Abaqus steel material and structures | Practical examples
Composite Fatigue Simulation with Subroutine in ABAQUS (unidirectional) for 3D Element
Fatigue in composites refers to the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads or stress cycles over time. When a composite material is subjected to cyclic loading, small cracks or microdamage can form within the material, which may grow and lead to failure after a certain number of loading cycles. This is a significant consideration in the design and analysis of composite structures, especially in applications subjected to repeated stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, or civil engineering.
In one of our other packages, we have used the UMAT subroutine in Abaqus to simulate fatigue in composites in two-dimensional space. The current project is more comprehensive, as it addresses composite fatigue in both 2D and 3D spaces. So you can use it for the simulation of both shells and solids. In this project, you will first become familiar with simulating composite fatigue in 2D space using the Abaqus UMAT subroutine. Then, we will provide a complete UMAT code along with Abaqus files for extending the simulation to 3D space, enabling the 3D simulation of composite fatigue in Abaqus.
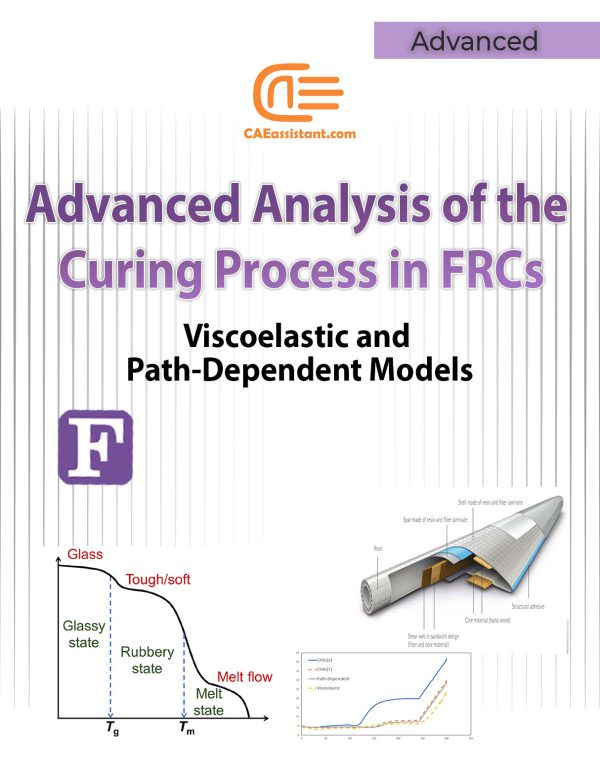
Using Viscoelastic and Path-Dependent Models for Analyzing the Curing Process in Fiber-Reinforced Composites With Abaqus subroutines
Hygrothermal effects on composite materials | Degradation in Fiber Reinforced Composites Abaqus Simulation: Python & Subroutines
In this tutorial, we explore the hygrothermal degradation composites using ABAQUS, a powerful tool for parallel finite element analysis. Industries like aerospace, marine, and automotive heavily rely on these composites due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. However, long-term exposure to moisture and temperature can degrade their mechanical properties, making an analysis of hygrothermal effects on composite materials essential for ensuring durability.
ABAQUS allows precise modeling of these environmental conditions through Python scripts and Fortran subroutines. This combination enables efficient simulations across multiple processors, offering insights into key elastic properties, such as Young’s modulus and shear modulus, under varying conditions. By leveraging the ABAQUS Python Scripting Micro Modeling (APSMM) algorithm and custom subroutines, engineers can predict the long-term performance of fiber-reinforced composites, optimizing design and enhancing material performance in critical sectors like aerospace and marine.
In the present Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis, we have presented the software skills that a person needs when he wants to perform a parallel finite element analysis such as a micro-macro scale analysis. The Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis covers all you need to write a python scripting code for noGUI environment and also Fortran code for the subroutine environment of Abaqus to execute a parallel finite element analysis via Abaqus software. You can download the syllabus of this package here.
MASTER COMPOSITE SIMULATION IN ABAQUS
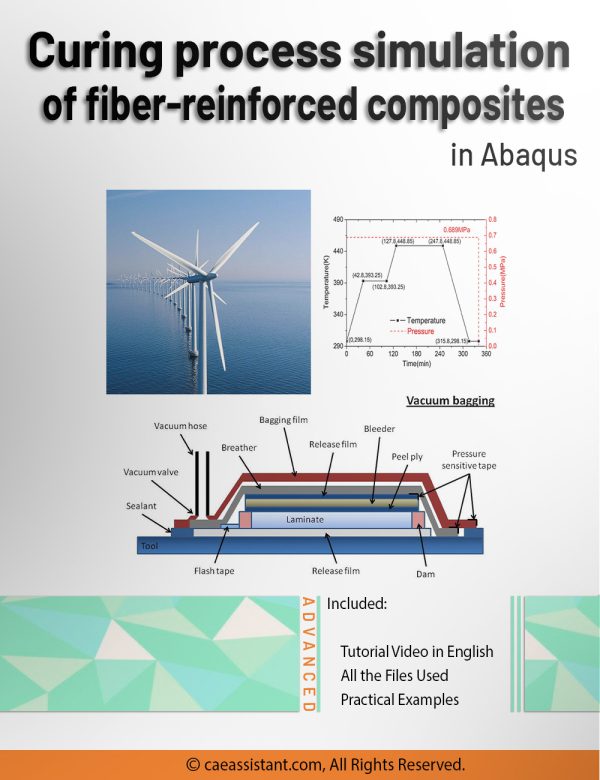
Abaqus Simulation of the Curing Process in Composites: A Specific Focus on the Pultrusion Method
Pultrusion is a crucial task for producing constant-profile composites by pulling fibers through a resin bath and heated die. Simulations play a vital role in optimizing parameters like pulling speed and die temperature to enhance product quality and efficiency. They predict material property changes and aid in process control, reducing reliance on extensive experimental trials. However, simulations face challenges such as accurately modeling complex material behaviors and requiring significant computational resources. These challenges underscore the need for precise simulation methods to improve Pultrusion processes. This study employs ABAQUS with user subroutines for detailed mechanical behavior simulations, including curing kinetics and resin properties. Key findings include insights into material property changes, and optimization strategies for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This research provides practical knowledge for implementing findings in real-world applications, advancing composite material production.
Notice that, pultrusion is a composite curing method, which may share some overlapping features with our Intermediate and Advanced curing packages. However, what sets pultrusion apart is that the composite passes over a heated die during the process. In this project, the die has also been modeled, with environmental heat applied to it using convection and a film subroutine. The heat is subsequently transferred to the sample through contact with the die. Afterward the die is removed. All these procedure is modeled in this project, with Abaqus CAE step-by-step. In contrast, in our Intermediate and Advanced packages for the oven curing of prepregs, no die has been modeled. The heat is applied without convection and, for simplicity, the heat is treated as a first-type boundary condition, which introduces some errors.
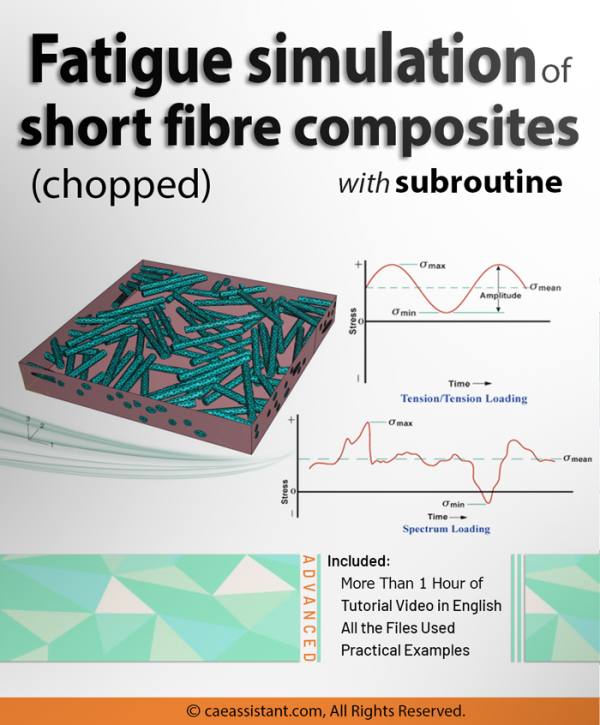
Note: The files and video which explains how to use the code are available. The PDF file will be available two weeks after purchase.Short fiber composite damage (Mean Field Homogenization Model)
Curing process simulation in Abaqus
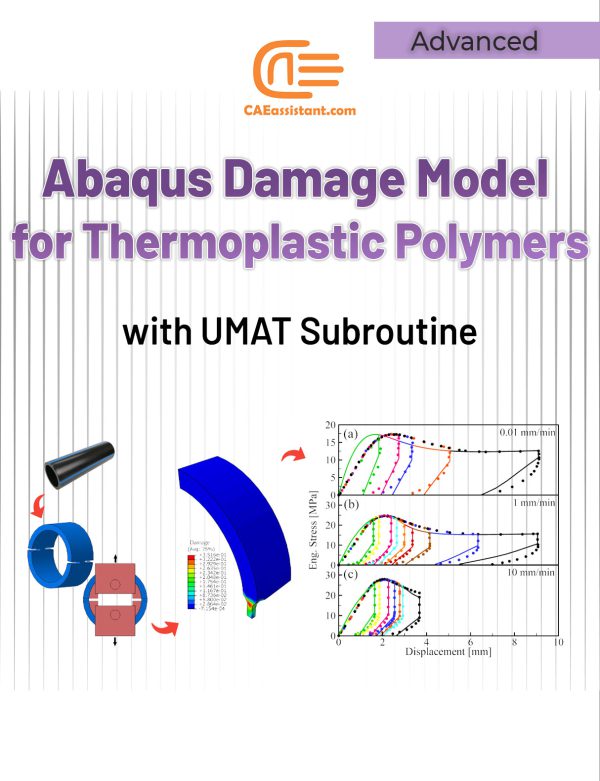
Damage Properties of Thermoplastic Polymers with UMAT Subroutine
Composite Pressure Vessel simulation in ABAQUS
Composite pressure vessel analysis with Semi-Geodesic winding
Full Composite fatigue Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
Full Composite damage Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
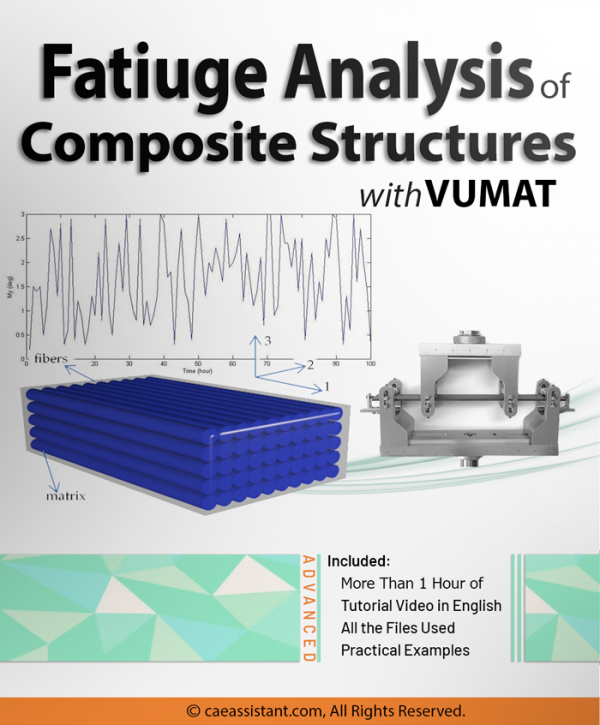
Composite Fatigue Simulation with VUMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS
Composite simulation for experts-Part-3
Pay attention to the syllabus and availability file details. some of the packages are fully available and some of them are partially available. If this is partially available it takes at least two months to be completely available.
If you are a graduate or Ph.D. student, if you are a university professor or an expert engineer in the industry who deals with simulation software, you are definitely familiar with the limitations of this software in defining the material properties, loading or meshing, interaction properties, and etc. You have certainly tried to define the properties of materials based on advanced fracture theories in finite element software and are familiar with their limitations and problems. Now, here is your solution. Start writing subroutines in finite element software and overcome the limitations. With the tutorials in the Golden Package, you will learn how to write 8 subroutines in Abaqus software professionally.Composite simulation for experts-Part-2
If you are a researcher, student, university professor, or Engineer in the company in the field of composite materials, this training package in simulating these materials in Abaqus software is the best selection. This training package is the second part of the composite for expert package and is focusing on the Simulation of woven composite damage in Abaqus, Composite Fatigue Simulation, Analysis of Composite pressure vessel with Semi-Geodesic winding, Simulation of composite Hashin damage in 3d continuum element (UMAT-VUMAT-USDFLD), and Abaqus composite modeling of Woven & Unidirectional + RVE method.