Concrete Damage Plasticity Simulation of FRP-Confined Concrete Columns in Abaqus
This tutorial package provides a comprehensive guide to implementing USDFLD subroutine in the context of Concrete Damage Plasticity Material Model. The tutorial focuses on key modeling aspects such as definition of concrete material properties using Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) Model. A theoretical background of the model will be presented and detailed explanation of the definition of all material properties will be given. The package will also explain the usage of the USDFLD subroutine to modify concrete material properties dynamically during simulation. Examples of implementing USDFLD in the context of CDP will be presented with focus on material properties that vary in function of pressure and axial strain defined as field variables.
All other modeling details will also be explained including boundary conditions, meshing, loading, and interactions.
By following the detailed steps in this tutorial, you will be able to create and analyze advanced FEM simulations in Abaqus with a focus on concrete having properties that vary during simulation.
Computational Predictions for Predicting the Performance of Structure
This package focuses on developing and applying predictive models for the structural analysis of steel and concrete components subjected to fire and subsequent earthquake loading. To accurately simulate the complex behavior of these structures, finite element analysis (FEA) using ABAQUS is employed. The Taguchi method optimizes the number of samples needed for FE analysis, and this method is used with SPSS after explanation its concept. However, due to the computational demands of FEA, various machine learning techniques, including regression models, Gene Expression Programming (GEP), Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS), and ensemble methods, are explored as surrogate models. These models are trained on large datasets of FEA results to predict structural responses efficiently. The performance of these models is evaluated using statistical metrics such as RMSE, NMSE, and coefficient of determination.
Abaqus advanced tutorials on concrete members
Welcome to the "Abaqus Advanced Tutorials on Concrete Members" course, designed to provide civil and structural engineers with cutting-edge expertise in finite element modeling (FEM) and simulation using Abaqus. This advanced-level course focuses on the detailed modeling of complex concrete and composite columns under various loading conditions. Topics include the simulation of tubed reinforced concrete columns, concrete-filled double skin steel columns, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite columns. Participants will delve into axial and eccentric compression loading scenarios, with a special focus on hollow and tapered cross-sections. The course also emphasizes comparing simulation results with experimental data from published research, ensuring practical relevance and accuracy. By the end of the course, learners will be equipped with the necessary skills to tackle advanced structural analysis challenges using Abaqus, reinforcing their understanding of concrete member behavior in real-world applications.
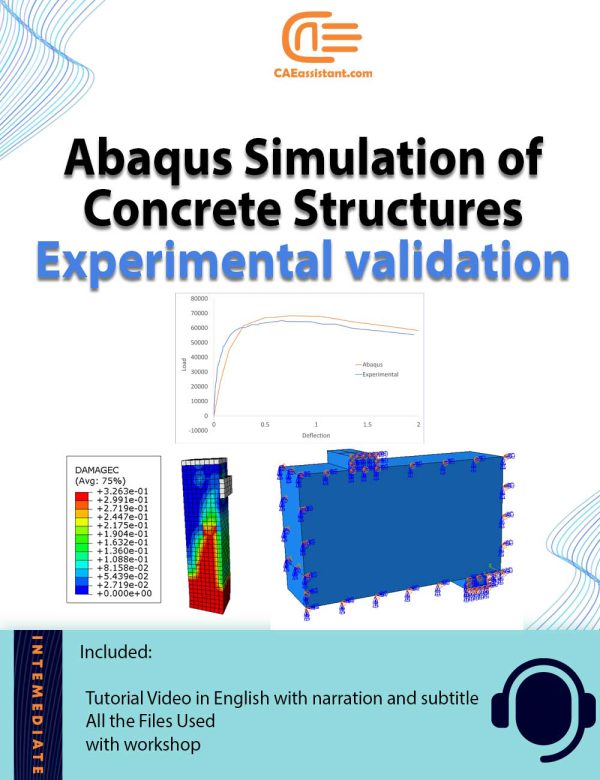
Analysis of Plain and Reinforced Concrete Structures with ABAQUS | Validation with Experiments
This comprehensive package offers four different workshops focused on the analysis of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete structures using ABAQUS. Designed for professionals, researchers, and students, it provides hands-on learning in modeling, simulating, and validating concrete structures under various conditions. Each workshop dives into specific aspects of concrete behavior, from flexural to compressive strength, incorporating the latest sustainable practices through the use of recycled materials. The package ensures mastery of ABAQUS, offering practical insights and a cost-effective path to advanced concrete analysis and safer, more durable infrastructure design.
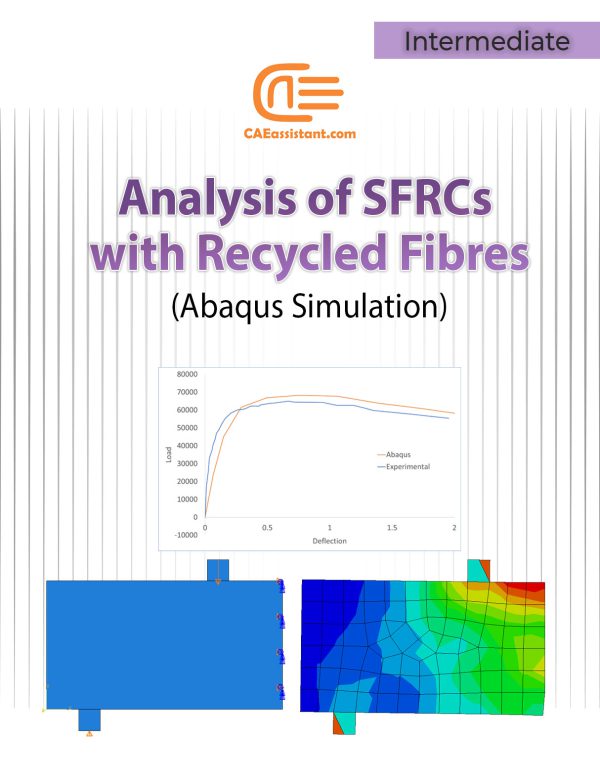
Note: Only the first workshop has video.Stress-strain characteristic of SFRC using recycled fibres | An Abaqus Simulation
This training utilizes Abaqus software to simulate and analyze the stress-strain characteristics of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) using recycled fibers. The importance of this work lies in its contribution to sustainable construction practices by validating the effectiveness of recycled steel fibers in enhancing concrete's mechanical properties. Through advanced finite element analysis (FEA), the project addresses challenges in accurately modeling SFRC's post-cracking behavior, ensuring that the simulations are aligned with experimental data for reliable results. Abaqus' capabilities in nonlinear material modeling, stress-strain simulation, and principal stress analysis significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of the research, making it a valuable tool for both academia and industry.
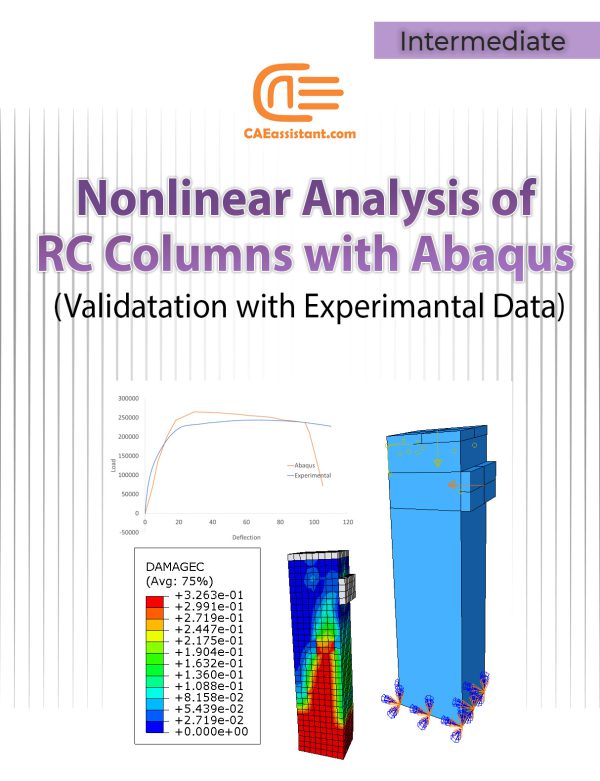
Nonlinear Analysis of RC Columns Using ABAQUS | Validation with Experimental Data
Reinforced Concrete (RC) columns are critical components in civil engineering, essential for the stability of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure during seismic events. This study leverages ABAQUS, a powerful finite element analysis (FEA) software, to simulate the seismic performance of RC columns. By modeling columns in 3D and using ABAQUS's advanced tools, we replicate experimental conditions to analyze their behavior under seismic loads. Numerical simulations offer the advantage of exploring various scenarios quickly and cost-effectively, while also allowing for extensive parametric studies. The study details how ABAQUS models both concrete and steel reinforcement, accounts for interaction effects, and applies appropriate loading and boundary conditions. The simulations provide valuable insights into failure modes, load-displacement responses, and crack patterns, offering a comprehensive understanding of RC column performance in seismic scenarios.
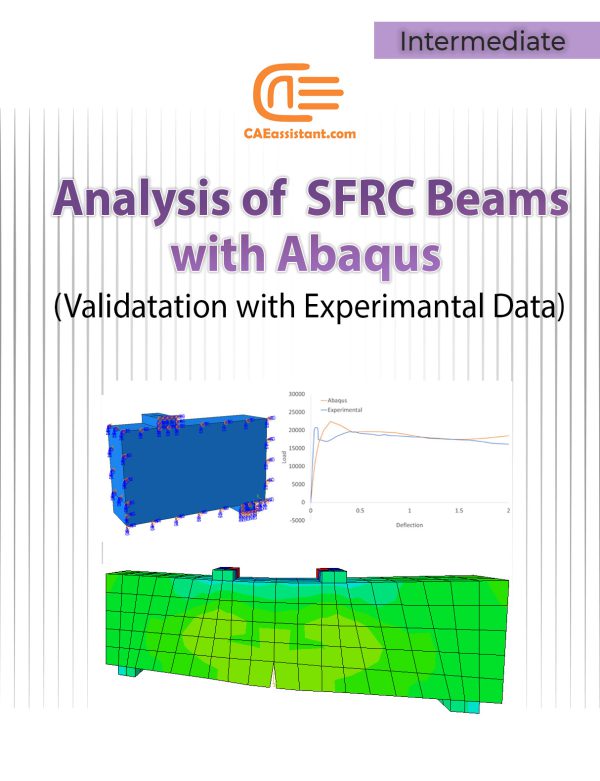
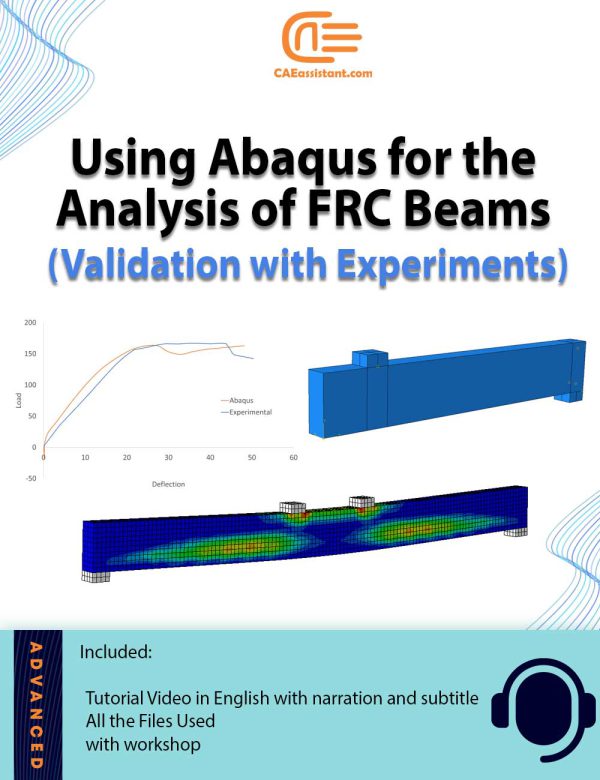
Analysis of Steel-Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) Beams with Abaqus
Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams | An Abaqus Simulation
Abaqus basic tutorials on concrete beams and columns
Welcome to the “Abaqus Basic Tutorials on Concrete Members,” a comprehensive course tailored for civil and structural engineers seeking to master finite element modeling (FEM) of concrete structures. This tutorial covers key concepts such as plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforced concrete members, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. The course guides learners through the application of boundary conditions, material properties, and various loading conditions in Abaqus. Key topics include plain concrete beam and column modeling, reinforcement modeling with steel bars and stirrups, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement techniques. Participants will also explore comparing simulation results with experimental data, as well as interpreting critical outcomes such as stress distribution and failure modes. Through hands-on workshops, learners will simulate structural behaviors under axial, lateral, and compression loads, ensuring a practical understanding of FEM for concrete members. By the end of this course, participants will be proficient in using Abaqus to model and analyze concrete structures, reinforced elements, and advanced composites, providing them with a strong foundation for structural analysis and design.
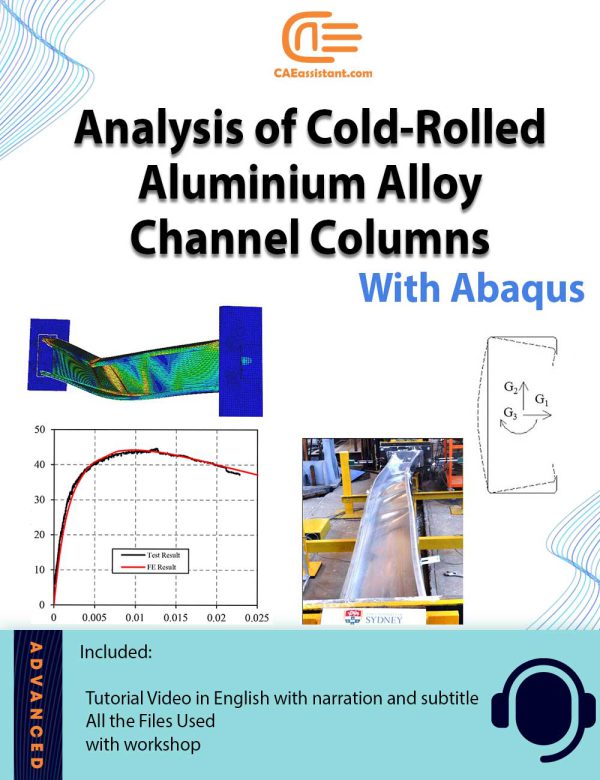
Analysis of Cold Rolled Aluminium Alloy Channel Columns With Abaqus CAE
Seismic Analysis in Post-Tensioned Concrete Gravity Dam Design Using Abaqus Subroutines
Fiber-based Model for High-Strength Steel Beam Analysis with Abaqus
Advanced Finite Element Analysis of Off-Axis Tunnel Cracking Laminates
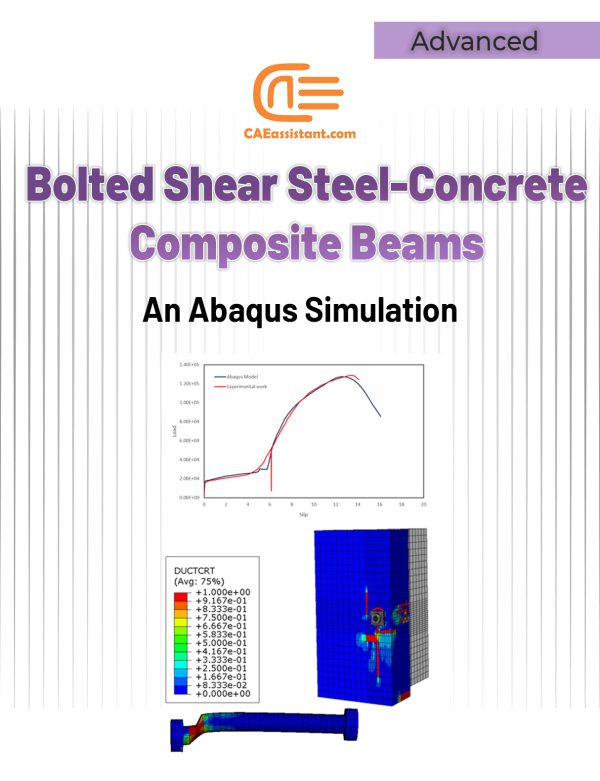
Bolting Steel to Concrete in Composite Beams: ABAQUS Simulation Validated Against Experiments
continuously reinforced concrete pavement (CRCP) Analysis
|
The increasing adoption of continuously reinforced concrete pavement (CRCP) in highway pavement design is driven by its demonstrated superior performance. Critical to evaluating the long-term effectiveness of CRCP is the understanding of early-age cracks, which has garnered significant interest from highway departments. This Abaqus Continuously reinforced concrete pavement modeling project aims to establish precise design parameters for CRCP and analyze the formation of crack patterns. By accounting for stress factors such as environmental conditions and CRCP shrinkage modeling, the project offers valuable insights into predicting the likelihood of crack initiation and propagation within the concrete slab. These insights are instrumental in enhancing the durability and performance of CRCP structures, thus advancing the efficiency and effectiveness of highway infrastructure. |
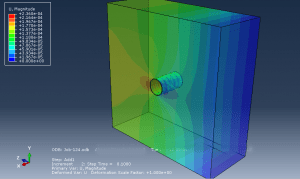
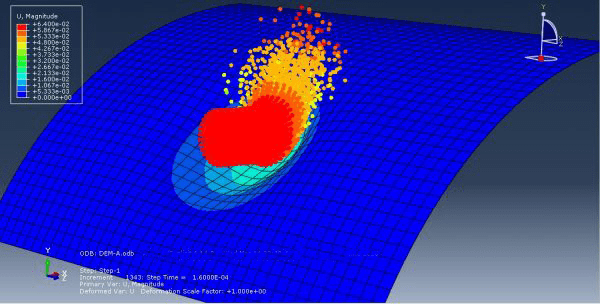
Johnson-Holmquist damage model in Abaqus
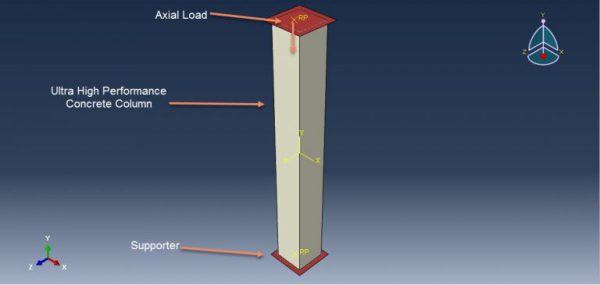
UHPC (Ultra-High Performance Concrete) structures simulation in Abaqus
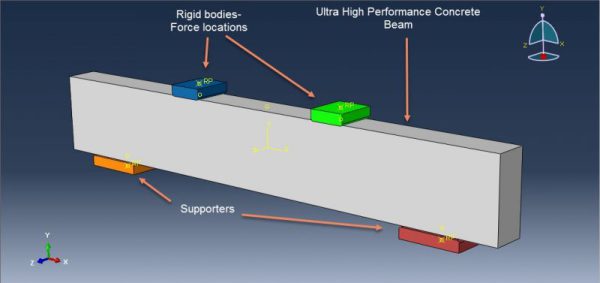
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) beams simulation in Abaqus
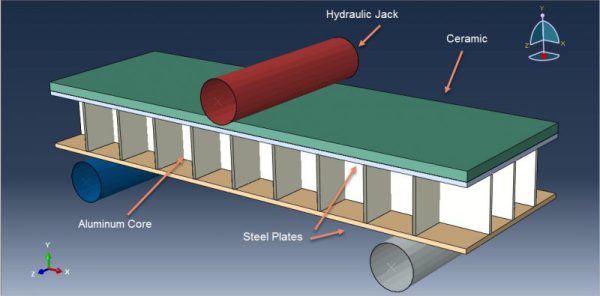
Abaqus for Civil Engineering Part-1
Tunnel excavation simulation using TBM in Abaqus
Soil Impact Analysis in Abaqus
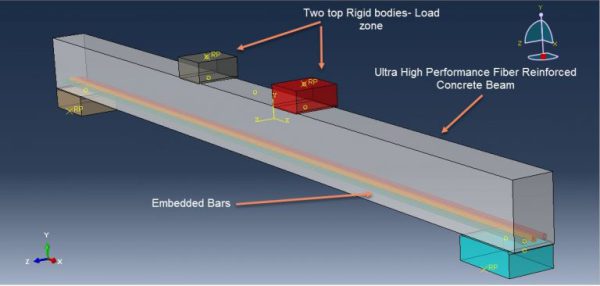
UHPFRC (Ultra-High-Performance Fiber Reinforced Concrete) structures in Abaqus
Composite pressure vessel analysis with Semi-Geodesic winding
Full Composite fatigue Add-on (Academic and industrial usage)