Simulation Methods & Techniques
Low-Velocity Impact simulation
Low-velocity impact refers to the collision between objects at relatively low speeds. While the impact energy may be lower compared to high-speed impacts, low-velocity impacts can still cause significant damage and deformation. Assessing the effects of low-velocity impact is crucial for various industries to ensure the structural integrity, safety, and performance of their products. For example, in the automotive industry, understanding the response of vehicles to low-velocity impacts is essential for designing crashworthy structures and improving occupant safety. In aerospace, assessing the impact resistance of aircraft components, such as fuselage panels or wings, helps ensure their ability to withstand ground handling incidents or bird strikes. In this package, you will learn how to do low-velocity impact simulations with several practical examples.
High Velocity Impact Simulation
High-velocity impact refers to the collision between two bodies at extremely high speeds, typically involving projectiles and targets. It is a phenomenon of great interest in various fields, including defense, aerospace, and automotive industries. High-velocity impact simulation in Abaqus is a computational approach used to analyze and predict the behavior of materials and structures subjected to such impacts. Abaqus, a powerful finite element analysis software, enables engineers and researchers to model and simulate the complex interactions between impacting bodies, accurately predicting factors like stress, strain, deformation, and damage. By simulating high-velocity impacts in Abaqus, engineers can gain valuable insights into the performance and integrity of materials and structures, ultimately aiding in the design of safer and more resilient systems. In this package, you will learn how to do these simulations in many practical examples.
Hypermesh Course for Beginners
This training package includes workshops that help you to learn about basics of hypermesh and how to use it. This is the most comprehensive tutorial containing ways to do the basic designing, importing and exporting abaqus file.
The subjects such as creating lines,nodes,2D mesh, surfaces, creating tetramesh, creating 3d bodies,enhancing mesh quality etc are covered in this tutorial.
Full Composite fatigue Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
This package is designed to instruct users on how to utilize the composite fatigue modeling Add-on, which removes the need to write a subroutine for composite fatigue modeling. Instead, users can select the composite type, input material properties, and generate the subroutine by clicking a button. The Add-on includes four types of composites, and the generated subroutine for all types is the UMAT. These four types are Unidirectional, Woven, short fiber composites (chopped), and wood. The fatigue criteria used for each type are the same as its respective package. For example, the fatigue criteria for woven composites are identical to that used in the "Simulation of woven composite fatigue in Abaqus" package. This Add-on provides a simple graphical user interface for composite fatigue modeling, which can be utilized for both academic and industrial applications.
Full Composite damage Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)
This package will teach you how to use the composite damage modeling Add-on. The Add-on eliminates the need for writing a subroutine for composite damage modeling. Instead, you only need to select the desired composite type, input the material properties, and click a button. The Add-on will then generate the subroutine for you. The Add-on includes four types of composites: Unidirectional, Woven, short fiber composites (chopped), and wood. The generated subroutine for all types is the VUSDFLD. The damage criteria used in each type is the same as the one used in its respective package. For instance, the damage criteria for the woven composite is identical to the one used in the "Simulation of woven composite damage in the Abaqus" package. This Add-on offers a user-friendly graphical user interface for composite damage modeling, which can be used for academic and industrial purposes.
Optimization in ABAQUS
Notice: 2 hours of the package is available now; during 1-month after purchase, it will be completed.
Optimization is a process of finding the best solution to a problem within a set of constraints. It involves maximizing or minimizing an objective function while satisfying a set of constraints. Optimization in Abaqus involves the use of advanced algorithms and techniques to improve the design of structures and systems. Abaqus provides a range of optimization tools, including topology optimization, size optimization, and shape optimization. These tools help in improving the performance of structures by reducing their weight, increasing their stiffness, and minimizing their stress levels. In this package, all types of optimization, such as Topology, will be discussed; after each lesson, there will be workshops to help you to understand optimization with practical examples.
Script to transfer load from CFD to structural model in Abaqus
FEA offers various loading types, such as force, pressure, and temperature, which can be applied to different parts of an object, such as points, surfaces, edges, nodes, and elements. Therefore, applying accurate loading conditions on these features is necessary for reliable simulation results and the safe design of structures. Sometimes, the loading conditions are obtained by another analysis, such as CFD, and need to be transferred and applied to the structural model for the structural analysis; during this transfer, the loads might not be appropriately applied to the model, especially when the loads are complicated like the pressure profile of a space rocket. So in this package, a Python script is presented to solve this issue and transfer the loads properly to the structural model.
Abaqus Bolt Load Tutorial: Simplify Bolt Modeling in Abaqus
Bolts and joints play a vital role in the stability and structural integrity of various engineering structures, including buildings, bridges, and machines. Bolts are used to fasten or connect different components together, providing a means of transferring loads and ensuring the continuity of load paths. Joints connect structural elements, allowing them to move and deform while maintaining their overall stability. Proper design and selection of bolts and joints are crucial to ensuring the safety and durability of the structure. Factors such as the type of load, the materials used, and the environmental conditions must be considered when selecting bolts and joints. Failure to properly design and install bolts and joints can result in catastrophic failure of the structure. In this package, you will learn how to model bolts and joints, simulating the failure of connections and other things with practical examples.
Eulerian Abaqus and CEL modeling
The Eulerian method is a numerical technique used to analyze fluid mechanics problems. In this approach, the fluid is treated as a fixed grid, where the nodes remain stationary while the fluid flows through them. The Eulerian Abaqus method can be used to analyze fluid-structure interactions, such as fluid impact on structures or the behavior of fluids in containers. To use the Eulerian method in Abaqus, the desired geometry must first be meshed using Eulerian elements. The material behavior of the fluid is then defined using appropriate equations of state. Finally, the boundary conditions and loading are applied, and the system is solved using the appropriate numerical method, such as the finite element method. This package will teach you how to use this method and various practical examples. Also, this package covers several practical examples in Abaqus CEL method.
Cold spray & Shot peening simulation in Abaqus
Cold spray is a process used to deposit materials onto a substrate by accelerating fine powder particles to high velocities using compressed gas. Upon impact with the substrate, the particles undergo rapid plastic deformation, disrupting surface oxide films and promoting bonding between metal surfaces. Unlike thermal spray processes, cold spray avoids thermal degradation and partial oxidation of the coating material, resulting in coatings with low porosity and oxygen content. The process is highly efficient, with deposition efficiencies often exceeding 90%. Shot peening is a metal treatment process that involves bombarding a surface with small, round metallic (usually steel), ceramic, or glass beads at high velocity. This process creates small indentations on the surface, which in turn introduces compressive residual stress into the material. These two processes are different and use for separate purposes but their simulations are the same.
Cold spray is particularly important in applications where thermal degradation or oxidation of the coating material is a concern or where the coating is required to be thick and free from defects. In this package, you will learn how to simulate this process with different methods, such as ALE and SPH, with different materials. For example, Cold spray simulation of steel particles impacts on the Inconel target using ALE method.
Abaqus Explosion
An explosion is a rapid and violent release of energy, usually accompanied by a loud noise, heat, and pressure waves. Explosions can be caused by a variety of factors such as chemical reactions, combustion, nuclear reactions, or mechanical failure. Explosions can cause severe damage to buildings, infrastructure, and human life. To minimize the impact of such incidents, accurate and reliable simulation of explosions is crucial. Explosion simulation involves modeling the complex interactions of blast waves, shock waves, and debris with the surrounding environment. By simulating explosions, engineers and scientists can identify potential risks and develop effective safety measures. In this package, you will learn how to model explosions in different situations with practical examples, such as Air blast explosion simulation inside an RC room and Subsurface explosion simulation on buried steel pipelines.
9 Practical Workshops for SPH in Abaqus💡 | Abaqus SPH Tutorial
Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Tutorial: Abaqus SPH (Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics) is a numerical method used in this software to model fluid-structure interaction problems. SPH in Abaqus is a meshless approach that uses a set of particles to discretize the fluid domain. The Abaqus SPH modeling tutorial is particularly useful for problems with large deformations, fragmentation, and free surface effects.
It can be used in combination with other Abaqus features, such as finite element analysis, to model coupled fluid-structure systems. This Abaqus SPH tutorial, created by CAE Assistant group, can help you understand and apply this method through practical examples, some of which include projectile impact simulation on a cementitious material, TNT explosion simulation inside a rock using the SPH method, bullet movement through a water pipe in Abaqus, and bird strike simulation in Abaqus.
Ductile Damage Abaqus model for 3D continuum element (VUMAT Subroutine)
In this package, the continuum damage mechanics framework for ductile materials is implemented and developed in ABAQUS by VUMAT Subroutine.
Constitutive modeling is treated within the framework of continuum damage mechanics (CDM) and the effect of micro-crack closure, which may decrease the rate of damage growth under compression, is incorporated and implemented.
The present package has been organized as follows. In the Introduction section, the basis of the CDM in ductile materials is explained, and the applications of the CDM are stated. In the Theory section, the CDM model formulation is briefly reviewed, and with micro-crack closure, the effect is described. In the Implementation section, an algorithm for the numerical integration of the damage constitutive equations is presented. In the VUMAT Subroutine section, the flowchart of the subroutine, and the subroutine structure, step by step, are explained in detail. How to run the VUMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS will be presented in this section. In the Verification section, the validation and verification of the numerical implementation will be evaluated, and the stability, convergence and accuracy of the results will be investigated. In the Application section, the applications of using the ductile damage model in mechanical processes are presented, and the prediction of damage growth and failure in mechanical processes is investigated.
Composite Fatigue Simulation with VUMAT Subroutine in ABAQUS
This training package consists of four chapters that help engineers and researchers in the industry to understand the fundamental concepts and necessary tools for simulating composite fatigue using VUMAT subroutine in ABAQUS. The first chapter provides an overview of the fatigue behavior of composite materials, including the factors contributing to fatigue failure. The second chapter explores the failure mechanisms of composite materials and the types of damage that can occur. The third chapter discusses the effects of fatigue on composite materials, including how it affects the material's properties and performance. Finally, the fourth chapter focuses on using the VUMAT subroutine in ABAQUS for composite fatigue analysis, including the material models and criteria used to simulate the behavior of composite materials under various loading conditions. By mastering the concepts and tools presented in this package, engineers can develop more durable and reliable composite structures that can withstand cyclic loading over extended periods of time.
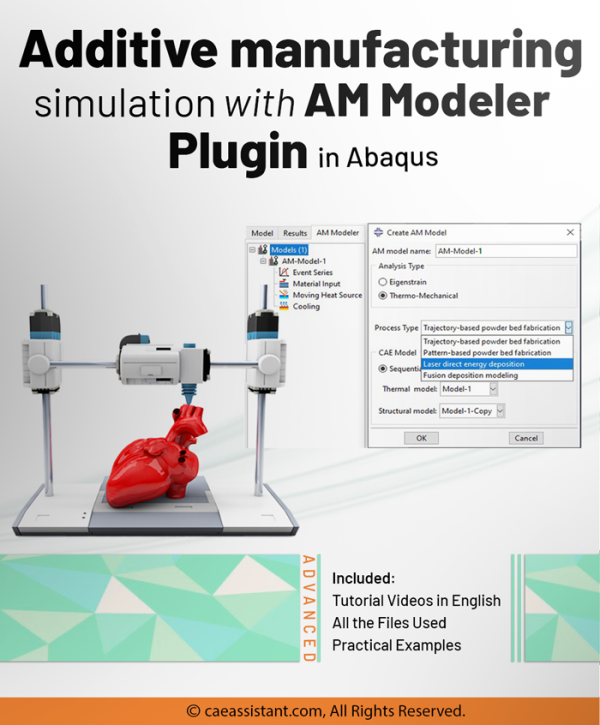
Additive manufacturing simulation with Abaqus AM modeler plugin
3D printing is the layer-by-layer creation of three-dimensional objects using materials such as plastic or metal, based on a digital design. Simulation of the 3D printing process involves software that predicts and enhances the printing process for efficient and accurate production. This training package includes the use of the Abaqus AM Modeler plug-in, which allows for selecting the type of 3D printing and conducting the simulation without coding. Two workshops will be taught to master the use of this plug-in: "Sequential Thermomechanical Analysis of Simple Cube One-Direction with LPBF 3D Printing Method Using the Trajectory-Based Method with AM Plug-In" and "3D Printing Simulation with Fusion Deposition Modeling and Laser Direct Energy Deposition Method with AM Plug-In".
Steel Damage types in Abaqus
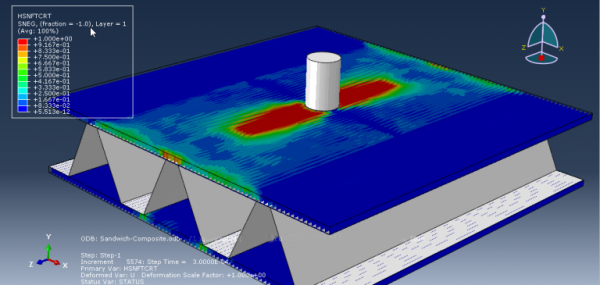
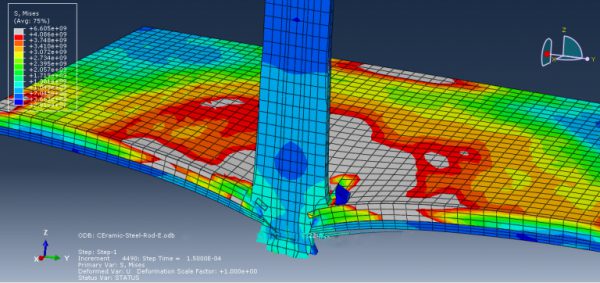
Steel materials are everywhere and used in almost every structure, from the building you live into the car you drive. Therefore, it’s essential to know the steel properties and behaviors when it’s under different loading conditions such as compression, tension, cyclic load, impact, etc. moreover, knowing the damage mechanism of steel structures helps to have better designing. In this tutorial package, you will learn how to analyze steel structures when they’re damaged with practical examples. There are five workshops here that could teach you the damage mechanism of steel structures: Simulation of bolt failure on the steal beam, reinforced concrete containment damage mechanism under internal explosion, tensile test of a steel specimen, impact on ceramic plate reinforced by steel plate, water jet cutting simulation.
Water Simulation in Abaqus
Water is the primary component of the Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living things. Therefore, we build dams to store the water and transfer it through piping systems to use it for daily activities and produce energy. In industries, we use it as a cooler, solvent, hydroforming, cutting, etc. In this package, there are nine practical examples, such as the ones mentioned to teach you how to simulate water in Abaqus. These examples are explosions in the depth of the water, gravity dam simulation subjected to the underwater explosion, ball impact to the water, water jet cutting, etc.
Acoustic simulation in Abaqus
The study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids, including issues like vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound, is the focus of the physics subfield of acoustics. A shock wave is a sort of disturbance that propagates across a medium faster than the local speed of sound. In industry, we use acoustic loading in cases such as hydraulic forming, SONAR, seismology, acoustic emission, vibration analysis, engine testing, etc. In this package, you will learn how to model acoustic loadings and shock loadings in four workshops: Deformation behavior of a stiffened panel subjected to underwater shock loading, Acoustic method-based numerical simulation of the electro-hydraulic forming process, Failure modes of concrete gravity dams simulation exposed to an underwater explosion, and Simulation of hull Coupled acoustic-structural response subjected to an underwater explosion.
Simulation of composite Puck damage in 3d continuum element in Abaqus (UMAT-USDFLD-VUMAT)
The Puck criterion is an essential damage model for composite materials, considering both fiber and matrix failures simultaneously. It provides a practical way to predict the onset of damage in composites under various loading conditions. This training package is focused on simulating composite PUCK damage in 3D continuum elements using UMAT, VUMAT, and USDFLD subroutines in Abaqus. It covers different types of failure in composites, including fiber failure, matrix cracking, delamination, and interfacial failure, as well as criteria for predicting failure modes in composites that are dependent or not dependent on each other, such as the Tsai-Wu and Tsai-Hill criterion, respectively. Additionally, the package covers composites' most commonly used damage criteria, including the Puck criterion. The package provides step-by-step guidance on simulating composite Puck damage using each of the subroutines mentioned above in Abaqus.
Python Scripting in Abaqus Full Tutorial
If you are a graduate or Ph.D. student, if you are a university professor or an expert engineer in the industry who deals with simulation software, you are definitely familiar with the limitations of this software in defining the material properties, loading or meshing, interaction properties, etc. You have certainly tried to define the properties of materials or geometry based on available features in the software, but sometimes you need to code on your own to define some complex issues.
Now, here is your solution. This full tutorial package includes 3 training packages that help you to learn how to use Python scripting in Abaqus software. This is likewise the most comprehensive tutorial for the script, and it is appropriate for beginners to advanced users.
Additive manufacturing simulation with Abaqus subroutine & python | Inherent Strain Method
3D printing is a technique for creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials such as plastic or metal based on a digital design. 3D printing simulation involves the use of software to predict and enhance the printing process, resulting in more efficient and precise production. This training package is based on the use of subroutines and Python scripting. Following an introduction to the 3D printing process, this method with all its details is explained. Two workshops are then conducted for this method. The first workshop covers 3D printing simulation of a gear with a uniform cross-section, while the second workshop covers a shaft with a non-uniform cross-section.
Abaqus CFD Analysis
Fluid-Structure Interaction also known as FSI is a multiphysics problem where the fluid and structure are coupled. The fluid flow can cause the structure to deform, and the deformation of the structure can affect the flow. So when you want to design something, you need to know how the structure will deform and how that deformation affects the flow. Common examples of FSI analysis are airplanes, cars, spacecrafts, and buildings. Other examples like junctions in piping systems, or the human circulatory system. CFD is a branch of research that uses numerical methods to solve the mathematical equations governing fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena. In Abaqus, you can model both methods. In this package, we present to you three workshops to get you started with Abaqus CFD and FSI: “Using Abaqus CFD methods, examining heat mixing and reverse flow characteristics in a T-junction”, “impact of air velocity over the short column”, “simulate fluid structure interaction on an aluminum body with a flexible tail in Abaqus”.
Simulation of woven composites damage in Abaqus
Woven composites are net-shaped composite structures that are fully interconnected by their yarns. Like a piece of cloth, the yarns are weaved together as warp and weft to create a composite structure. This package includes several components. First, it begins with an introduction to woven composites. Next, it provides a detailed explanation of macro modeling and offers guidance on how to perform it. The damage criteria employed in this package is a modified version of the Hashin criteria specifically designed for woven composites. Furthermore, the package demonstrates how to model damage using the USDFLD subroutine and Hashin relations. The subroutine is thoroughly explained, line by line, and a workshop is conducted to facilitate learning and practical application. Finally, the subroutine's validity is confirmed through a verification process.