element analysis. Industries like aerospace, marine, and automotive heavily rely on these composites due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. However, long-term exposure to moisture and temperature can degrade their mechanical properties, making an analysis of hygrothermal effects on composite materials essential for ensuring durability.
ABAQUS allows precise modeling of these environmental conditions through Python scripts and Fortran subroutines. This combination enables efficient simulations across multiple processors, offering insights into key elastic properties, such as Young’s modulus and shear modulus, under varying conditions. By leveraging the ABAQUS Python Scripting Micro Modeling (APSMM) algorithm and custom subroutines, engineers can predict the long-term performance of fiber-reinforced composites, optimizing design and enhancing material performance in critical sectors like aerospace and marine.
In the present Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis, we have presented the software skills that a person needs when he wants to perform a parallel finite element analysis such as a micro-macro scale analysis. The Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis covers all you need to write a python scripting code for noGUI environment and also Fortran code for the subroutine environment of Abaqus to execute a parallel finite element analysis via Abaqus software. You can download the syllabus of this package here.
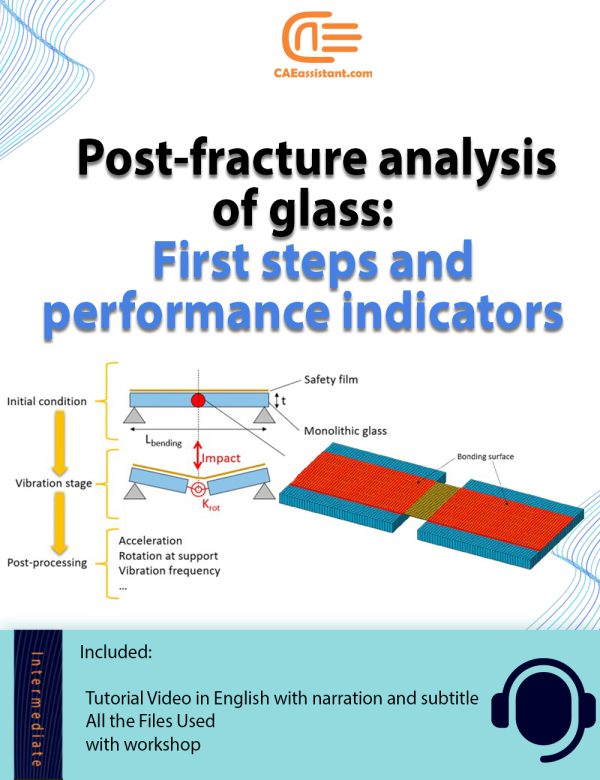
Glass Fracture Analysis with Abaqus | Post-Fracture
This tutorial explores a finite element method (FEM) simulation using Abaqus to analyze the post-fracture behavior of structural glass members retrofitted with anti-shatter safety films. In particular, it focuses on simulating and calibrating the vibration response of cracked glass elements under repeated impacts and temperature gradients, contributing to a comprehensive analysis of critical phenomena that take place in the post-fracture stage. This tutorial follows the methodology outlined in the research article “Effects of post-fracture repeated impacts and short-term temperature gradients on monolithic glass elements bonded by safety films”.
Key aspects include modeling glass fracture, assigning material properties, and defining boundary conditions to assess the vibration frequency and load-bearing capacity of cracked monolithic glass members. Additional topics cover basic concepts of dynamic identification techniques, definition of performance indicators for glass retrofit efficiency, and frequency sensitivity analysis of monolothic retrofitted glass elements under various operational and ambient conditions. The simulation results help quantify the expected contribution and residual strength of safety films in post-fracture scenarios, providing a robust framework for structural engineers to extend this investigation to other glass configurations.
This tutorial is ideal for users who want to understand FEM modeling in Abaqus and perform detailed simulations involving complex material interactions, with a focus on practical applications in glass retrofit technology.
Advanced Finite Element Analysis of Off-Axis Tunnel Cracking Laminates
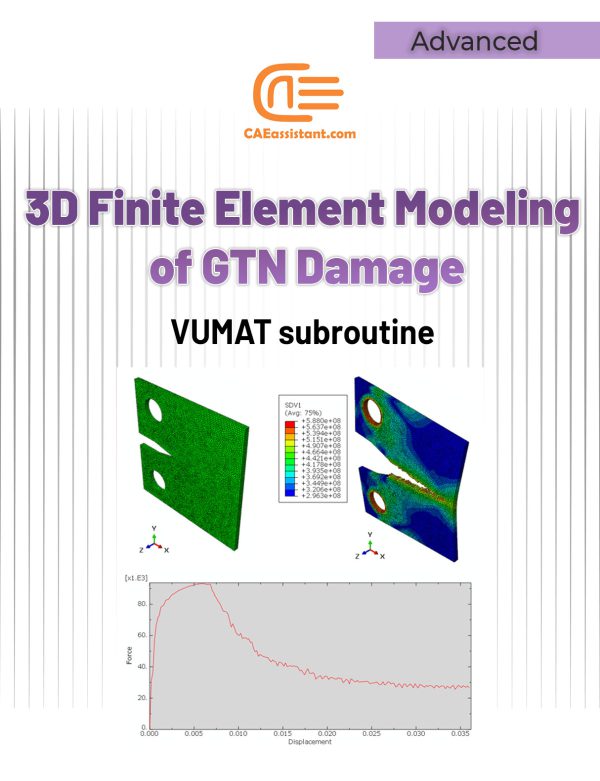
3D Simulation of Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) Damage Model
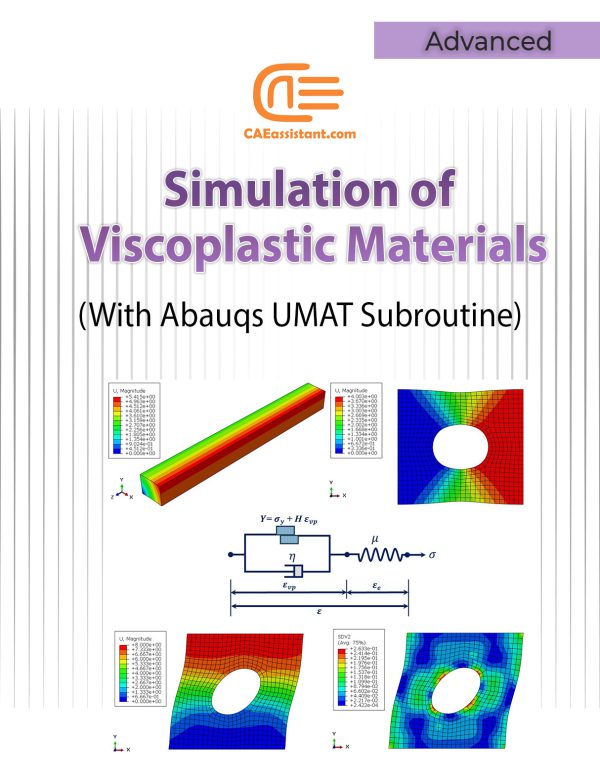
Viscoplasticity Abaqus Simulation Using UMAT Subroutine | Perzyna Viscoplastic Model
Abaqus User element tutorial | UEL advanced level
Abaqus Simulation of the Curing Process in Composites: A Specific Focus on the Pultrusion Method
Pultrusion is a crucial task for producing constant-profile composites by pulling fibers through a resin bath and heated die. Simulations play a vital role in optimizing parameters like pulling speed and die temperature to enhance product quality and efficiency. They predict material property changes and aid in process control, reducing reliance on extensive experimental trials. However, simulations face challenges such as accurately modeling complex material behaviors and requiring significant computational resources. These challenges underscore the need for precise simulation methods to improve Pultrusion processes. This study employs ABAQUS with user subroutines for detailed mechanical behavior simulations, including curing kinetics and resin properties. Key findings include insights into material property changes, and optimization strategies for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This research provides practical knowledge for implementing findings in real-world applications, advancing composite material production.
Notice that, pultrusion is a composite curing method, which may share some overlapping features with our Intermediate and Advanced curing packages. However, what sets pultrusion apart is that the composite passes over a heated die during the process. In this project, the die has also been modeled, with environmental heat applied to it using convection and a film subroutine. The heat is subsequently transferred to the sample through contact with the die. Afterward the die is removed. All these procedure is modeled in this project, with Abaqus CAE step-by-step. In contrast, in our Intermediate and Advanced packages for the oven curing of prepregs, no die has been modeled. The heat is applied without convection and, for simplicity, the heat is treated as a first-type boundary condition, which introduces some errors.
Note: The files and video which explains how to use the code are available. The PDF file will be available two weeks after purchase.Elastomeric Foam Simulation Using Abaqus Subroutines
Theta Protection Creep Model | Turbine Blade Creep Life Accurate Prediction | Creep Failure in Turbine Blades
Creep is one of the most significant failure modes in many components where the working temperature and stresses are high for a prolonged period of time. Existing creep models in commercial analysis software like Abaqus are not adequate to model all stages of creep namely – primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. Theta projection method is a convenient method proven to predict all stages of creep, especially the tertiary stage where strain rates are high leading to internal damage and fracture. The aim of the project is to develop a user subroutine for Abaqus to model creep in components using the Theta projection method. The constitutive model for the Theta projection method based on the accumulation of internal state variables such as hardening, recovery, and damage developed by (R.W.Evans, 1984) is adopted to compile a Fortran code for the user subroutine. The user subroutine is validated through test cases and comparing the results with experimental creep data. Creep analysis of a sample gas turbine blade (Turbine Blade Creep) is then performed in Abaqus through the user subroutine and the results are interpreted.
Results of test cases validate the accuracy of the Theta Projection Method in predicting all primary, secondary, and tertiary stages of creep than existing creep models in Abaqus (Creep Failure in Turbine Blades). Results at interpolated & extrapolated stress & temperature conditions with robust weighted least square regression material constants show the convenience in creep modeling with less input data than existing models. The results of creep analysis not only predicted the creep life but also indicated the internal damage accumulation. Thus, creep modeling of components through the user subroutine at different load conditions could lead us to more reliable creep life predictions and also indicate the regions of high creep strain for improvements in the early stages of design.
Dynamic Response of Rail Track Analysis Under a Moving Load
Railway tracks are subjected to moving loads of trains and this causes vibration and degradation of the track. The judgment of these vibrations is important to design the railway tracks. Therefore, the rail track analysis become important. The design involves the permissible speed of trains and the maximum axle load of the train. The model given here creates a 3D geometry of a railway track and applies a moving load in the form of a wheel. A user can change the speeds and the properties of the material including geometry as per their needs.