Essential Abaqus Training for Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Techniques
This beginner-friendly Abaqus course offers a complete guide to mastering finite element simulations through step-by-step tutorials and practical workshops. It covers essential topics such as Abaqus/CAE basics, finite element theory, composite material simulation, and thermal and impact analyses. Advanced sections delve into UMAT/VUMAT subroutines and Python scripting, equipping users with skills to automate workflows and solve complex engineering problems. Workshops include real-world examples like cantilever beams, forming processes, and fracture simulations. Perfect for engineering students and professionals, this course helps you build a solid foundation in Abaqus and expand your simulation capabilities.
Domino Effect Simulation in Abaqus | With a Review of Contact Definition Methods in Abaqus Explicit
This project focuses on the domino effect simulation with Abaqus CAE, a widely recognized finite element program. The domino effect refers to a chain reaction where one event triggers a series of similar events. It often leads to larger and unpredictable consequences. The project highlights the challenges of defining contact between components in Abaqus, a crucial aspect of domino effect simulation. The provided video explains the step-by-step modeling process. However, since one of the key challenges in this topic is defining contact, we have also attached a separate PDF. It covers defining contact in Abaqus Explicit. It includes its formulations and methods. The PDF will provide you with a better understanding of the modeling process. You can also apply it to model other problems.
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
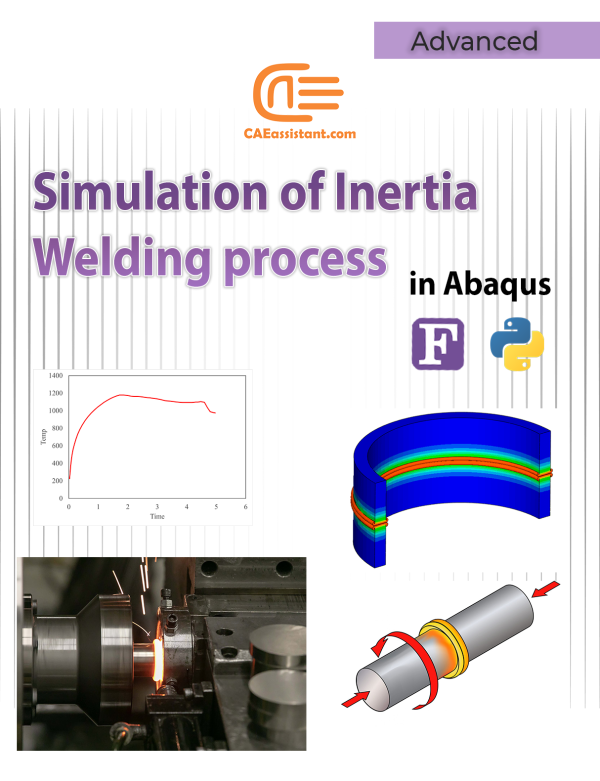
Simulation of Inertia Welding process in Abaqus | Fortran Subroutines and Python Scripts
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to simulating inertia friction welding process using Abaqus, a powerful Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tool. Inertia welding process, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, is a solid-state process that joins metal parts using kinetic energy. The simulation focuses on modeling frictional heating, temperature distribution, and material behavior through integrated Fortran subroutines and Python scripts. These scripts automate tasks such as remeshing and model generation, enhancing efficiency. Key steps include defining axisymmetric models, applying material properties, and simulating thermal and mechanical interactions during the inertia welding process. This guide equips researchers and engineers with a robust methodology for inertia welding simulation, to optimize welding parameters and analyze weld quality.
COMPREHENSIVE ABAQUS TUTORIAL FOR CIVIL ENGINEERS
COMPREHENSIVE ABAQUS COURSE FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
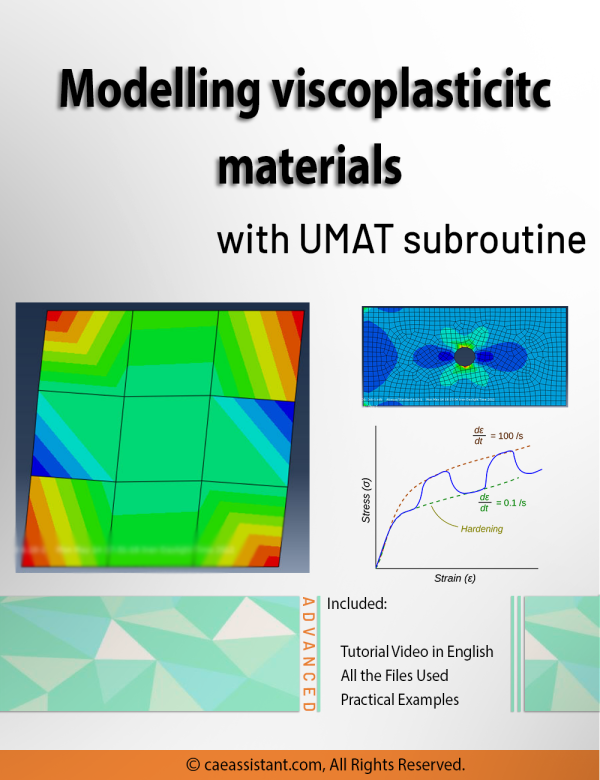
Viscoplasticity Abaqus Simulation Using UMAT Subroutine | Perzyna Viscoplastic Model
Viscoplasticity describes the rate-dependent inelastic behavior of materials, where deformation depends on both stress magnitude and application speed. This concept is crucial in many engineering applications, such as designing structures under dynamic loads, modeling soil behavior during earthquakes, and developing materials with specific mechanical properties. Viscoplasticity Abaqus simulation, especially using Abaqus with UMAT subroutines, are vital for understanding, predicting, and optimizing the behavior of viscoplastic materials. This tutorial focuses on implementing the Perzyna viscoplasticity model in Abaqus. The Perzyna viscoplastic model, a strain rate-dependent viscoplasticity model, relates stress to strain through specific constitutive relations. This involves defining plastic strain rate based on stress state, internal variables, and relaxation time. The tutorial provides general UMAT codes for viscoplastic analysis, yielding results like stress fields essential for various engineering applications. These simulations help in predicting permanent deformations, assessing structural failure points, and analyzing stability under different loads, benefiting fields such as aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and energy.
Abaqus Simulation of the Curing Process in Composites: A Specific Focus on the Pultrusion Method
Pultrusion is a crucial task for producing constant-profile composites by pulling fibers through a resin bath and heated die. Simulations play a vital role in optimizing parameters like pulling speed and die temperature to enhance product quality and efficiency. They predict material property changes and aid in process control, reducing reliance on extensive experimental trials. However, simulations face challenges such as accurately modeling complex material behaviors and requiring significant computational resources. These challenges underscore the need for precise simulation methods to improve Pultrusion processes. This study employs ABAQUS with user subroutines for detailed mechanical behavior simulations, including curing kinetics and resin properties. Key findings include insights into material property changes, and optimization strategies for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This research provides practical knowledge for implementing findings in real-world applications, advancing composite material production.
Notice that, pultrusion is a composite curing method, which may share some overlapping features with our Intermediate and Advanced curing packages. However, what sets pultrusion apart is that the composite passes over a heated die during the process. In this project, the die has also been modeled, with environmental heat applied to it using convection and a film subroutine. The heat is subsequently transferred to the sample through contact with the die. Afterward the die is removed. All these procedure is modeled in this project, with Abaqus CAE step-by-step. In contrast, in our Intermediate and Advanced packages for the oven curing of prepregs, no die has been modeled. The heat is applied without convection and, for simplicity, the heat is treated as a first-type boundary condition, which introduces some errors.
Note: The files and video which explains how to use the code are available. The PDF file will be available two weeks after purchase.Elastomeric Foam Simulation Using Abaqus Subroutines
Abaqus convergence tutorial | Introduction to Nonlinearity and Convergence in ABAQUS
This package introduces nonlinear problems and convergence issues in Abaqus. Solution convergence in Abaqus refers to the process of refining the numerical solution until it reaches a stable and accurate state. Convergence is of great importance especially when your problem is nonlinear; So, the analyst must know the different sources of nonlinearity and then can decide how to handle the nonlinearity to make solution convergence. Sometimes the linear approximation can be useful, otherwise implementing the different numerical techniques may lead to convergence.
Through this tutorial, different nonlinearity sources are introduced and the difference between linear and nonlinear problems is discussed. With this knowledge, you can decide whether you can use linear approximation for your nonlinear problem or not. Moreover, you will understand the different numerical techniques which are used to solve nonlinear problems such as Newton-Raphson.
All of the theories in this package are implemented in two practical workshops. These workshops include modeling nonlinear behavior in Abaqus and its convergence study and checking different numerical techniques convergence behavior using both as-built material in Abaqus/CAE and UMAT subroutine.
Simulation of Pitting Corrosion Mechanism with Scripting in Abaqus
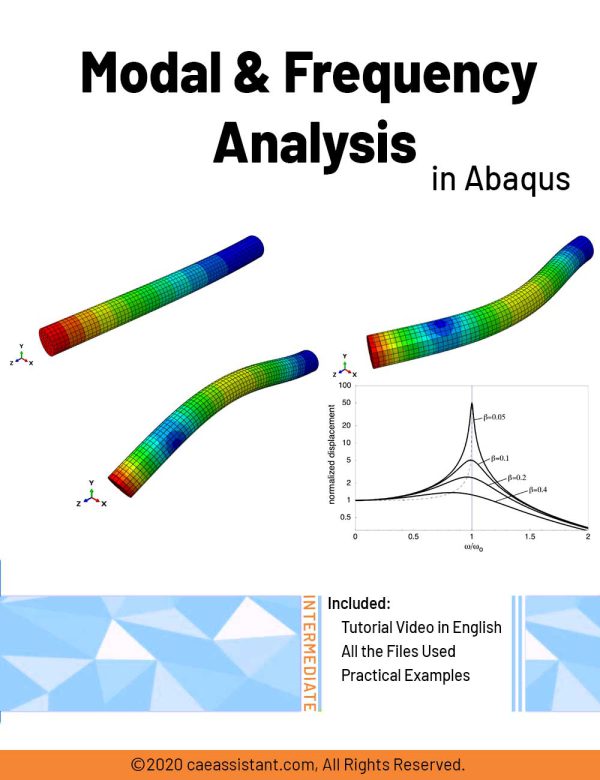
Modal and Frequency Analysis in Abaqus | Abaqus modal Analysis
Tread wear simulation in Abaqus
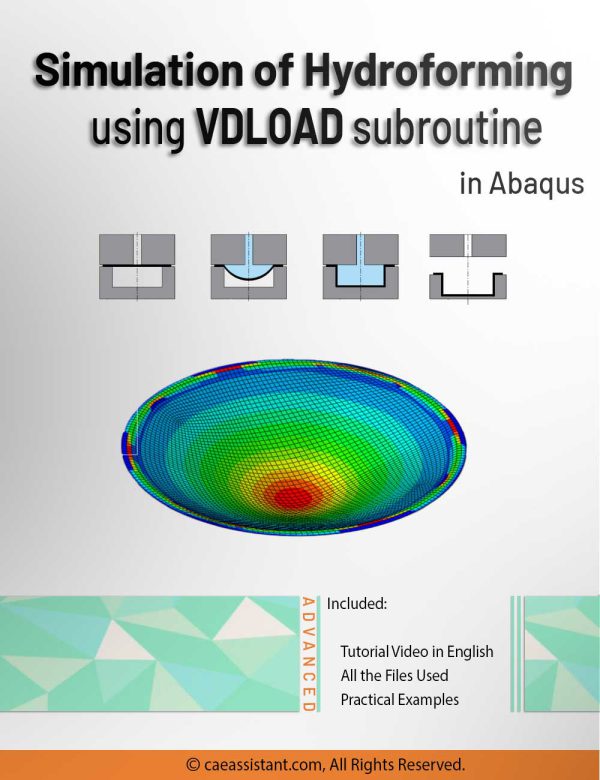
Hydroforming process simulation using VDLOAD subroutine in Abaqus
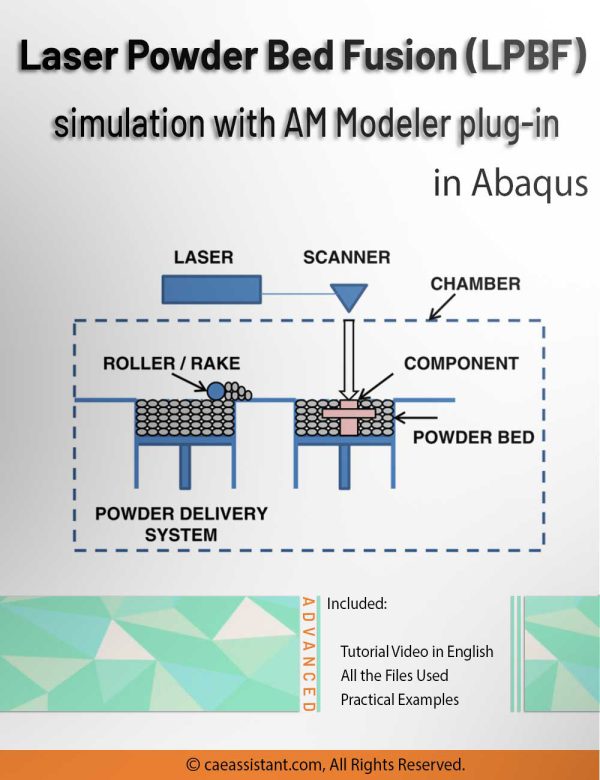
LPBF Printing Simulation in Abaqus | 3D Printing with Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process (LPBF) Method
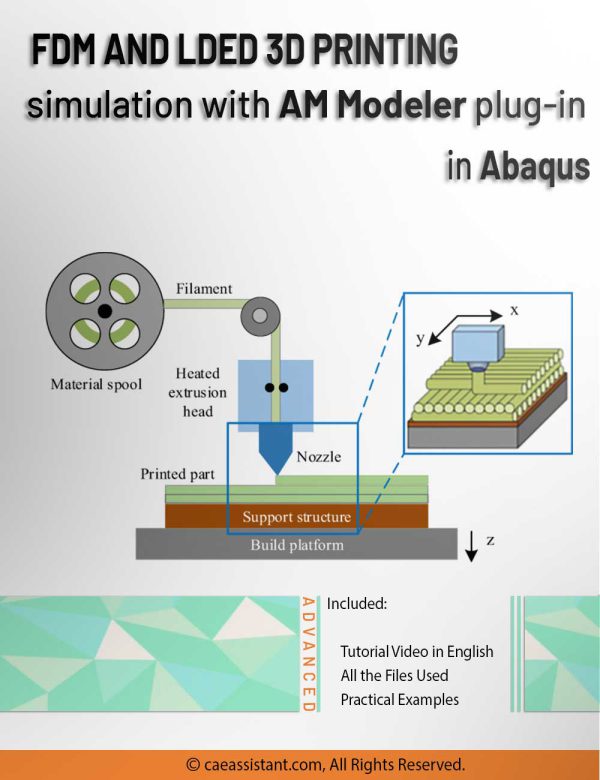
FDM Simulation in Abaqus | Simulating 3D Printing with Fused Deposition Modeling