Computational Predictions for Predicting the Performance of Structure
This package focuses on developing and applying predictive models for the structural analysis of steel and concrete components subjected to fire and subsequent earthquake loading. To accurately simulate the complex behavior of these structures, finite element analysis (FEA) using ABAQUS is employed. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept. However, due to the computational demands of FEA, various machine learning techniques, including regression models, Gene Expression Programming (GEP), Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS), and ensemble methods, are explored as surrogate models. These models are trained on large datasets of FEA results to predict structural responses efficiently. The performance of these models is evaluated using statistical metrics such as RMSE, NMSE, and coefficient of determination.
Damage Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Tunnels under Internal Water Pressure
This tutorial package equips you with the knowledge and tools to simulate the behavior of reinforced concrete tunnels (RCTs) subjected to internal water pressure. It combines the power of finite element (FE) modeling with artificial intelligence (AI) for efficient and accurate analysis. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques such as regression, GEP, ML, DL, hybrid, and ensemble models, we significantly reduce computational costs and time while achieving high accuracy in predicting structural responses and optimizing designs.
A Comprehensive Tutorial for Soft Body Impact Composites Simulation
This comprehensive tutorial package focuses on simulating soft body impact composites on laminated composite materials using the Finite Element Method (FEM) in Abaqus. The course covers key topics such as soft body modeling, metal material modeling, composite material modeling, composite to composite interface modeling, metal to composite interface modeling, interaction between soft bodies and FML, interaction between layers, and Python scripting for parametric studies. Users will explore different material models and learn about impact failure mechanisms, including matrix failure, fiber failure, shear failure, and delamination. The course is structured into lessons that cover theoretical aspects, followed by hands-on workshops to model soft body impacts, apply material properties, and analyze post-processing results such as forces, displacements, and energy dissipation. It also includes an advanced section on Python scripting, enabling users to automate parametric studies for complex simulations. This package is ideal for engineers, researchers, and students looking to deepen their understanding of soft body impact phenomena and composite material behavior.
Computational Modeling of Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) Behavior
This course equips engineers with the tools to design and analyze Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) and Reinforced Concrete Shear Walls (RCSW) subjected to explosive loads. Traditional Finite Element (FE) simulation is time-consuming and requires numerous samples for accurate results. This package offers a more efficient approach using Artificial Intelligence (AI) models trained on FEA data. You'll learn to develop FE models of SPSW and RCSW in ABAQUS software, considering material properties, interactions, and boundary conditions. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
We then delve into AI modeling using MATLAB. Explore various methods like regression, Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and ensemble models to predict the behavior of SPSW and RCSW under blast loads. Statistical analysis helps compare model accuracy. By combining FE analysis with AI models, you'll gain a powerful tool for designing blast-resistant structures while saving time and resources.
Abaqus advanced tutorials on concrete members
Welcome to the "Abaqus Advanced Tutorials on Concrete Members" course, designed to provide civil and structural engineers with cutting-edge expertise in finite element modeling (FEM) and simulation using Abaqus. This advanced-level course focuses on the detailed modeling of complex concrete and composite columns under various loading conditions. Topics include the simulation of tubed reinforced concrete columns, concrete-filled double skin steel columns, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite columns. Participants will delve into axial and eccentric compression loading scenarios, with a special focus on hollow and tapered cross-sections. The course also emphasizes comparing simulation results with experimental data from published research, ensuring practical relevance and accuracy. By the end of the course, learners will be equipped with the necessary skills to tackle advanced structural analysis challenges using Abaqus, reinforcing their understanding of concrete member behavior in real-world applications.
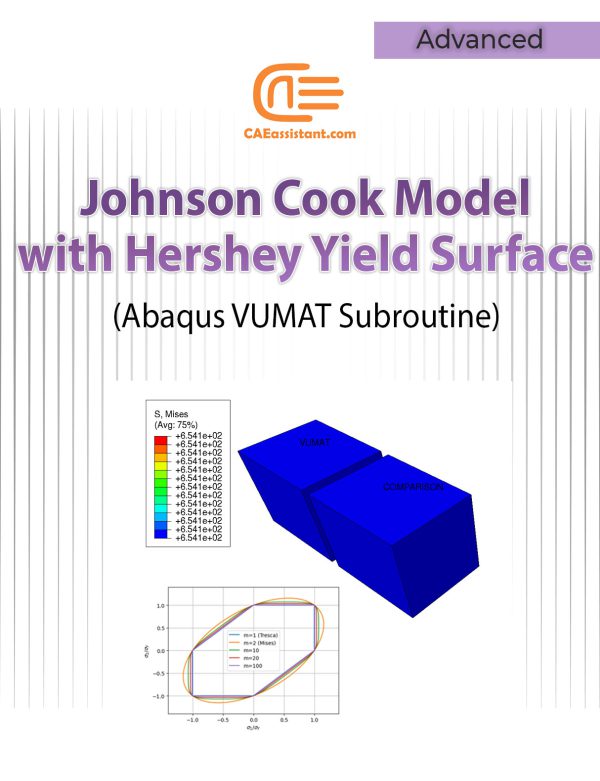
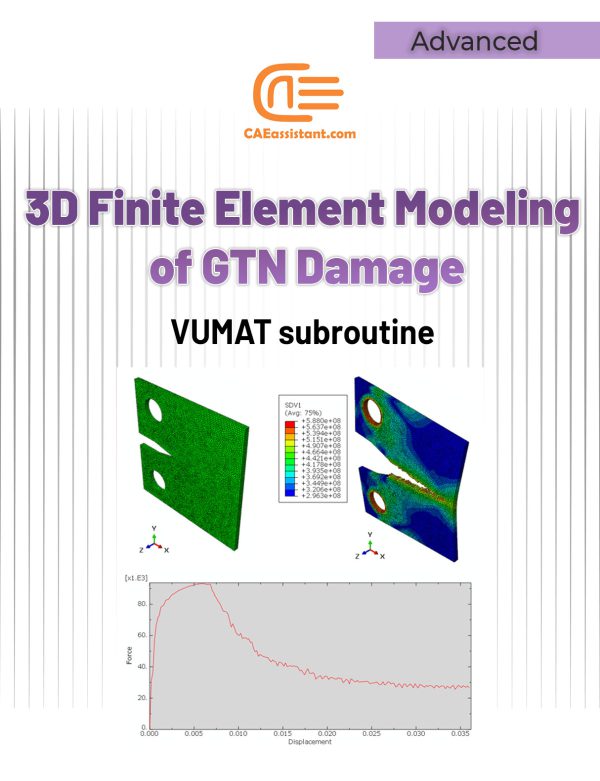
Modified Johnson Cook viscoplastic model with the Hershey yield surface | VUMAT Subroutine for 3D continuum elements
This project offers a set of Abaqus models for 3D continuum elements, integrating a VUMAT subroutine that implements the Modified Johnson Cook (MJC) viscoplastic model and the Hershey yield surface. The MJC model simulates material behavior under varying strain rates and temperatures, while the Hershey yield surface predicts complex yielding behavior. Together, they provide highly accurate simulations of materials under extreme conditions such as impacts and high temperatures. Ideal for industries like automotive, aerospace, and defense, this package supports critical applications like crash testing, metal forming, and ballistic analysis. The model has been implemented for 3D continuum elements.
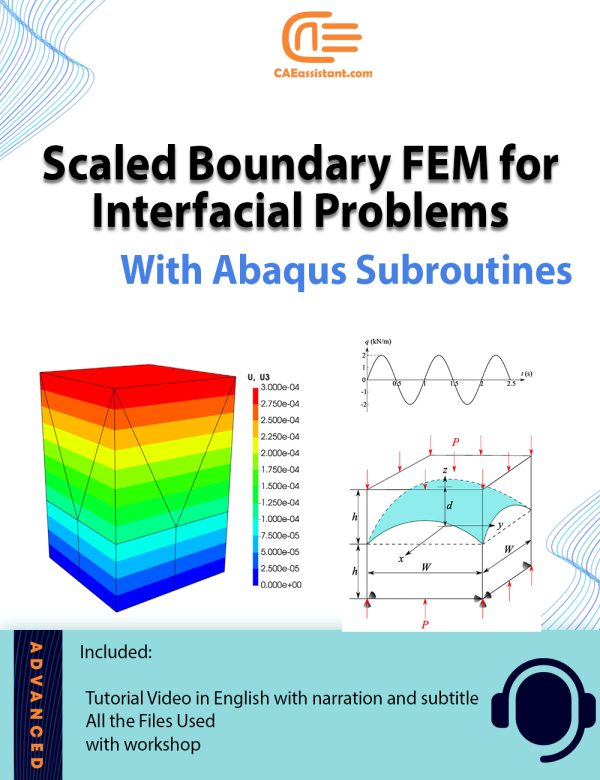
Note: The inp and Fortran files are only applicable in Linux.Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method (SBFEM) Modeling Files for ABAQUS
The Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method (SBFEM) enhances traditional Finite Element Analysis (FEA). It provides flexibility in handling complex geometries and interfaces. Integrated into ABAQUS, SBFEM allows for the creation of polyhedral elements, reducing meshing challenges. It effectively manages non-matching meshes and complex boundary conditions, particularly in interfacial problems like contact mechanics and fracture analysis. ABAQUS supports custom user elements (UEL), enabling direct integration of SBFEM with advanced solvers, improving efficiency and expanding its applicability to complex engineering problems. The open-source implementation allows for customization, making SBFEM in ABAQUS a powerful tool for precise and efficient simulations. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios requiring advanced FEA.
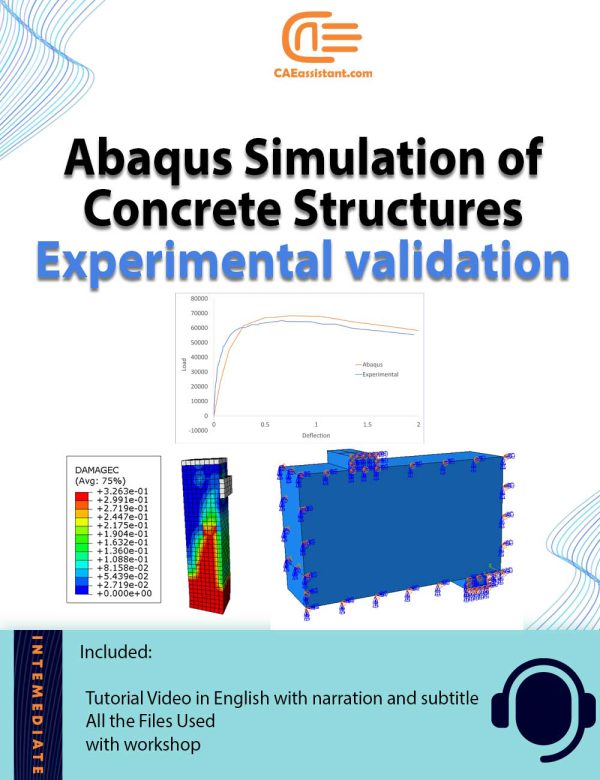
Analysis of Plain and Reinforced Concrete Structures with ABAQUS | Validation with Experiments
This comprehensive package offers four different workshops focused on the analysis of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete structures using ABAQUS. Designed for professionals, researchers, and students, it provides hands-on learning in modeling, simulating, and validating concrete structures under various conditions. Each workshop dives into specific aspects of concrete behavior, from flexural to compressive strength, incorporating the latest sustainable practices through the use of recycled materials. The package ensures mastery of ABAQUS, offering practical insights and a cost-effective path to advanced concrete analysis and safer, more durable infrastructure design.
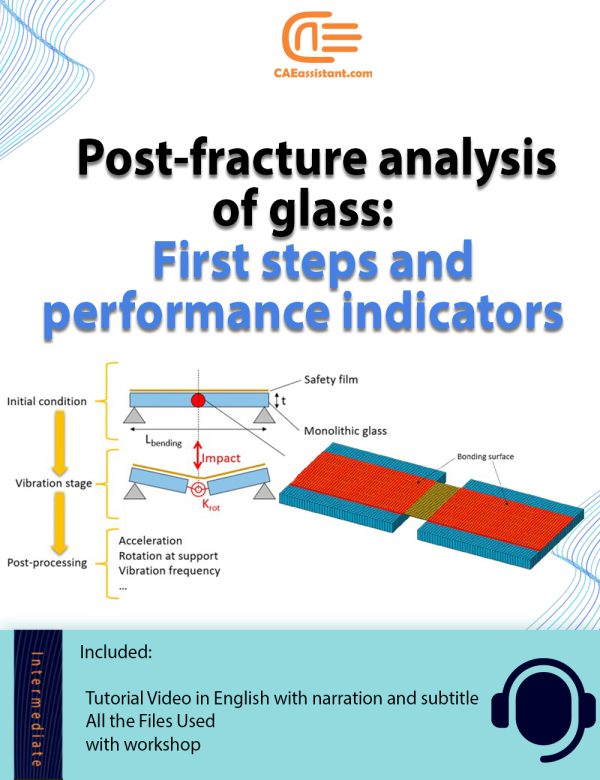
Note: Only the first workshop has video.Glass Fracture Analysis with Abaqus | Post-Fracture
This tutorial explores a finite element method (FEM) simulation using Abaqus to analyze the post-fracture behavior of structural glass members retrofitted with anti-shatter safety films. In particular, it focuses on simulating and calibrating the vibration response of cracked glass elements under repeated impacts and temperature gradients, contributing to a comprehensive analysis of critical phenomena that take place in the post-fracture stage. This tutorial follows the methodology outlined in the research article “Effects of post-fracture repeated impacts and short-term temperature gradients on monolithic glass elements bonded by safety films”.
Key aspects include modeling glass fracture, assigning material properties, and defining boundary conditions to assess the vibration frequency and load-bearing capacity of cracked monolithic glass members. Additional topics cover basic concepts of dynamic identification techniques, definition of performance indicators for glass retrofit efficiency, and frequency sensitivity analysis of monolothic retrofitted glass elements under various operational and ambient conditions. The simulation results help quantify the expected contribution and residual strength of safety films in post-fracture scenarios, providing a robust framework for structural engineers to extend this investigation to other glass configurations.
This tutorial is ideal for users who want to understand FEM modeling in Abaqus and perform detailed simulations involving complex material interactions, with a focus on practical applications in glass retrofit technology.
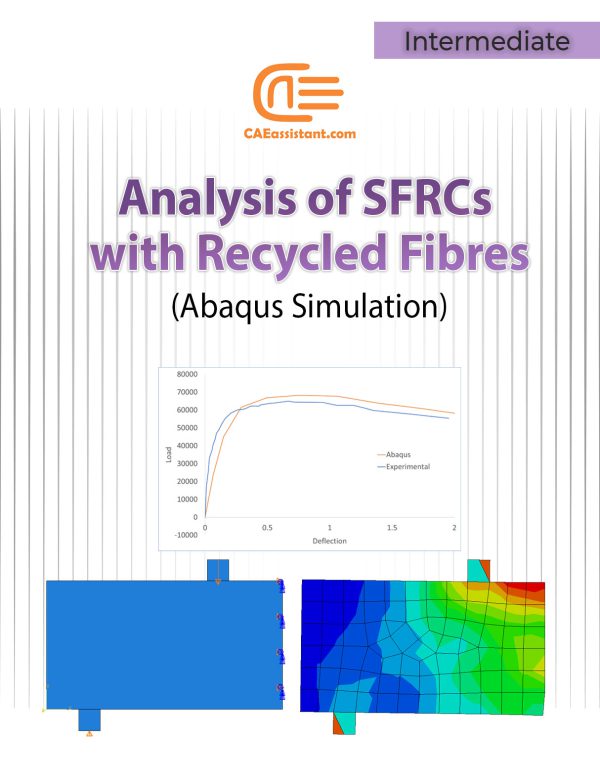
Stress-strain characteristic of SFRC using recycled fibres | An Abaqus Simulation
This training utilizes Abaqus software to simulate and analyze the stress-strain characteristics of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) using recycled fibers. The importance of this work lies in its contribution to sustainable construction practices by validating the effectiveness of recycled steel fibers in enhancing concrete's mechanical properties. Through advanced finite element analysis (FEA), the project addresses challenges in accurately modeling SFRC's post-cracking behavior, ensuring that the simulations are aligned with experimental data for reliable results. Abaqus' capabilities in nonlinear material modeling, stress-strain simulation, and principal stress analysis significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of the research, making it a valuable tool for both academia and industry.
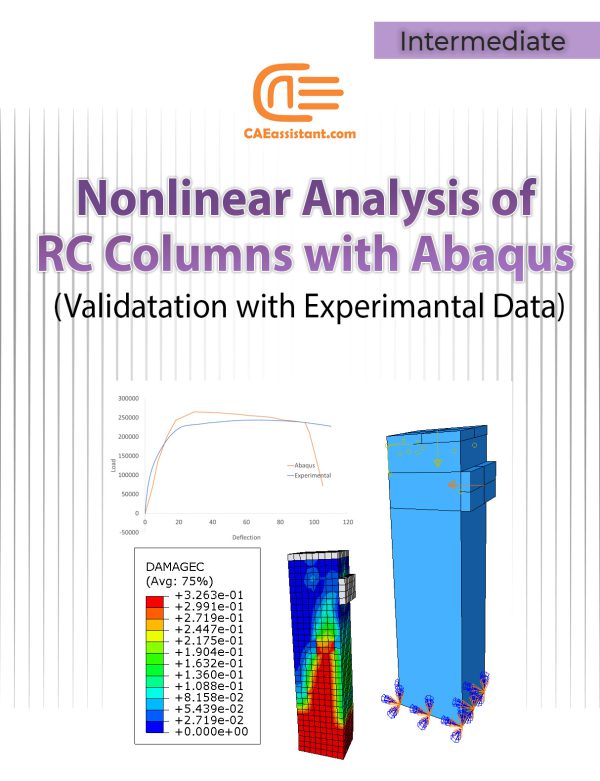
Nonlinear Analysis of RC Columns Using ABAQUS | Validation with Experimental Data
Reinforced Concrete (RC) columns are critical components in civil engineering, essential for the stability of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure during seismic events. This study leverages ABAQUS, a powerful finite element analysis (FEA) software, to simulate the seismic performance of RC columns. By modeling columns in 3D and using ABAQUS's advanced tools, we replicate experimental conditions to analyze their behavior under seismic loads. Numerical simulations offer the advantage of exploring various scenarios quickly and cost-effectively, while also allowing for extensive parametric studies. The study details how ABAQUS models both concrete and steel reinforcement, accounts for interaction effects, and applies appropriate loading and boundary conditions. The simulations provide valuable insights into failure modes, load-displacement responses, and crack patterns, offering a comprehensive understanding of RC column performance in seismic scenarios.
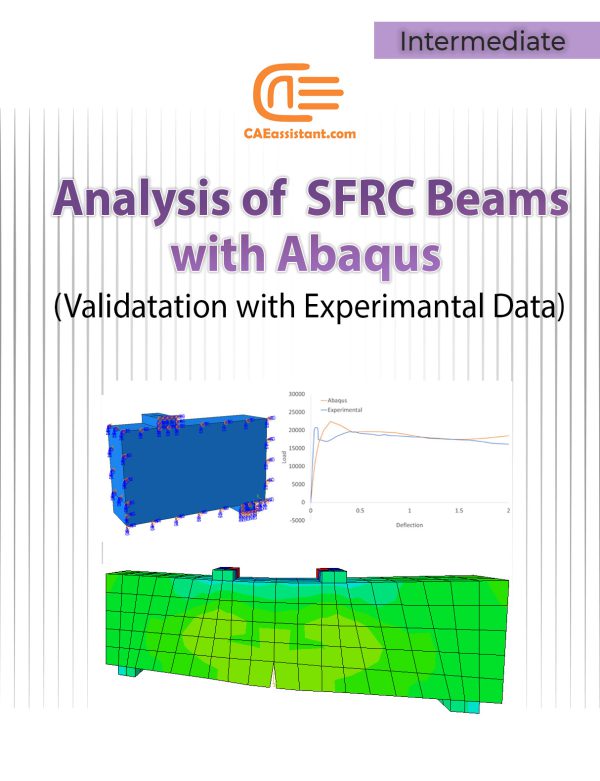
Analysis of Steel-Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) Beams with Abaqus
Machine Learning for Composite Materials with Abaqus
This tutorial package delves into an advanced inverse modeling approach for predicting carbon fiber properties in composite materials using a machine learning (ML) technique. Focused on machine learning for composite materials applications, it covers the use of Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) to build a surrogate model for accurate predictions of fiber properties based on data from unidirectional (UD) lamina. By leveraging Finite Element (FE) homogenization, synthetic data is generated for training the GPR model, accounting for variations in fiber, matrix properties, and volume fractions. This framework’s efficiency and accuracy are validated using real-world data, highlighting its potential as a computational alternative to traditional experimental methods. The package includes detailed explanations, case studies, and practical exercises, equipping users with hands-on experience in applying this ML-based approach to composite material analysis.
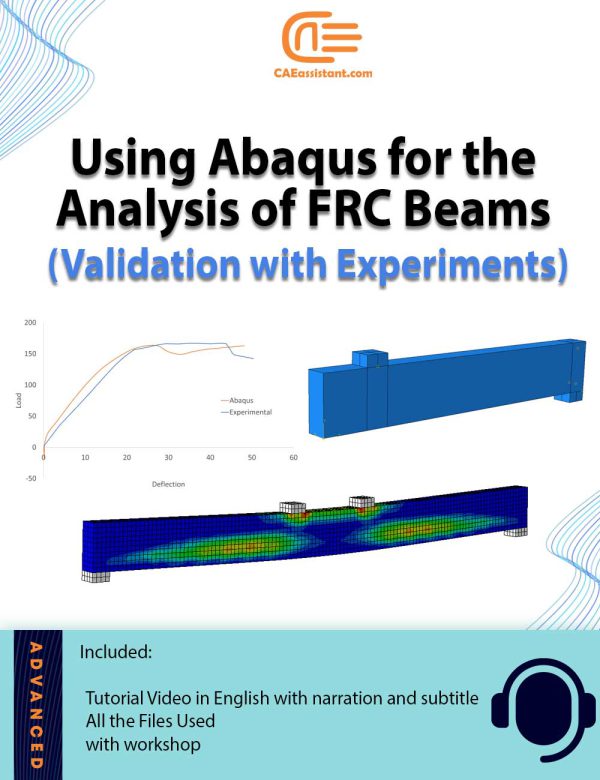
Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams | An Abaqus Simulation
Abaqus basic tutorials on concrete beams and columns
Welcome to the “Abaqus Basic Tutorials on Concrete Members,” a comprehensive course tailored for civil and structural engineers seeking to master finite element modeling (FEM) of concrete structures. This tutorial covers key concepts such as plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforced concrete members, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. The course guides learners through the application of boundary conditions, material properties, and various loading conditions in Abaqus. Key topics include plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforcement modeling with steel bars and stirrups, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement techniques. Participants will also explore comparing simulation results with experimental data, as well as interpreting critical outcomes such as stress distribution and failure modes. Through hands-on workshops, learners will simulate structural behaviors under axial, lateral, and compression loads, ensuring a practical understanding of FEM for concrete members. By the end of this course, participants will be proficient in using Abaqus to model and analyze concrete structures, reinforced elements, and advanced composites, providing them with a strong foundation for structural analysis and design.