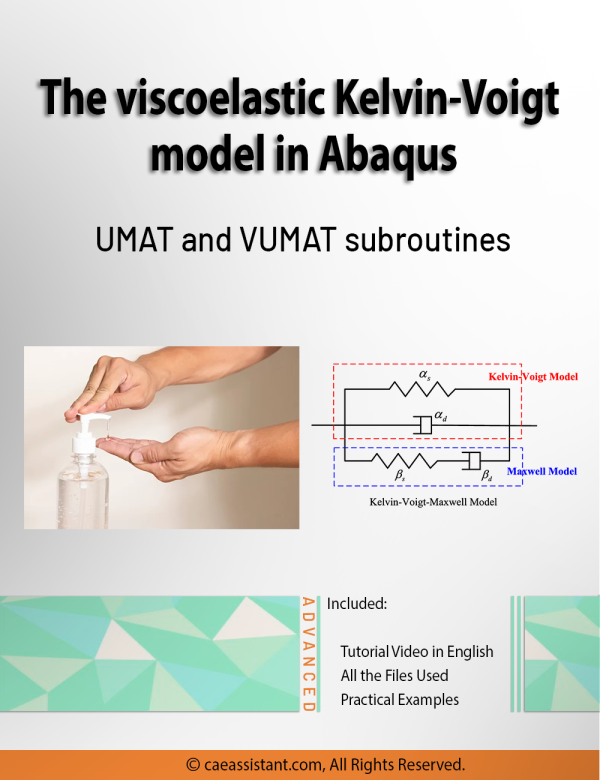
Abaqus Kelvin Voigt Model (Viscoelastic) Simulation Using UMAT and VUMAT Subroutines
This research presents a precise three-dimensional mechanical response of viscoelastic materials using Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model. We performed this kelvin voigt model Abaqus simulation using both UMAT and VUMAT subroutines for standard and explicit solvers.
The behavior of viscoelastic materials is a state between the behavior of a liquid and a solid. In other words, they behave both like liquids and solids. That is to say, there are many natural and synthetic materials that are classified as viscoelastic materials; From the biological structures of the body such as skin, cartilage and tissue to concrete, foams, rubbers, and synthetic polymers. Due to these unique properties, viscoelastic materials have many applications.
In this regard, the primary goals of this study include the development and implementation of an accurate three-dimensional Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model, and the integration of viscoelastic properties into the analysis, which can improve the prediction of viscoelastic materials response under different boundary and loading conditions.
This tutorial, by customizing the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines to simulate flexible samples behavior, contributes to the advancement of viscoelastic materials design and analysis.
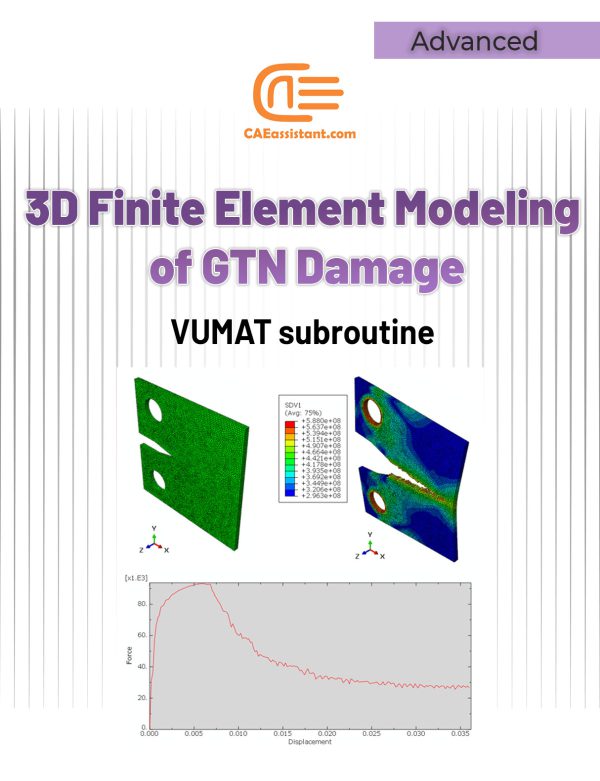
3D Simulation of Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) Damage Model
Simulation of an Ultrasonic Transducer (3D Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Turning Tool)
Since the invention of ultrasonic vibration assisted turning, this process has been widely considered and investigated. The reason for this consideration is the unique features of this process which include reducing machining forces, reducing wear and friction, increasing the tool life, creating periodic cutting conditions, increasing the machinability of difficult-to-cut material, increasing the surface quality, creating a hierarchical structure (micro-nano textures) on the surface and so on. Different methods have hitherto been used to apply ultrasonic vibration to the tip of the tool during the turning process. In this research, a unique horn has been designed and constructed to convert linear vibrations of piezoelectrics to three-dimensional vibrations (longitudinal vibrations along the z-axis, bending vibrations around the x-axis, and bending vibrations around the y-axis). The advantage of this ultrasonic machining tool compared with other similar tools is that in most other tools it is only possible to apply one-dimensional (linear) and two-dimensional (elliptical) vibrations, while this tool can create three-dimensional vibrations. Additionally, since the nature of the designed horn can lead to the creation of three-dimensional vibrations, there is no need for piezoelectric half-rings (which are stimulated by a 180-phase difference) to create bending vibrations around the x and y axes. Reduction of costs as well as the simplicity of applying three-dimensional vibrations in this new method can play an important role in industrializing the process of three-dimensional ultrasonic vibration assisted turning.
In this example, how to model all the components of an ultrasonic transducer and its modal and harmonic analysis are taught in full detail.
Laser Forming Process Tutorial in Abaqus
Friction Stir Welding simulation Tutorial | FSW Advanced level
In this tutorial, how to define increments of thermal strains, in order to model thermal expansion, is taught. The implementation of thermal expansion in model is done with UEXPAN and VUEXPAN subroutines for Abaqus/Standard solver (implicit method). In user subroutines UEXPAN or VUEXPAN, the increments of thermal strains can be defined as functions of predefined field variables, temperature, and state variables.
UEXPAN and VUEXPAN are called for all integration points of part elements where the definition of material or gasket behavior includes user-subroutine-defined thermal expansion.
The subroutines are used when the material’s thermal expansion behavior is too complex to model with the "EXPANSION" option in the Abaqus software environment. For example, the subroutines are used in problems where the thermal strains are complexly dependent on temperature, predefined field variables, and state variables, and there is a need to update these variables.
The user subroutine UEXPAN is called twice per element point in each iteration during coupled thermal-electrical-structural or coupled temperature-displacement analyses.