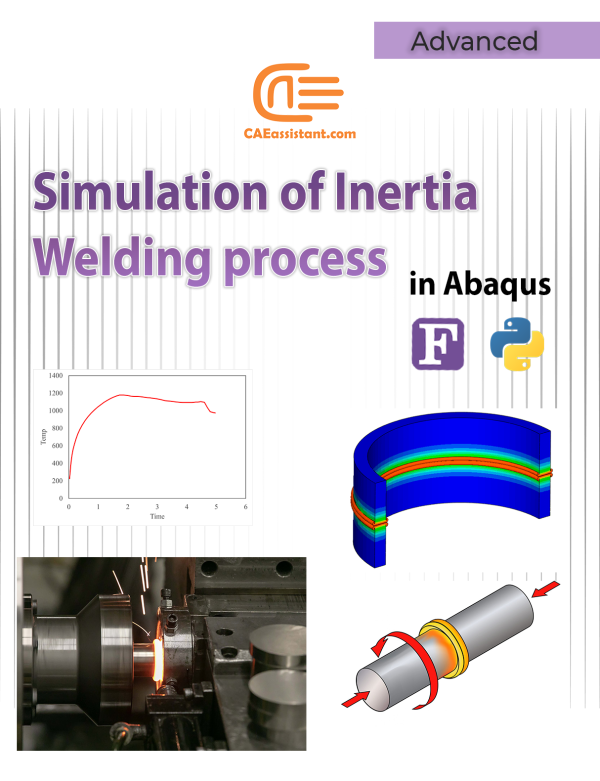
Simulation of Inertia Welding process in Abaqus | Fortran Subroutines and Python Scripts
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to simulating inertia friction welding process using Abaqus, a powerful Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tool. Inertia welding process, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, is a solid-state process that joins metal parts using kinetic energy. The simulation focuses on modeling frictional heating, temperature distribution, and material behavior through integrated Fortran subroutines and Python scripts. These scripts automate tasks such as remeshing and model generation, enhancing efficiency. Key steps include defining axisymmetric models, applying material properties, and simulating thermal and mechanical interactions during the inertia welding process. This guide equips researchers and engineers with a robust methodology for inertia welding simulation, to optimize welding parameters and analyze weld quality.
Using Viscoelastic and Path-Dependent Models for Analyzing the Curing Process in Fiber-Reinforced Composites With Abaqus subroutines
Brittle Damage in Abaqus | Brittle Cracking Abaqus
Brittle materials, such as ceramics, glass, and concrete, break or fracture easily under stress without extensive deformation. Unlike ductile materials, brittle materials snap suddenly, lacking the flexibility to rearrange their atomic structure under strain. These materials have low tensile strength but strong compressive resistance, making them vulnerable to brittle cracking Abaqus simulations when stretched or pulled.
Understanding brittle material damage is crucial in safety-critical fields like civil engineering, aerospace, and manufacturing, where unexpected fractures can lead to catastrophic failures. Simulations help engineers predict when and how brittle materials may break, guiding safer design choices. Brittle cracking Abaqus can be modeled using various methods, including the Johnson-Holmquist (JH) model, XFEM, and energy-based approaches, each suited to different types of loading conditions.
For dynamic, high-strain applications like impacts, the JH model is effective, particularly in Abaqus/Explicit with specific damage parameters. For general crack modeling, XFEM is versatile, allowing cracks to form naturally without predefined paths. The energy-based method is useful for slow-loading scenarios, defining an energy threshold for fracture initiation. Each method requires careful input of material properties, mesh refinement, and load conditions to reveal potential failure points and improve material performance in real applications.
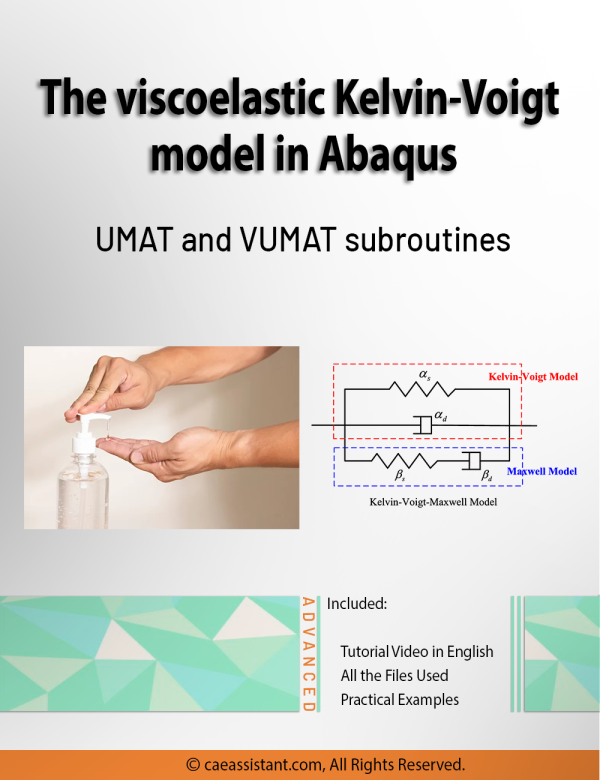
Abaqus Kelvin Voigt Model (Viscoelastic) Simulation Using UMAT and VUMAT Subroutines
This research presents a precise three-dimensional mechanical response of viscoelastic materials using Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model. We performed this kelvin voigt model Abaqus simulation using both UMAT and VUMAT subroutines for standard and explicit solvers.
The behavior of viscoelastic materials is a state between the behavior of a liquid and a solid. In other words, they behave both like liquids and solids. That is to say, there are many natural and synthetic materials that are classified as viscoelastic materials; From the biological structures of the body such as skin, cartilage and tissue to concrete, foams, rubbers, and synthetic polymers. Due to these unique properties, viscoelastic materials have many applications.
In this regard, the primary goals of this study include the development and implementation of an accurate three-dimensional Abaqus kelvin voigt viscoelastic model, and the integration of viscoelastic properties into the analysis, which can improve the prediction of viscoelastic materials response under different boundary and loading conditions.
This tutorial, by customizing the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines to simulate flexible samples behavior, contributes to the advancement of viscoelastic materials design and analysis.
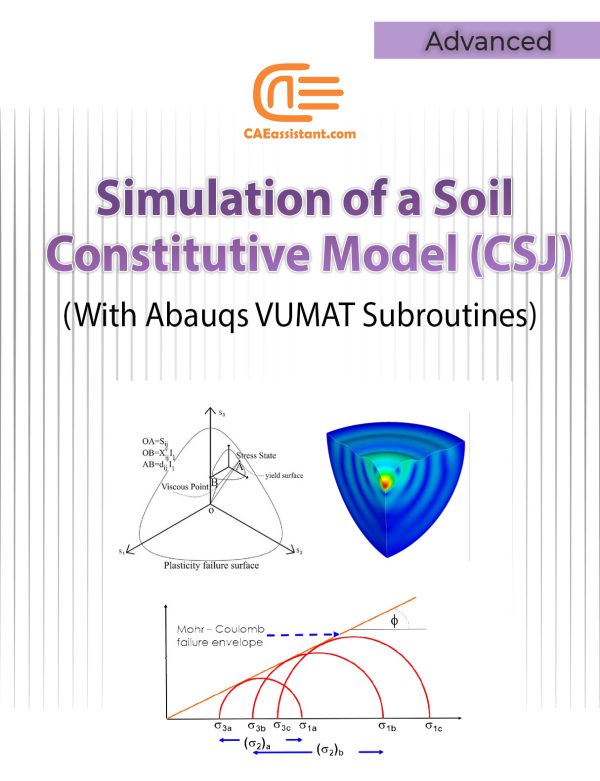
Implementation of Soil Constitutive Models in Abaqus | With a Special Focus on CSJ Models
Constitutive model implemented in calculation code, play an important role in the material behaviors prediction. In the field of geotechnical engineering there are numerous soil constitutive models. By installing these models in a finite element code such as Abaqus, their development, efficiency and advancement can be increased. Also, more and more complex engineering problems can be solved by this method. But to do this, you need a proper understanding of the mathematical and programming basics of these models. This tutorial focuses on implementing advanced constitutive models in Abaqus, particularly for simulating soil behavior. Focusing on the CJS model, this tutorial tries to teach how to work and how to program these models in Abaqus code. It includes detailed explanations of VUMAT and UMAT subroutines and practical examples of implementing the CJS model.
Note: In this project, we have discussed the UMAT and VUMAT subroutines, their specifications, and features. You will become familiar with the implementation of both UMAT and VUMAT subroutines. However, the specific focus of this project, for which we have provided the necessary files and run the analysis, is on using the VUMAT model. If you need to use Abaqus for this project with the standard solver, you will need to write the UMAT subroutine yourself.
Concrete Damage Plasticity Simulation of FRP-Confined Concrete Columns in Abaqus
This tutorial package provides a comprehensive guide to implementing USDFLD subroutine in the context of Concrete Damage Plasticity Material Model. The tutorial focuses on key modeling aspects such as definition of concrete material properties using Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) Model. A theoretical background of the model will be presented and detailed explanation of the definition of all material properties will be given. The package will also explain the usage of the USDFLD subroutine to modify concrete material properties dynamically during simulation. Examples of implementing USDFLD in the context of CDP will be presented with focus on material properties that vary in function of pressure and axial strain defined as field variables.
All other modeling details will also be explained including boundary conditions, meshing, loading, and interactions.
By following the detailed steps in this tutorial, you will be able to create and analyze advanced FEM simulations in Abaqus with a focus on concrete having properties that vary during simulation.
Computational Predictions for Predicting the Performance of Structure
This package focuses on developing and applying predictive models for the structural analysis of steel and concrete components subjected to fire and subsequent earthquake loading. To accurately simulate the complex behavior of these structures, finite element analysis (FEA) using ABAQUS is employed. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept. However, due to the computational demands of FEA, various machine learning techniques, including regression models, Gene Expression Programming (GEP), Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS), and ensemble methods, are explored as surrogate models. These models are trained on large datasets of FEA results to predict structural responses efficiently. The performance of these models is evaluated using statistical metrics such as RMSE, NMSE, and coefficient of determination.
Damage Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Tunnels under Internal Water Pressure
This tutorial package equips you with the knowledge and tools to simulate the behavior of reinforced concrete tunnels (RCTs) subjected to internal water pressure. It combines the power of finite element (FE) modeling with artificial intelligence (AI) for efficient and accurate analysis. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques such as regression, GEP, ML, DL, hybrid, and ensemble models, we significantly reduce computational costs and time while achieving high accuracy in predicting structural responses and optimizing designs.
A Comprehensive Tutorial for Soft Body Impact Composites Simulation
This comprehensive tutorial package focuses on simulating soft body impact composites on laminated composite materials using the Finite Element Method (FEM) in Abaqus. The course covers key topics such as soft body modeling, metal material modeling, composite material modeling, composite to composite interface modeling, metal to composite interface modeling, interaction between soft bodies and FML, interaction between layers, and Python scripting for parametric studies. Users will explore different material models and learn about impact failure mechanisms, including matrix failure, fiber failure, shear failure, and delamination. The course is structured into lessons that cover theoretical aspects, followed by hands-on workshops to model soft body impacts, apply material properties, and analyze post-processing results such as forces, displacements, and energy dissipation. It also includes an advanced section on Python scripting, enabling users to automate parametric studies for complex simulations. This package is ideal for engineers, researchers, and students looking to deepen their understanding of soft body impact phenomena and composite material behavior.
Computational Modeling of Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) Behavior
This course equips engineers with the tools to design and analyze Steel Plate Shear Wall (SPSW) and Reinforced Concrete Shear Walls (RCSW) subjected to explosive loads. Traditional Finite Element (FE) simulation is time-consuming and requires numerous samples for accurate results. This package offers a more efficient approach using Artificial Intelligence (AI) models trained on FEA data. You'll learn to develop FE models of SPSW and RCSW in ABAQUS software, considering material properties, interactions, and boundary conditions. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept.
We then delve into AI modeling using MATLAB. Explore various methods like regression, Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and ensemble models to predict the behavior of SPSW and RCSW under blast loads. Statistical analysis helps compare model accuracy. By combining FE analysis with AI models, you'll gain a powerful tool for designing blast-resistant structures while saving time and resources.
Abaqus advanced tutorials on concrete members
Welcome to the "Abaqus Advanced Tutorials on Concrete Members" course, designed to provide civil and structural engineers with cutting-edge expertise in finite element modeling (FEM) and simulation using Abaqus. This advanced-level course focuses on the detailed modeling of complex concrete and composite columns under various loading conditions. Topics include the simulation of tubed reinforced concrete columns, concrete-filled double skin steel columns, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite columns. Participants will delve into axial and eccentric compression loading scenarios, with a special focus on hollow and tapered cross-sections. The course also emphasizes comparing simulation results with experimental data from published research, ensuring practical relevance and accuracy. By the end of the course, learners will be equipped with the necessary skills to tackle advanced structural analysis challenges using Abaqus, reinforcing their understanding of concrete member behavior in real-world applications.
Hygrothermal effects on composite materials | Degradation in Fiber Reinforced Composites Abaqus Simulation: Python & Subroutines
In this tutorial, we explore the hygrothermal degradation composites using ABAQUS, a powerful tool for parallel finite element analysis. Industries like aerospace, marine, and automotive heavily rely on these composites due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. However, long-term exposure to moisture and temperature can degrade their mechanical properties, making an analysis of hygrothermal effects on composite materials essential for ensuring durability.
ABAQUS allows precise modeling of these environmental conditions through Python scripts and Fortran subroutines. This combination enables efficient simulations across multiple processors, offering insights into key elastic properties, such as Young’s modulus and shear modulus, under varying conditions. By leveraging the ABAQUS Python Scripting Micro Modeling (APSMM) algorithm and custom subroutines, engineers can predict the long-term performance of fiber-reinforced composites, optimizing design and enhancing material performance in critical sectors like aerospace and marine.
In the present Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis, we have presented the software skills that a person needs when he wants to perform a parallel finite element analysis such as a micro-macro scale analysis. The Abaqus tutorial for parallel finite element analysis covers all you need to write a python scripting code for noGUI environment and also Fortran code for the subroutine environment of Abaqus to execute a parallel finite element analysis via Abaqus software. You can download the syllabus of this package here.
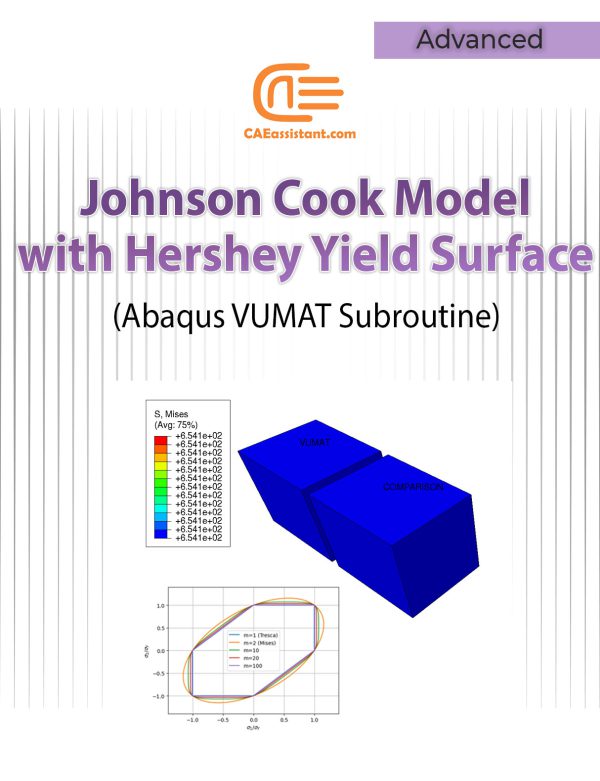
Modified Johnson Cook viscoplastic model with the Hershey yield surface | VUMAT Subroutine for 3D continuum elements
This project offers a set of Abaqus models for 3D continuum elements, integrating a VUMAT subroutine that implements the Modified Johnson Cook (MJC) viscoplastic model and the Hershey yield surface. The MJC model simulates material behavior under varying strain rates and temperatures, while the Hershey yield surface predicts complex yielding behavior. Together, they provide highly accurate simulations of materials under extreme conditions such as impacts and high temperatures. Ideal for industries like automotive, aerospace, and defense, this package supports critical applications like crash testing, metal forming, and ballistic analysis. The model has been implemented for 3D continuum elements.
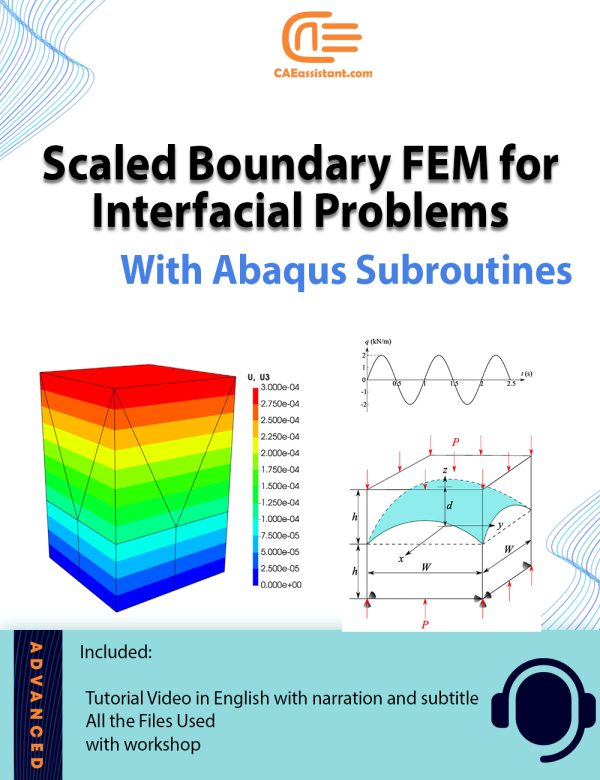
Note: The inp and Fortran files are only applicable in Linux.Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method (SBFEM) Modeling Files for ABAQUS
The Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method (SBFEM) enhances traditional Finite Element Analysis (FEA). It provides flexibility in handling complex geometries and interfaces. Integrated into ABAQUS, SBFEM allows for the creation of polyhedral elements, reducing meshing challenges. It effectively manages non-matching meshes and complex boundary conditions, particularly in interfacial problems like contact mechanics and fracture analysis. ABAQUS supports custom user elements (UEL), enabling direct integration of SBFEM with advanced solvers, improving efficiency and expanding its applicability to complex engineering problems. The open-source implementation allows for customization, making SBFEM in ABAQUS a powerful tool for precise and efficient simulations. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios requiring advanced FEA.
Bicycle Stress Analysis with Ansys Mechanical
This tutorial package offers a comprehensive introduction to linear-static analysis using Ansys Mechanical, focusing on a bicycle stress analysis with the case study which is a bicycle crank made from Aluminum 6061-T6. Whether you're a beginner looking to get started with FEA or an experienced engineer seeking to refine your skills, the package provides a strong foundation in the fundamental techniques needed to succeed in real-world applications.
The tutorial covers the essential steps in finite element analysis (FEA), including the model setup, simulation, and interpretation of results. By leveraging Ansys Mechanical, users will perform a full simulation on the crank geometry to assess stress distribution, deformation, and safety under load conditions. Key topics include mesh generation along with mesh refinement, and the application of boundary conditions. The tutorial guides users through material property assignment, mesh independence, and validation with hand calculations, ensuring accuracy.
Ansys-specific features, including post-processing tools for analyzing total deformation, bending stress, and the factor of safety, are thoroughly demonstrated. This package also highlights the power and efficiency of Ansys Mechanical, emphasizing its user-friendly interface and ability to handle complex simulations with greater precision compared to competitors, making it one of the best-in-class structural analysis FEA software.
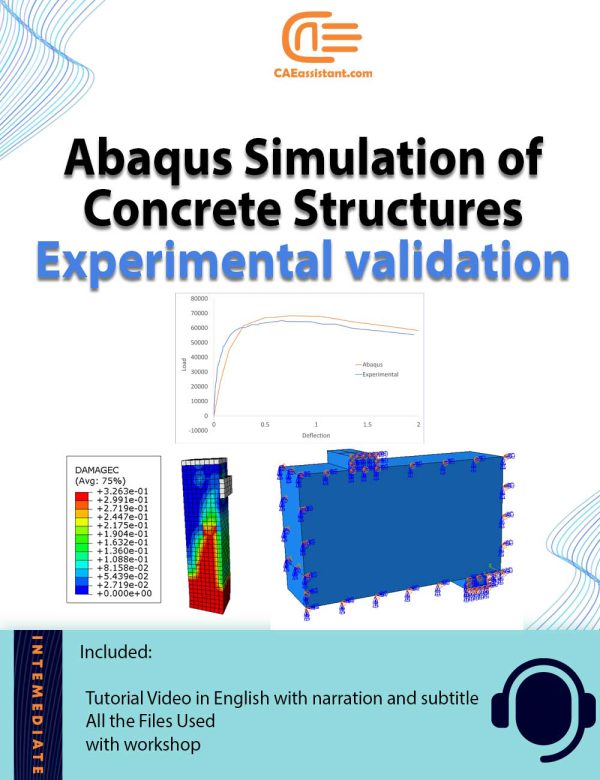
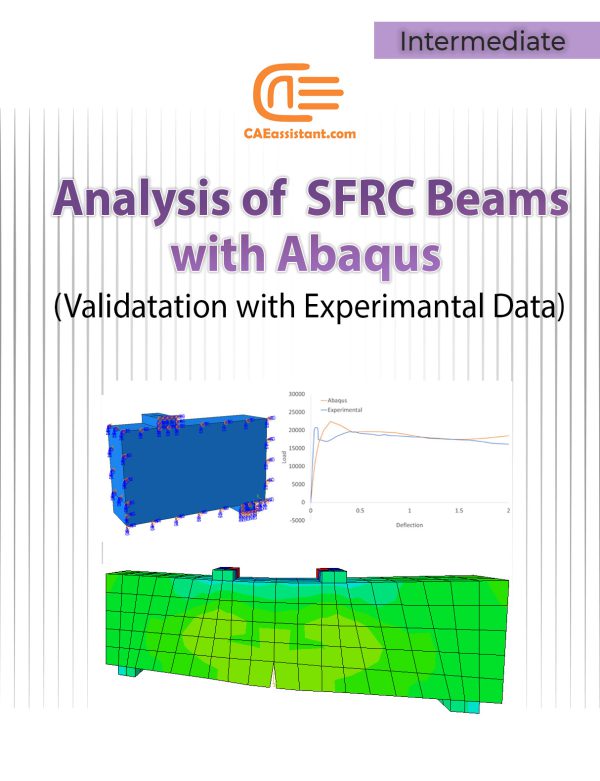
Analysis of Plain and Reinforced Concrete Structures with ABAQUS | Validation with Experiments
This comprehensive package offers four different workshops focused on the analysis of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete structures using ABAQUS. Designed for professionals, researchers, and students, it provides hands-on learning in modeling, simulating, and validating concrete structures under various conditions. Each workshop dives into specific aspects of concrete behavior, from flexural to compressive strength, incorporating the latest sustainable practices through the use of recycled materials. The package ensures mastery of ABAQUS, offering practical insights and a cost-effective path to advanced concrete analysis and safer, more durable infrastructure design.
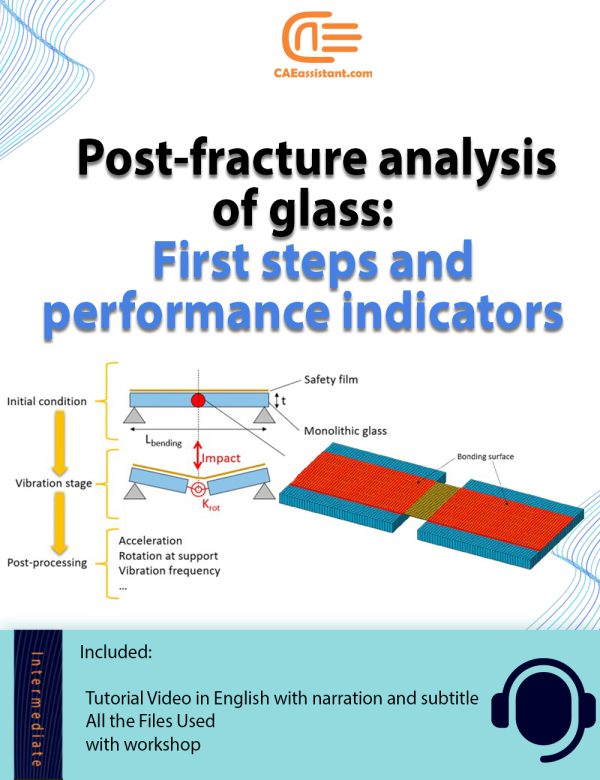
Note: Only the first workshop has video.Glass Fracture Analysis with Abaqus | Post-Fracture
This tutorial explores a finite element method (FEM) simulation using Abaqus to analyze the post-fracture behavior of structural glass members retrofitted with anti-shatter safety films. In particular, it focuses on simulating and calibrating the vibration response of cracked glass elements under repeated impacts and temperature gradients, contributing to a comprehensive analysis of critical phenomena that take place in the post-fracture stage. This tutorial follows the methodology outlined in the research article “Effects of post-fracture repeated impacts and short-term temperature gradients on monolithic glass elements bonded by safety films”.
Key aspects include modeling glass fracture, assigning material properties, and defining boundary conditions to assess the vibration frequency and load-bearing capacity of cracked monolithic glass members. Additional topics cover basic concepts of dynamic identification techniques, definition of performance indicators for glass retrofit efficiency, and frequency sensitivity analysis of monolothic retrofitted glass elements under various operational and ambient conditions. The simulation results help quantify the expected contribution and residual strength of safety films in post-fracture scenarios, providing a robust framework for structural engineers to extend this investigation to other glass configurations.
This tutorial is ideal for users who want to understand FEM modeling in Abaqus and perform detailed simulations involving complex material interactions, with a focus on practical applications in glass retrofit technology.
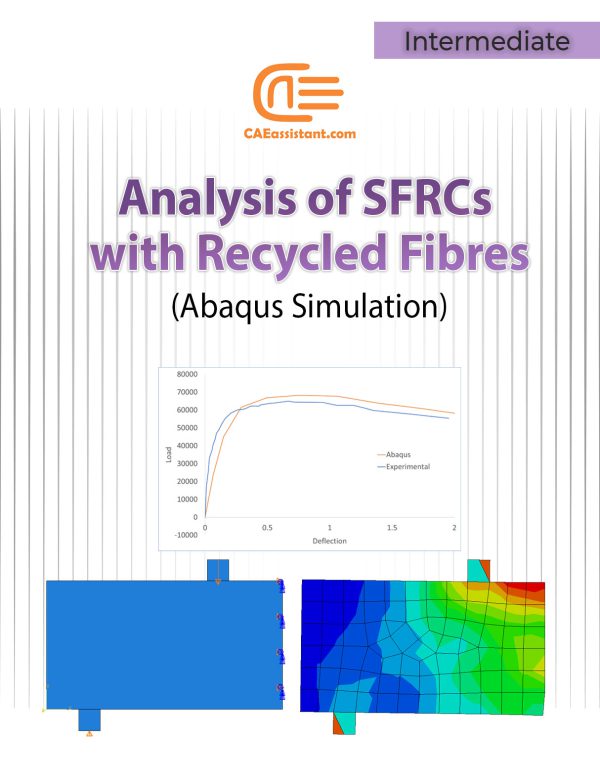
Stress-strain characteristic of SFRC using recycled fibres | An Abaqus Simulation
This training utilizes Abaqus software to simulate and analyze the stress-strain characteristics of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) using recycled fibers. The importance of this work lies in its contribution to sustainable construction practices by validating the effectiveness of recycled steel fibers in enhancing concrete's mechanical properties. Through advanced finite element analysis (FEA), the project addresses challenges in accurately modeling SFRC's post-cracking behavior, ensuring that the simulations are aligned with experimental data for reliable results. Abaqus' capabilities in nonlinear material modeling, stress-strain simulation, and principal stress analysis significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of the research, making it a valuable tool for both academia and industry.
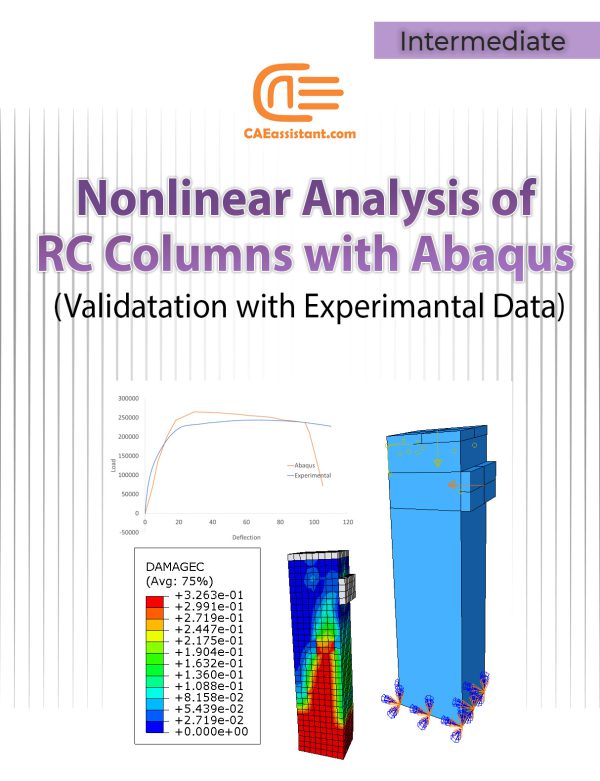
Nonlinear Analysis of RC Columns Using ABAQUS | Validation with Experimental Data
Reinforced Concrete (RC) columns are critical components in civil engineering, essential for the stability of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure during seismic events. This study leverages ABAQUS, a powerful finite element analysis (FEA) software, to simulate the seismic performance of RC columns. By modeling columns in 3D and using ABAQUS's advanced tools, we replicate experimental conditions to analyze their behavior under seismic loads. Numerical simulations offer the advantage of exploring various scenarios quickly and cost-effectively, while also allowing for extensive parametric studies. The study details how ABAQUS models both concrete and steel reinforcement, accounts for interaction effects, and applies appropriate loading and boundary conditions. The simulations provide valuable insights into failure modes, load-displacement responses, and crack patterns, offering a comprehensive understanding of RC column performance in seismic scenarios.