CEL in Abaqus
Using a Lagrangian-Eulerian contact, Eulerian materials can come into contact with Lagrangian elements. Simulations performed in this way are called CEL in Abaqus. The most important feature of this simulation method is its easy use of General Contact explicit in Abaqus. Because this method allows us to simulate completely physically or the interaction between a liquid and a structure. It should be mentioned, other methods like SPH are also used to simulate liquid and a structure. “SPH in Abaqus: the package is available in this link.
Introduction to CEL in Abaqus:
In Lagrangian analysis, the nodes are fixed on the material and the elements are deformed by deforming the whole material, but in the Eulerian method, the nodes are fixed in space and do not deform with the deformation of our material elements, so the boundary of the elements is on the boundary of Eulerian material, In general, it does not match. For more information, you can use this link.
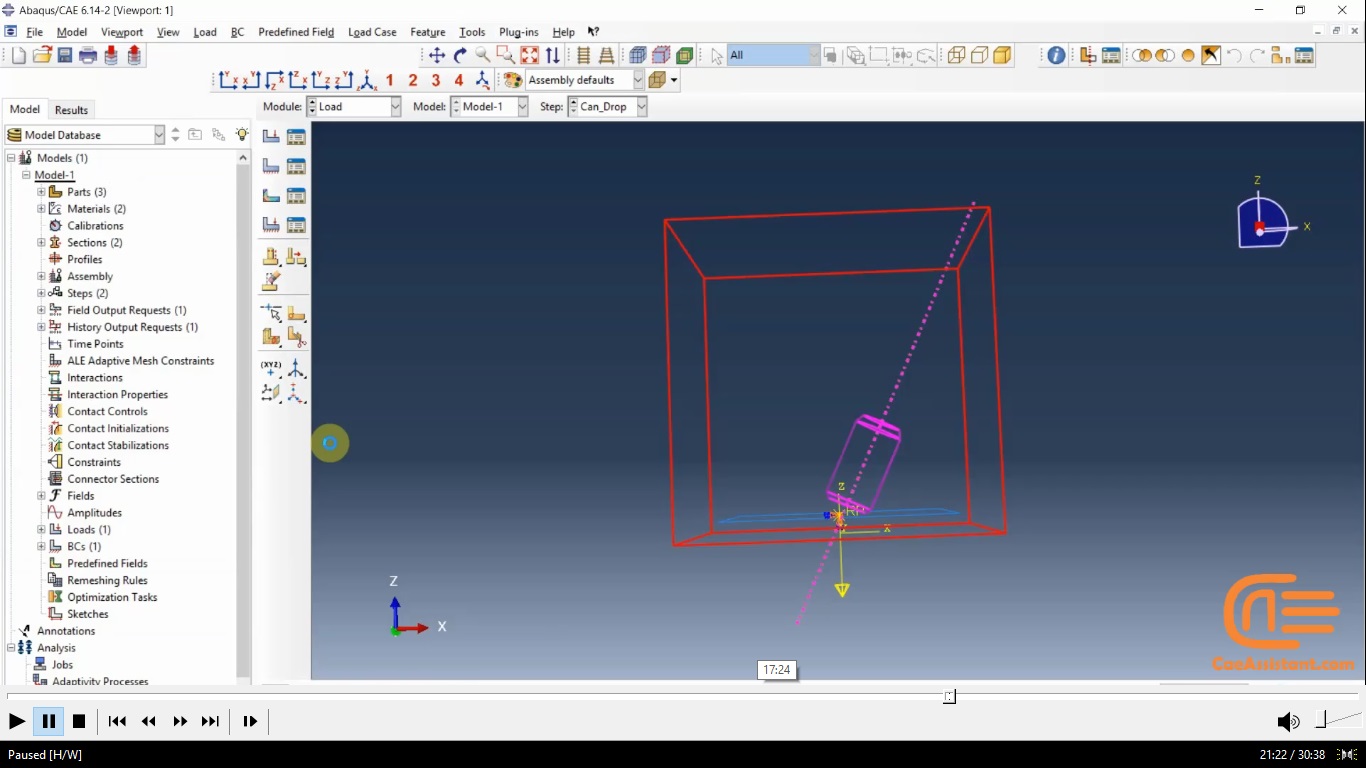
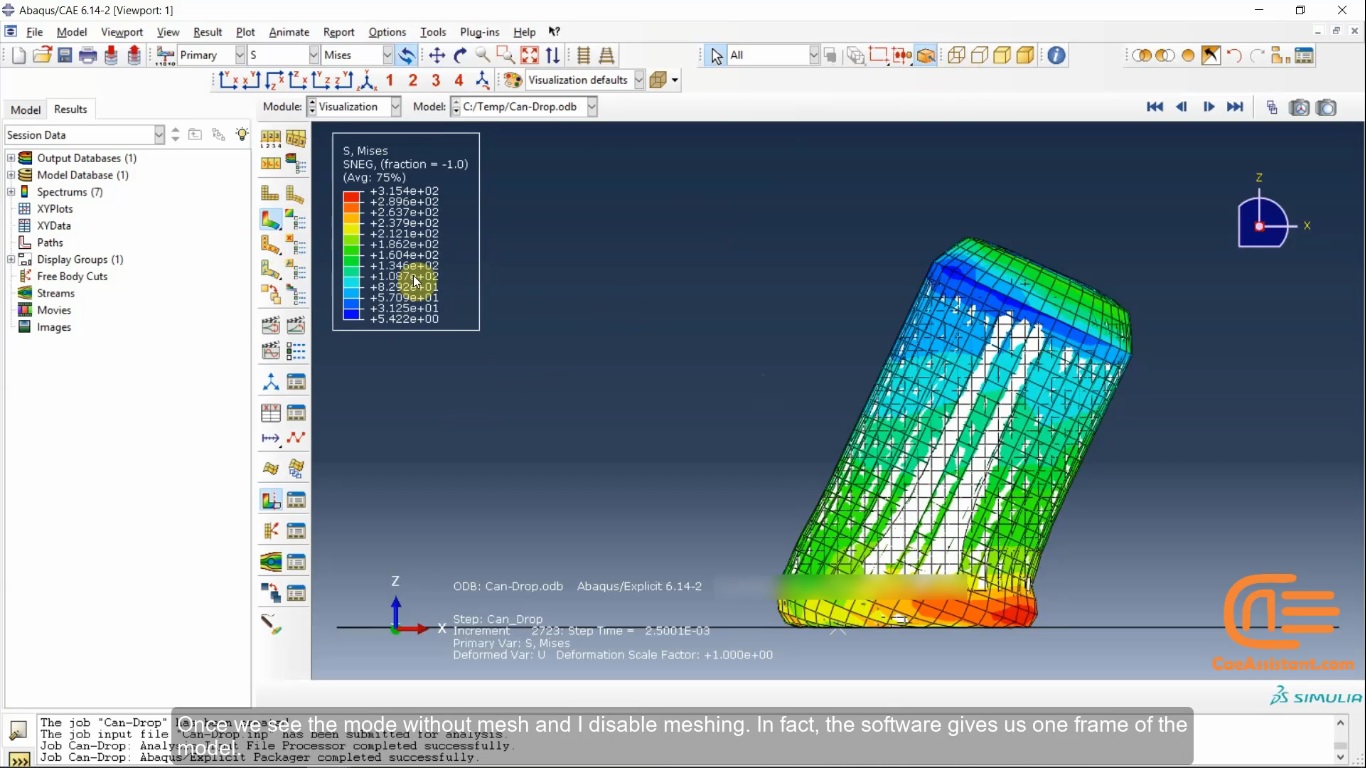
Workshop 1 for Can drop:
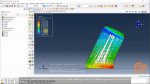
In this workshop, we analyze the falling of a soda can on the ground in a Lagrangian-Eulerian space. Complete how to create an Eulerian-Lagrangian space, how to define the volume fraction for an Eulerian material, how to define the initial velocity for a soda can, use a dynamic explicit solver, and finally view the results of stresses, velocities, and other outputs you can learn in this workshop.
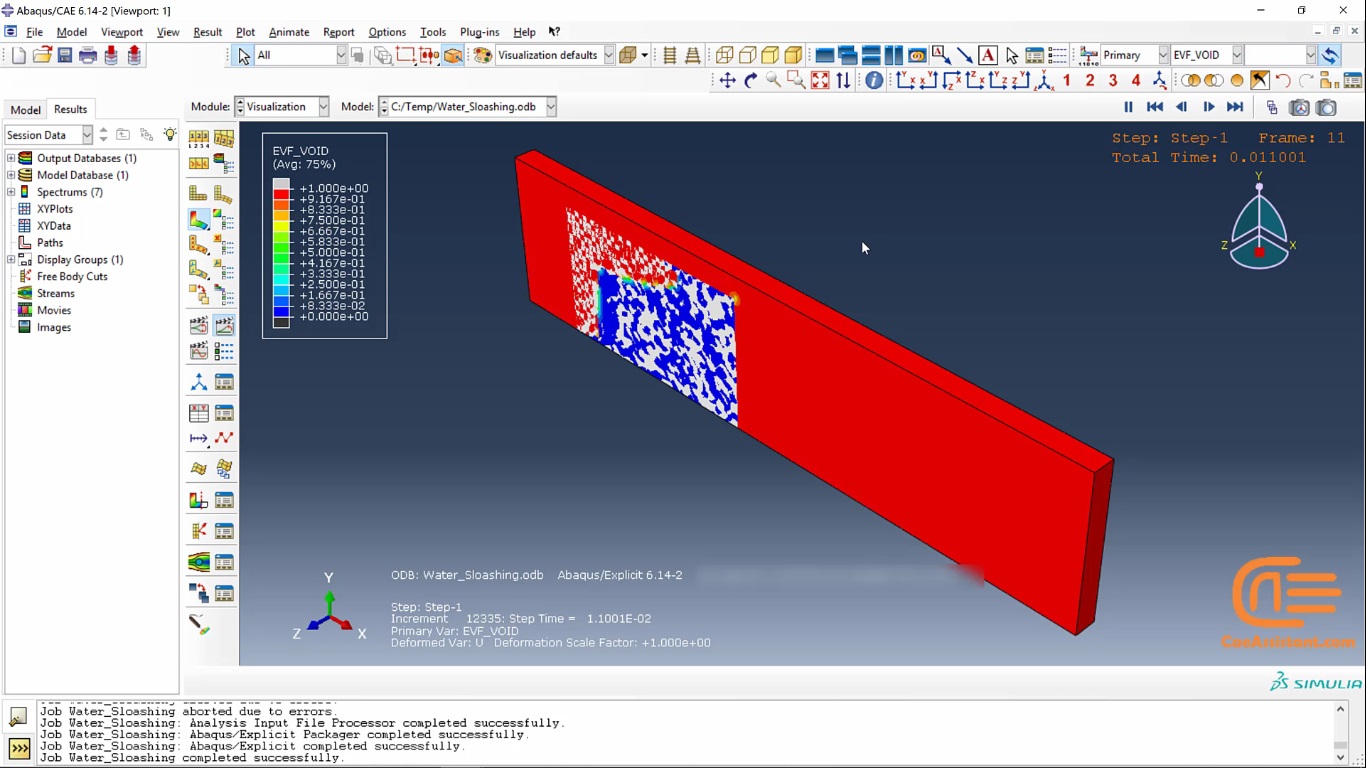
Workshop 2 for Water Sloashing :
In this workshop, we analyzed the movement of water inside the flash tank. In this analysis and simulation, we use Eulerian-Lagrangian elements. You should know, these types of elements are not necessarily filled with matter and may only belong to a part of the space. In this exercise, we also discuss how to define the volume fraction for an Eulerian part, use the dynamic explicit solver, and finally analyze the results.
You can watch demo here.
Users ask these questions
In social media, users asked questions regarding Abaqus CEL issues, and we answered a few of them; you can see them below.
I. CEL analysis
Q: Hi, I need the EOS(equation of state) parameter of clay for material modeling in the CEL (Euler type) type in Abaqus.
I try to model the uplift force for removing rigid object from seabed clay.
A: Hi, Generally, if you need parameters of any equation of state or other variables in any equations and theories, you must look into articles, website data sheets, or experimental results.
If you need any help in case of CEL simulation, refer to this link: CEL Analysis in Abaqus
I hope I could have helped you.
II. CEL analysis in Abaqus
Q: Hello there, guys. I use ABAQUS and the CEL technique to perform the sloshing analysis.
We used the tank plate as a rigid body because we didn’t have much time.
The purpose of this investigation is to determine the maximum pressure at the tank plate. However, because the tank plate is a rigid body, the pressure behavior at the tank plate is not visible. However, we can only see the pressure at the liquid level.
Is there a way to use liquid pressure to acquire the pressure result of a tank plate?
Actually, I don’t comprehend the pressure at the liquid, and I’m looking for your assistance. I appreciate it….
A: Hello,
I wonder why did you model a rigid body. You can just use solid or shell elements. If you need more information on how to use CEL analysis in Abaqus, refer to this link:
I hope make it worth your while.
Best wishes.
III. Sloshing analysis with the CEL
Q: Hello there, guys. I use ABAQUS to perform the sloshing analysis using the CEL approach. The effect of baffle in the tank is what we’re looking for. The displacement boundary condition was applied to the tank plate. We can see that the behavior is accurate, but the liquid’s behavior is strange. Please take a look at the picture provided. The water in the tank leaks… the tank is made of a rigid body, thus it’s not a problem with the property. Has anyone else encountered this issue?
A: Greetings,
Your model needs to be checked. It doesn’t matter if you used the baffle or not. If you model this analysis correctly, there shouldn’t be a problem. I recommend referring to the link below. According to this tutorial, you will be simulating your own model without a problem.
Best wishes.









Taksheel Talukdar –
A really simple and what is the most important a clear course. This course helped me to do my academic project.
Oliver Davies –
Thank you for your course. I have a question. Could we use CEL for some steady-state analysis such as rolling?